















Botanical art
Prior names
Glinus oppositifolia, orth.var.
Mollugo spergula
Mollugo oppositifolia
Glinus spergula
Etymology
Glinus from the Greek 'glinos' meaning a plant with sweet sap. May have been a reference to maple. Oppositifolius from the Latin 'oppositus' meaning standing against or opposed and 'folium' meaning a leaf, referring to the leaves arranged opposite each other.
Distribution and status
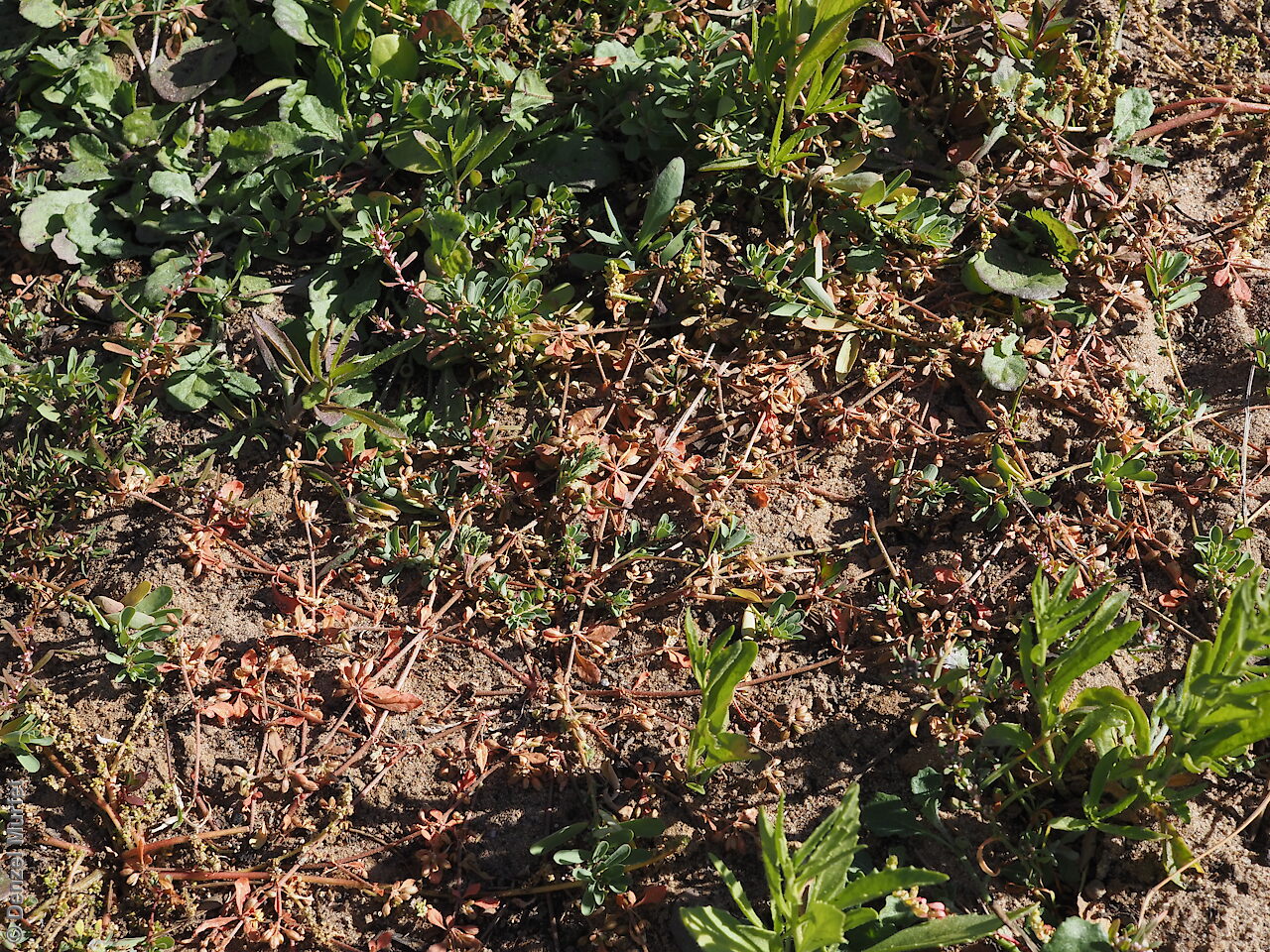
