














Botanical art
Prior names
Mesembryanthemum rossii
Carpobrotus aequilaterus, partly
Common names
Angular Pig-face
Karkalla
Native Pigface
Etymology
Carpobrotus from the Greek 'karpos' meaning fruit and 'brotos' meaning edible, referring to the succulent fruit which was eaten traditionally by Aboringinal people. Rossii named after William J. Clunies-Ross (1850-1914), a college lecturer, scientist and botanical collector who first collected the plant.
Distribution and status
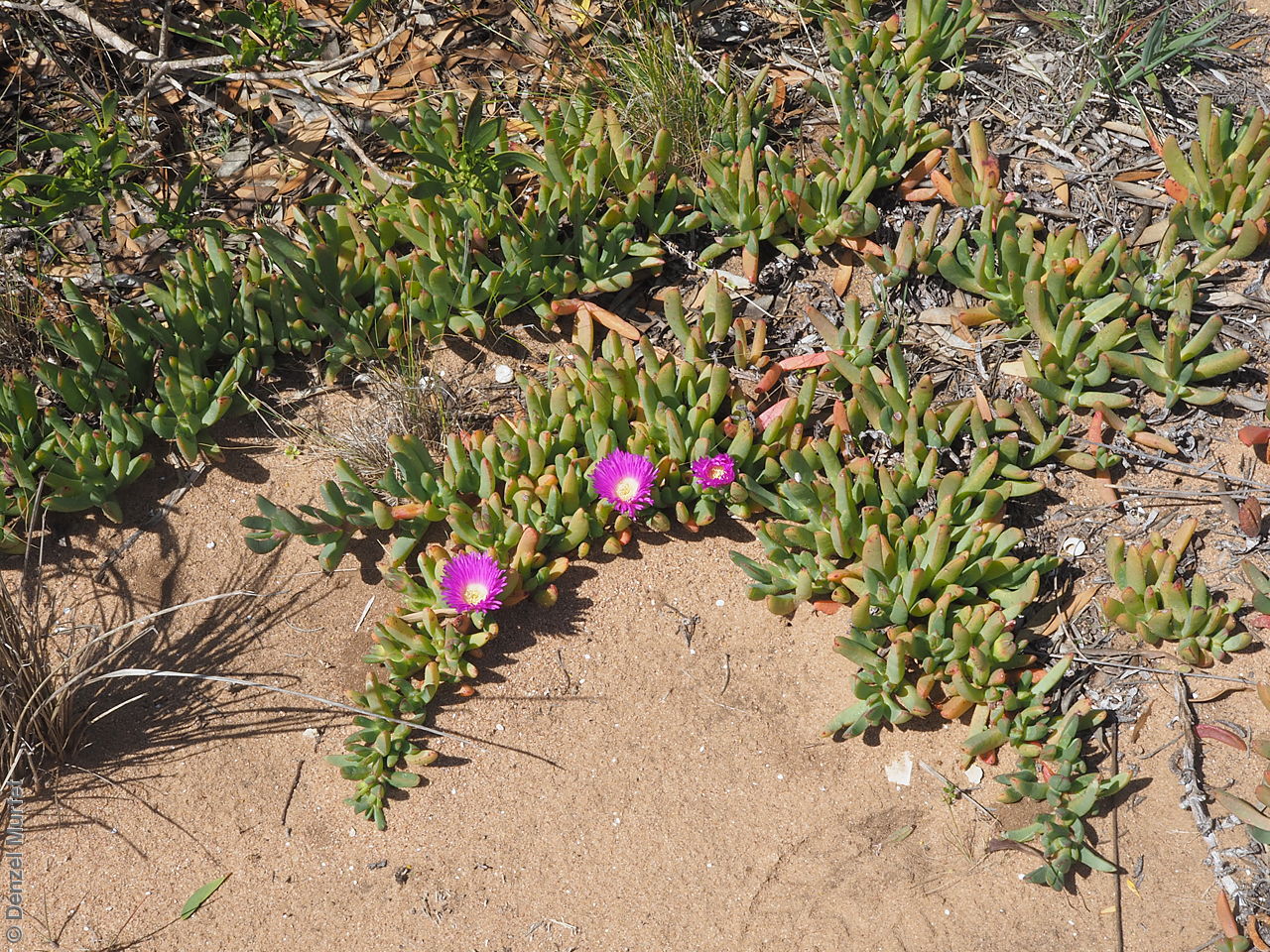
Found across the southern part of South Australia from the west coast to the lower South-east growing mainly on coastal dunes. Also found in Western Australia, Victoria and Tasmania. Native. Common in South Australia. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: Nullarbor, Flinders Ranges, Eyre Peninsula, Northern Lofty, Yorke Peninsula, Southern Lofty, Kangaroo Island, South Eastern, Green Adelaide
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
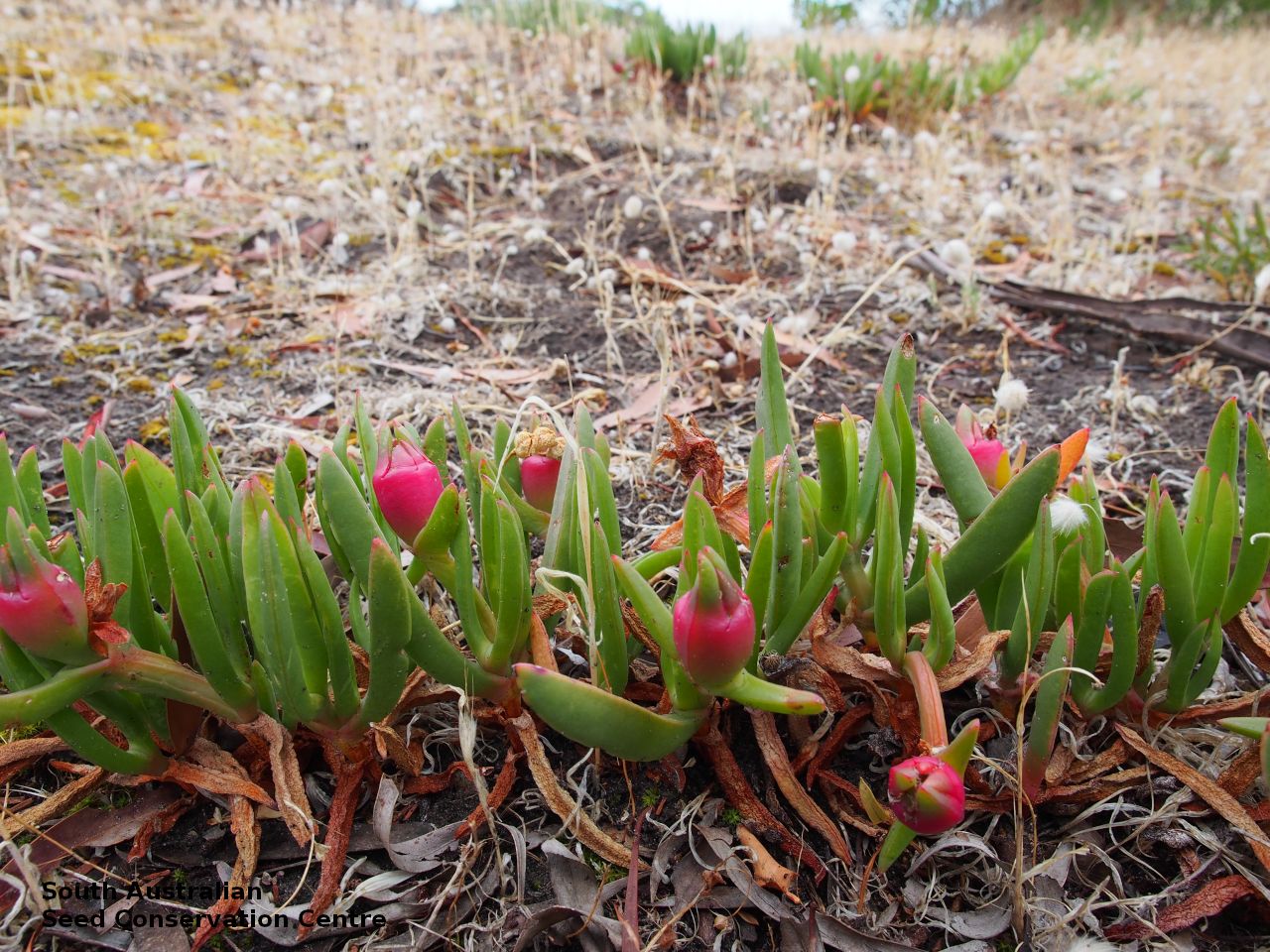
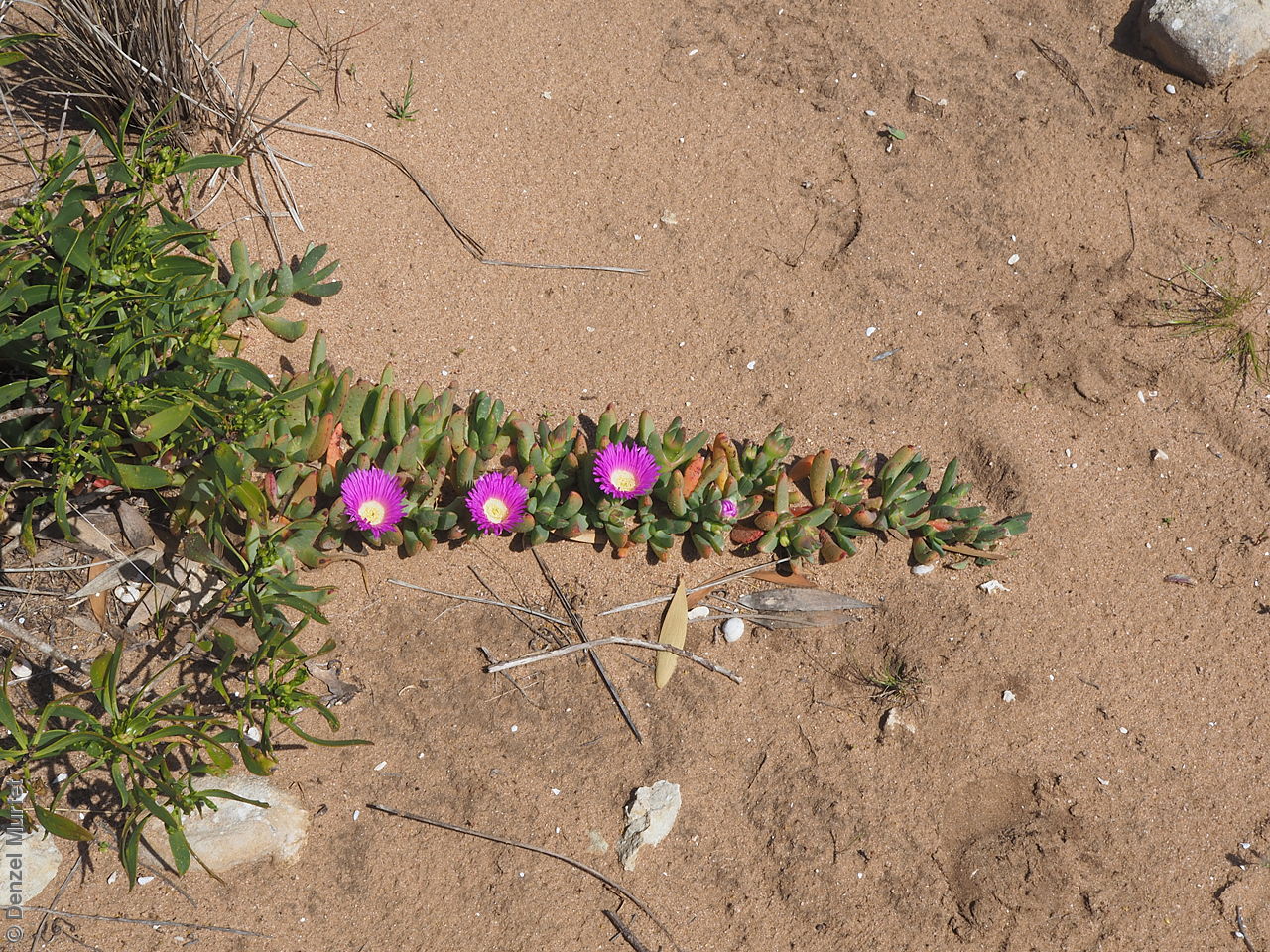
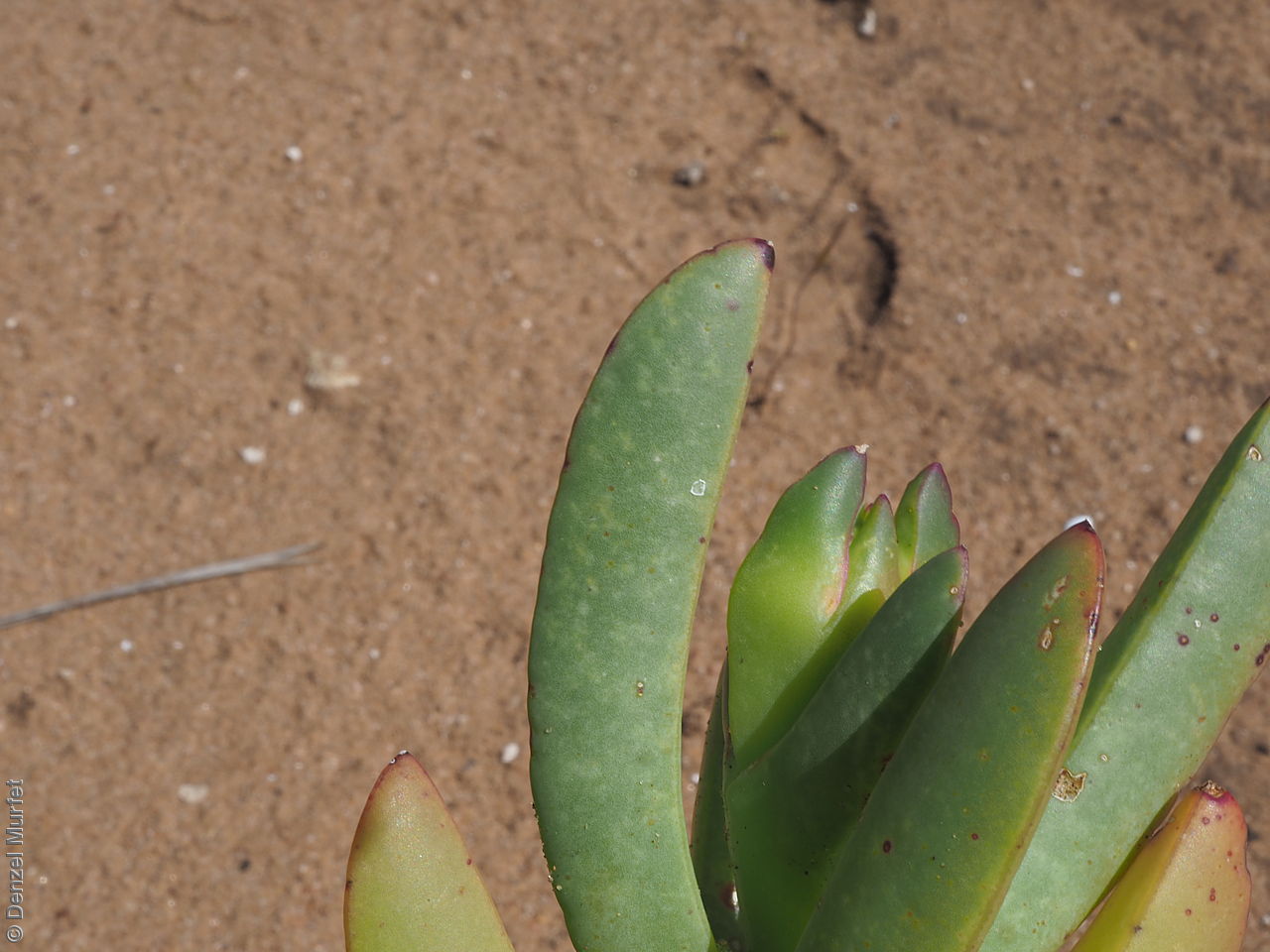
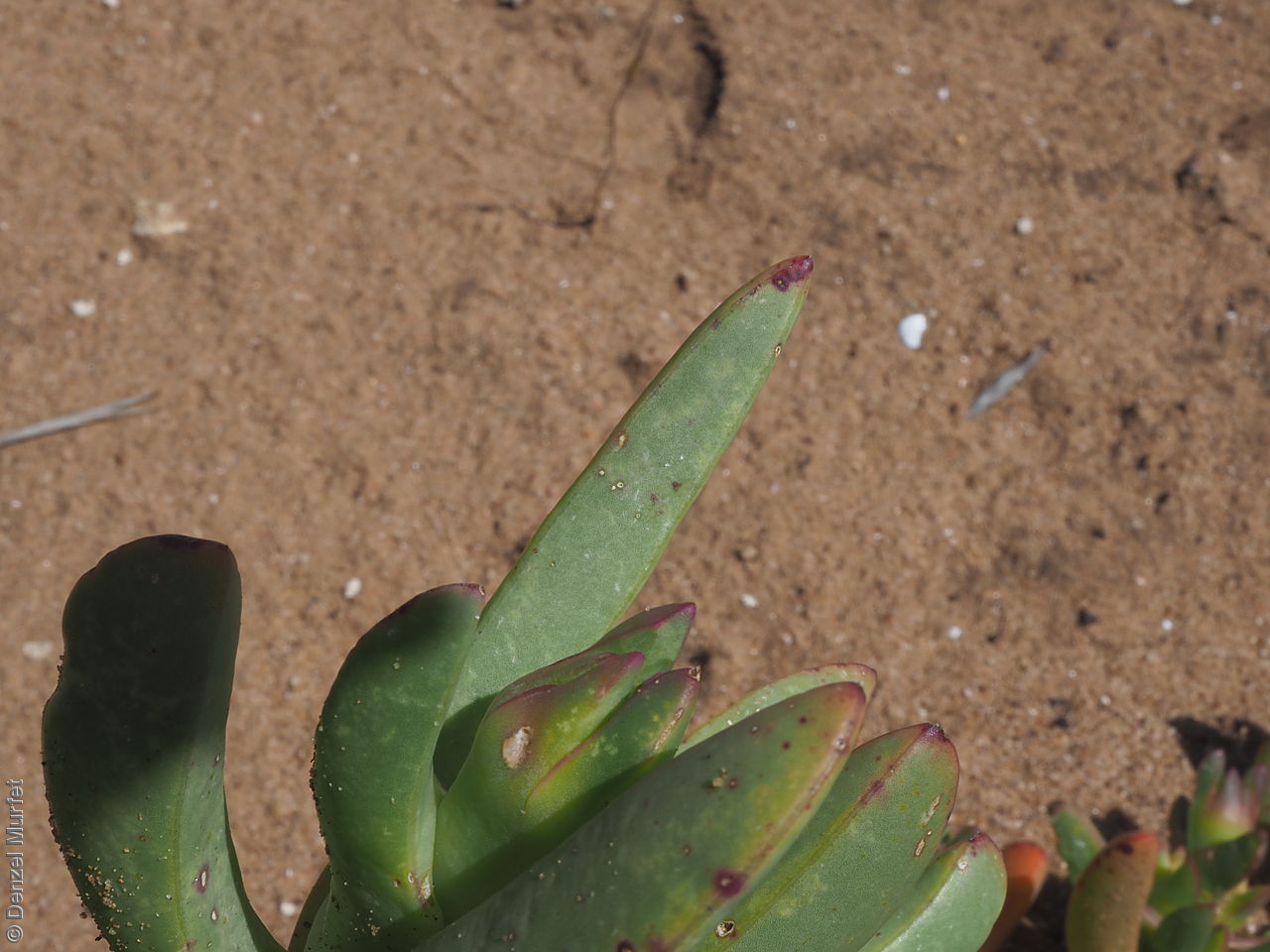
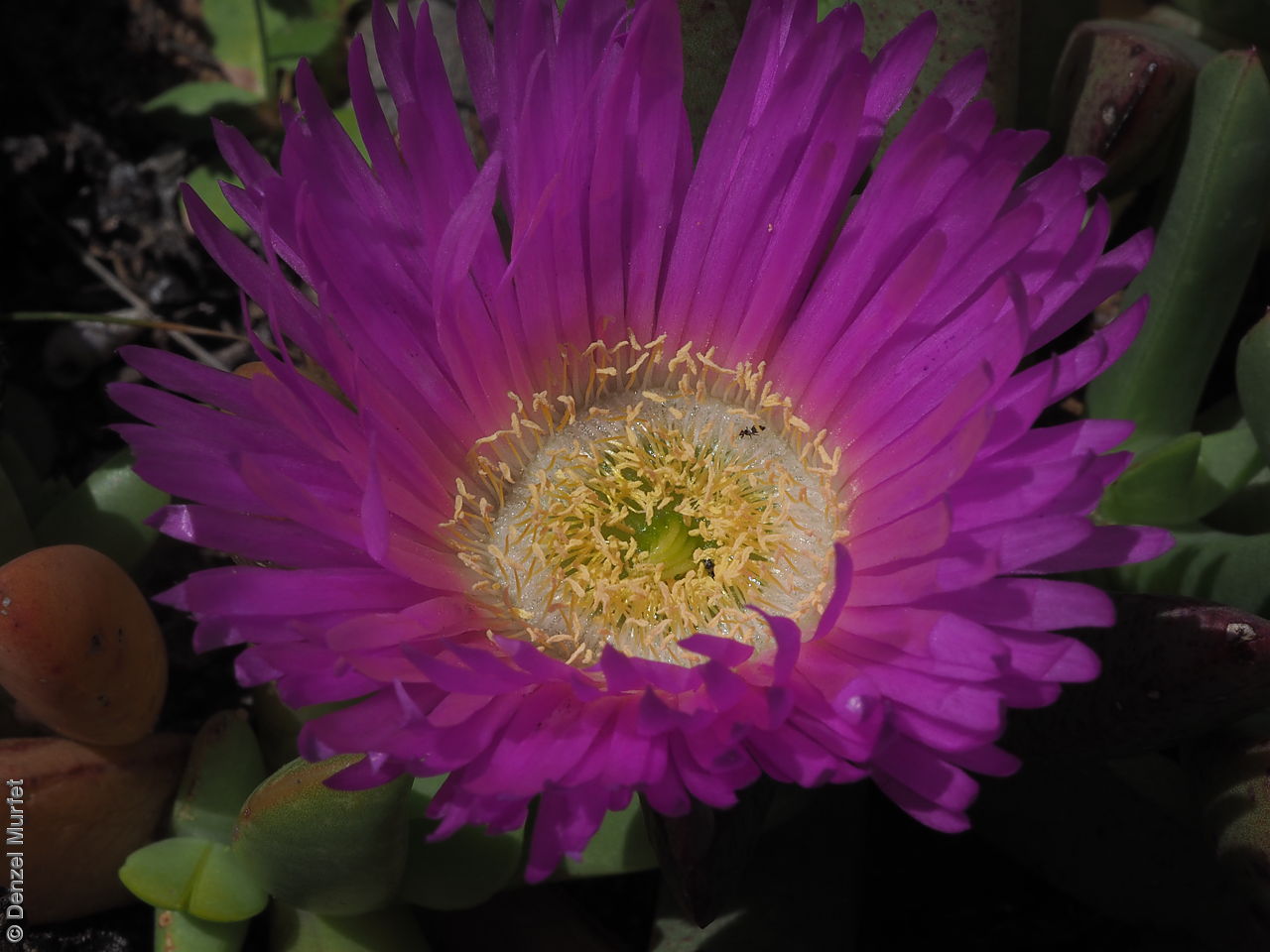
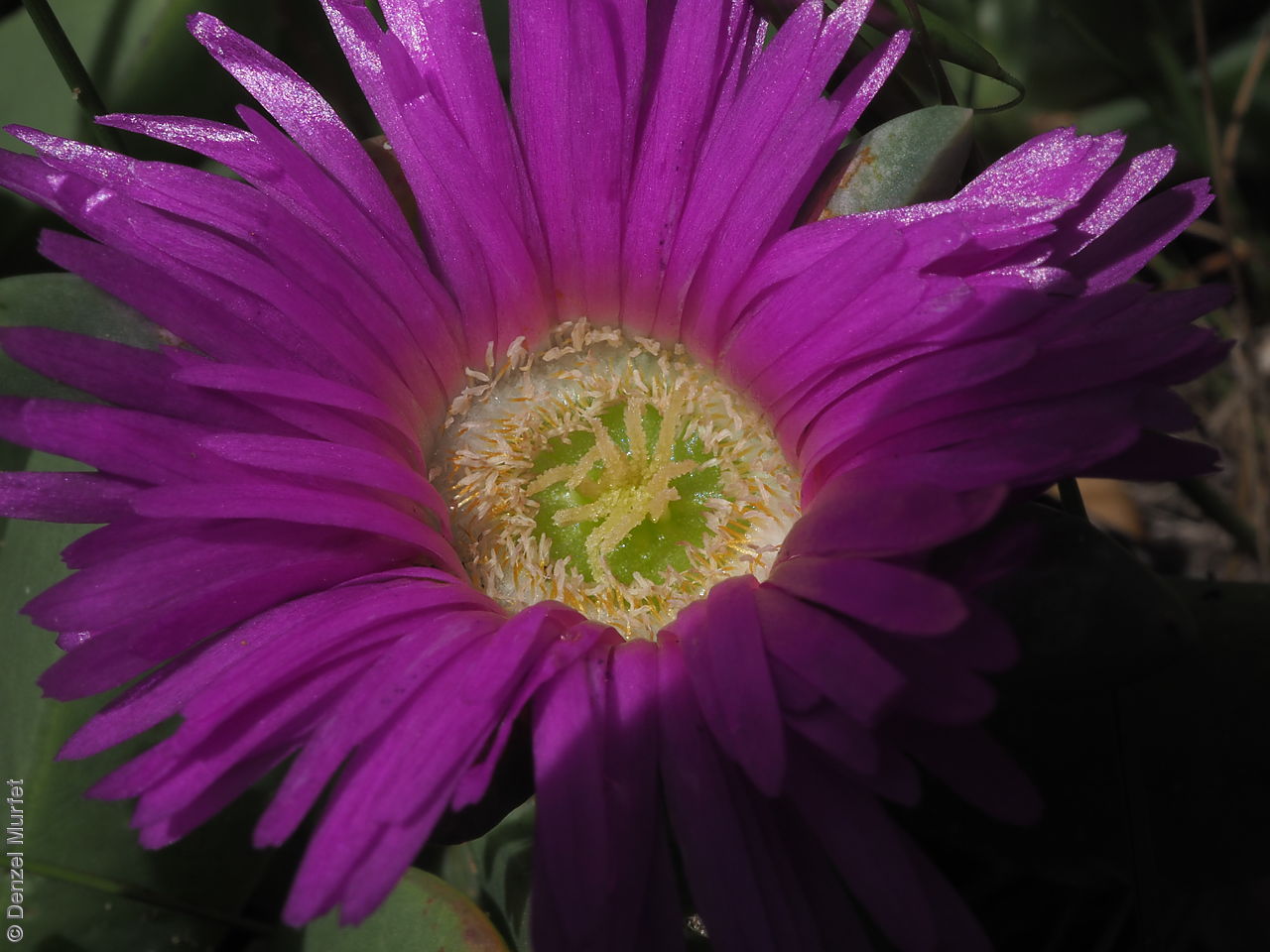
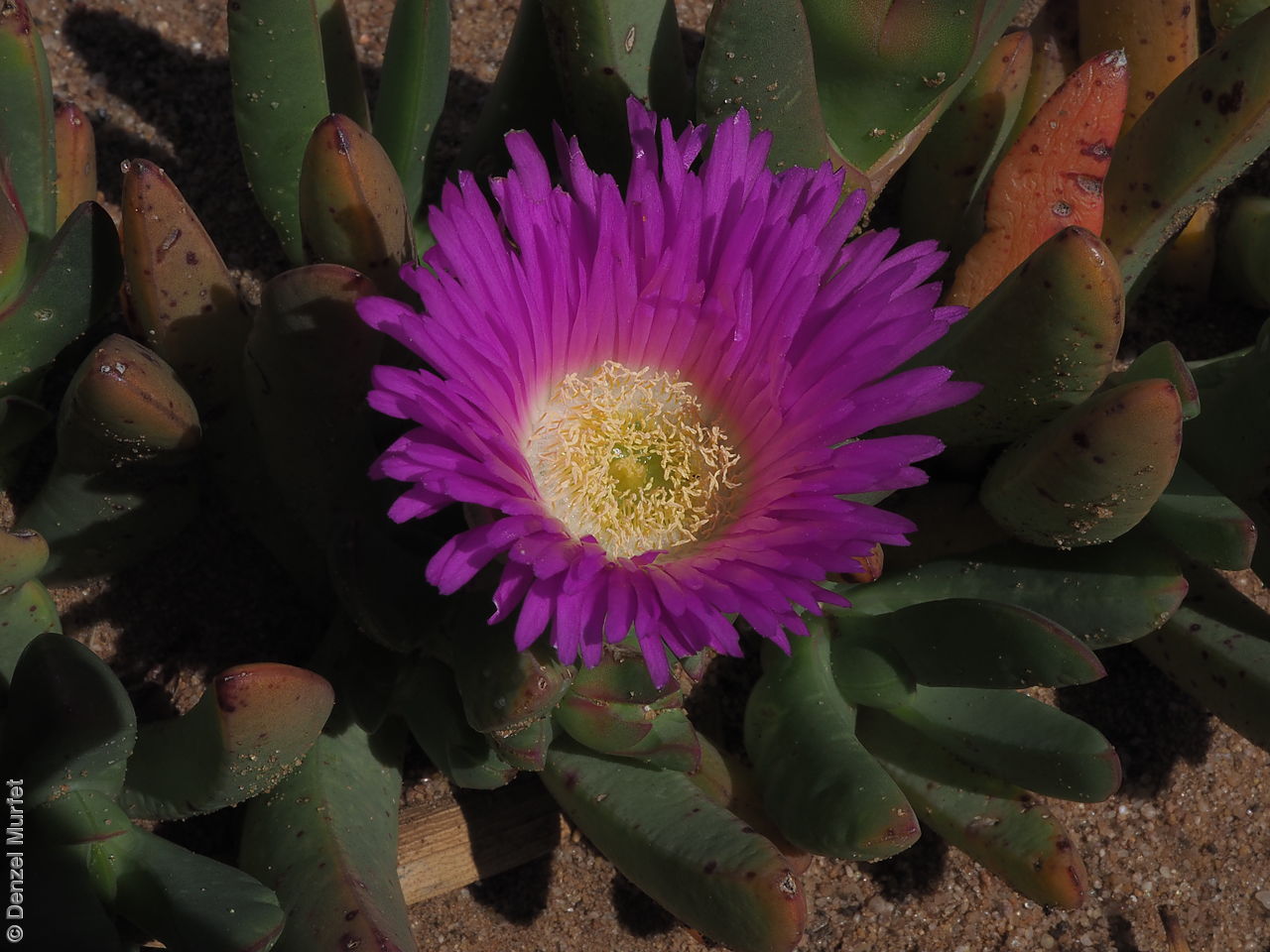
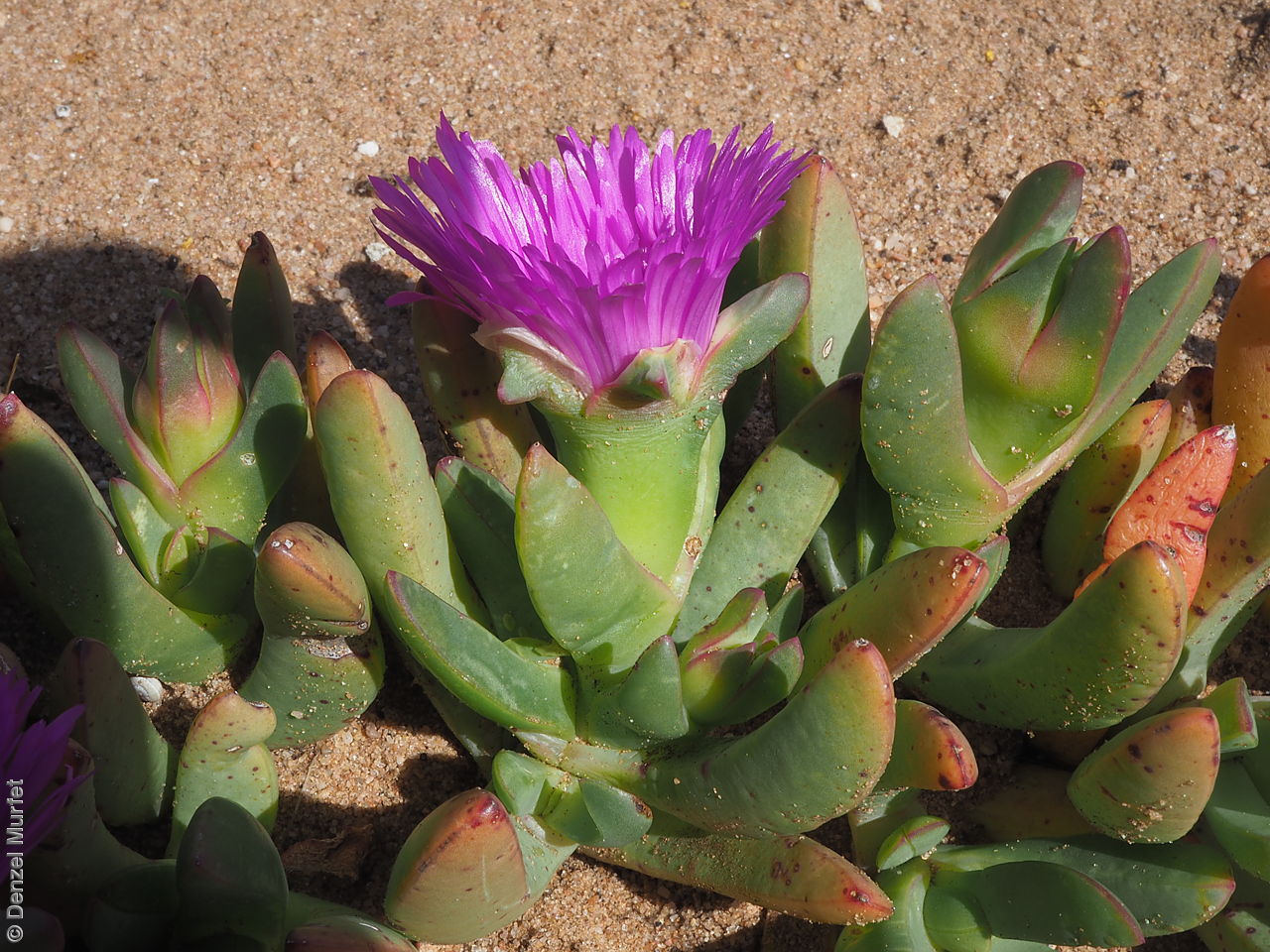
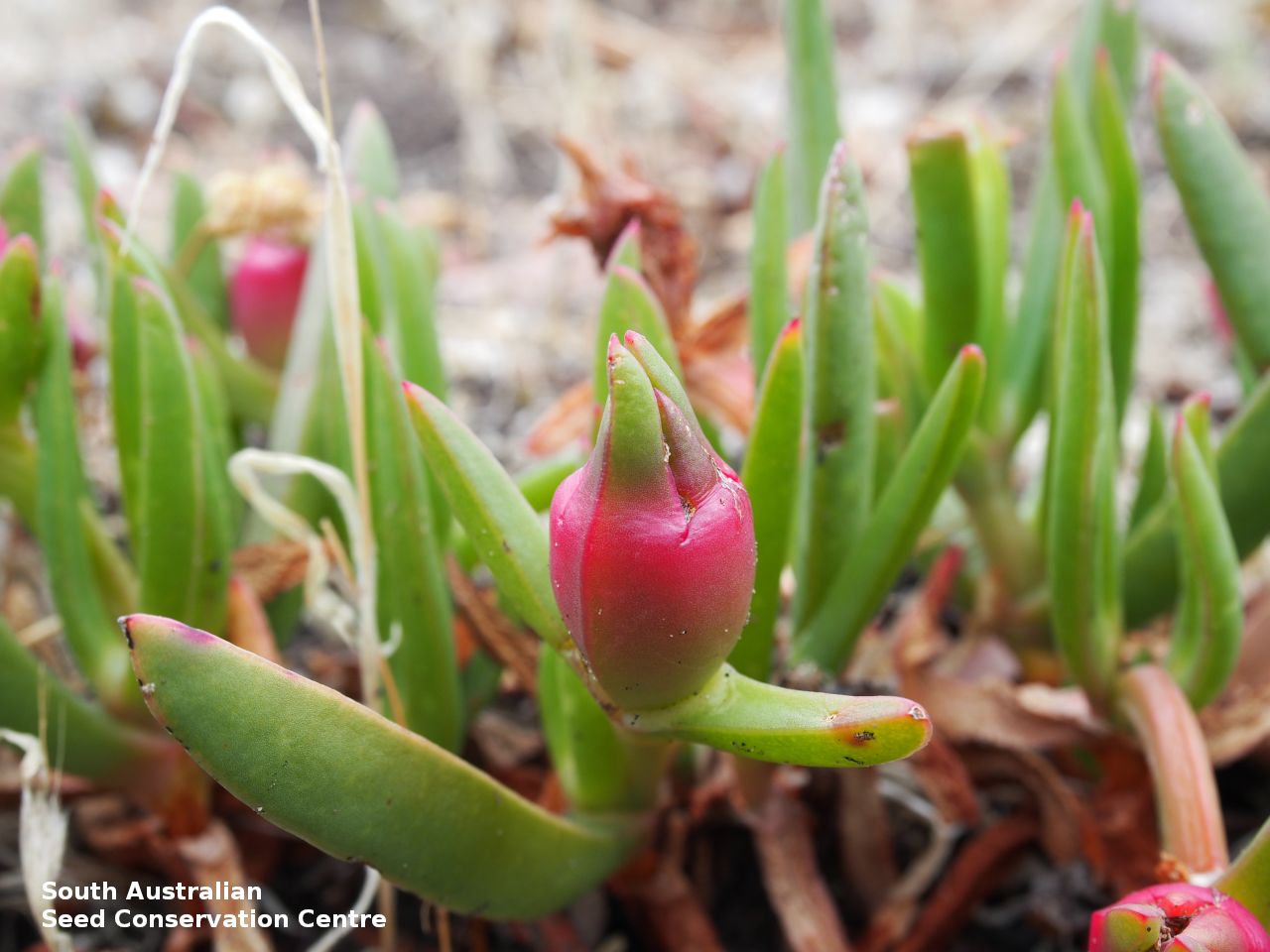
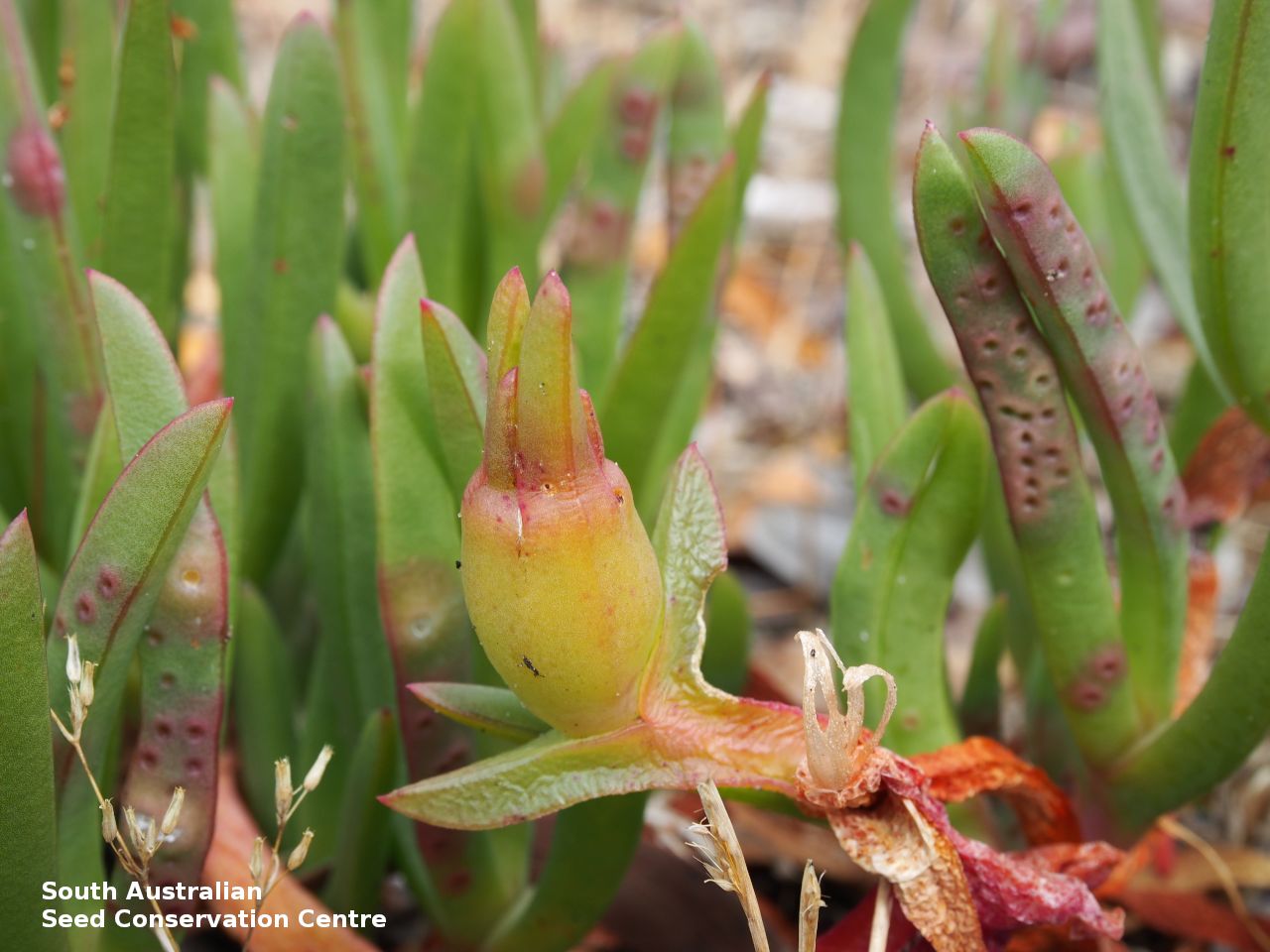
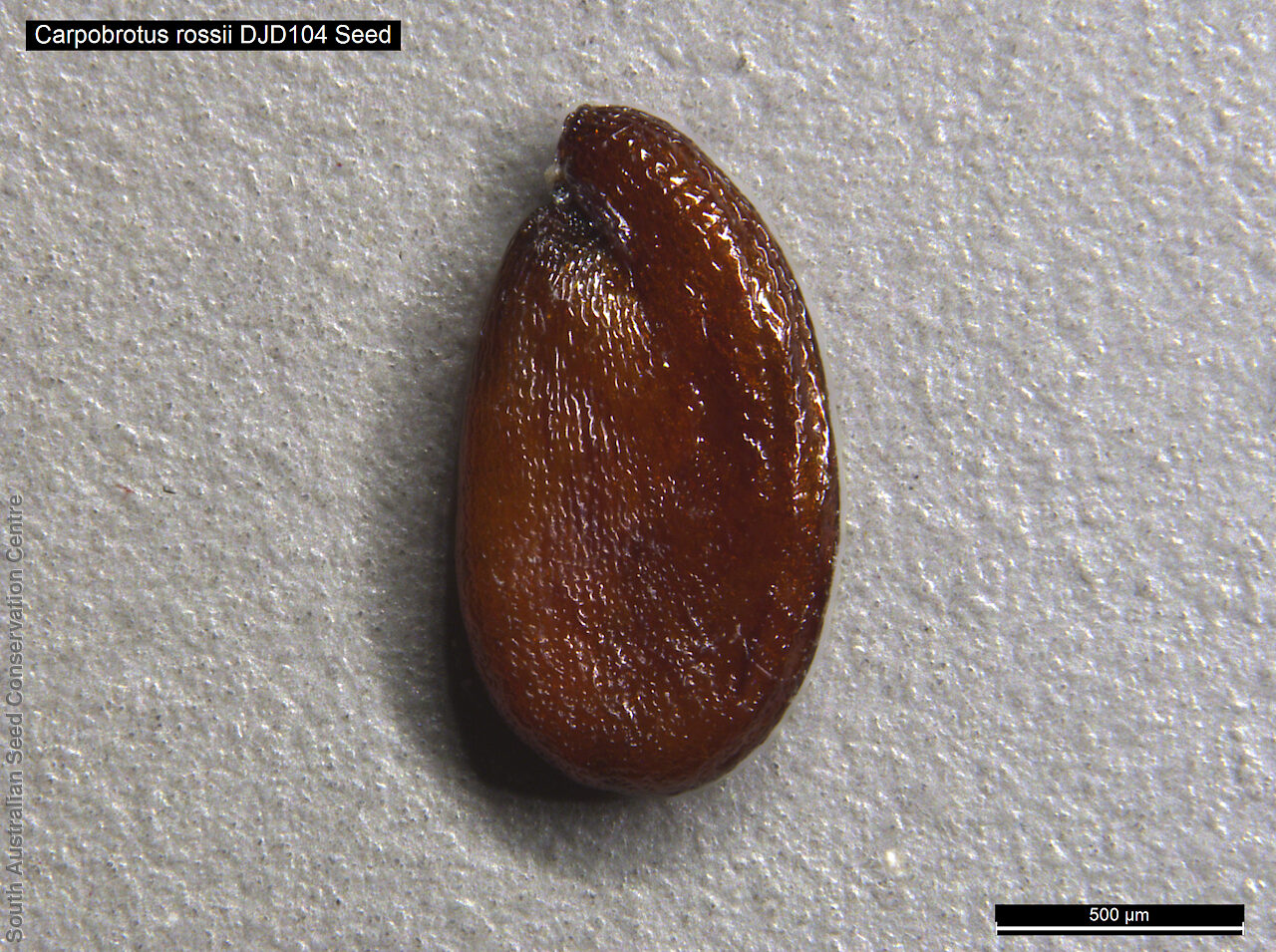
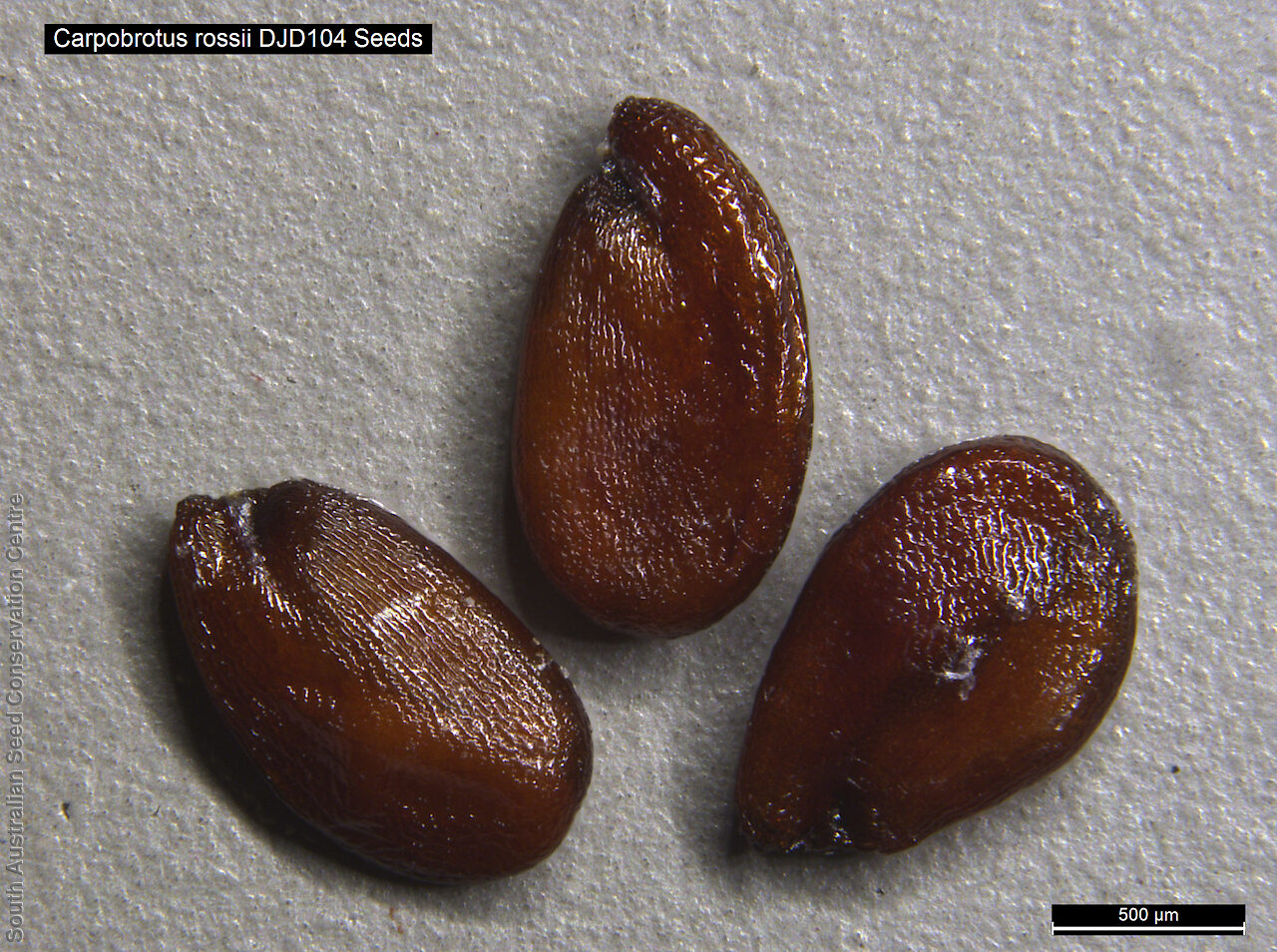
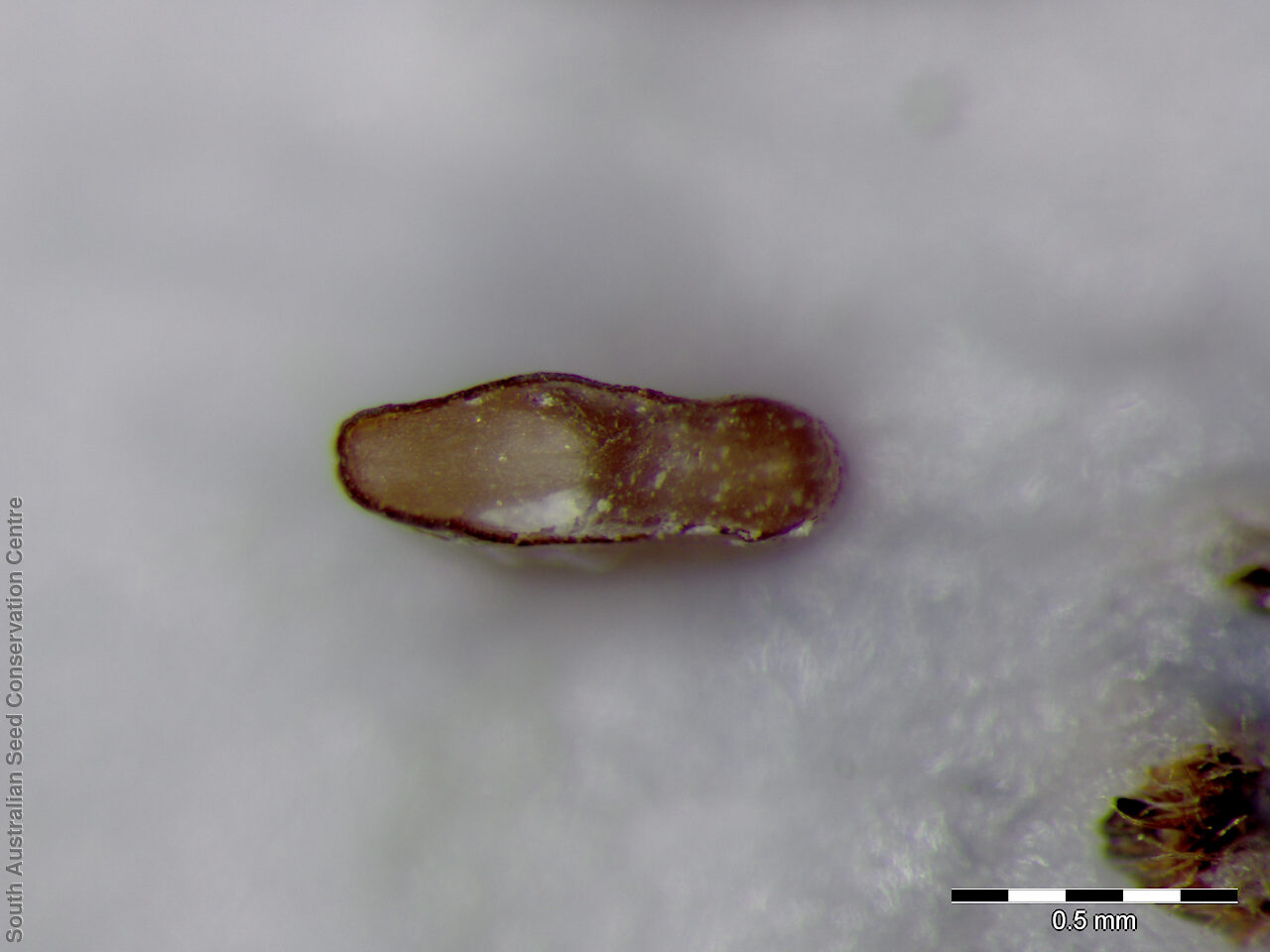
Prostrate, succulent perennial plant with stems to 1 m long or more and 11 mm diameter. Leaves to 10 cm long and 11 mm thick, usually distinctly incurved, green to glaucous, usually thicker than wide near the middle with faces usually slightly convex. Flowers large, daisy-liked, light purple merging to white at and near base. Flowering between August and October. Fruits are fleshy, plump red globular fruit to 25 mm long, slightly compressed. Seeds are semi-flat reniform brown seed to 1.5 mm long and 0.8 mm wide. Seed embryo type is peripheral.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between November and January. Collect mature fruits, those that are fat and turning red with brown seeds inside. Break open the fruits and wash the content in water. Drain the liquid leaving behind the seeds. Place the wet seeds onto paper towels and leave to dry. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Seed viability is usually high. Seeds are non-dormant, viable seed should germinate readily without any treatment.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 32,100 (7.2 g) 32,100 (7.2 g) | 43 | 3-Nov-2005 | DJD104 South Eastern | 28-Mar-2006 | 100% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.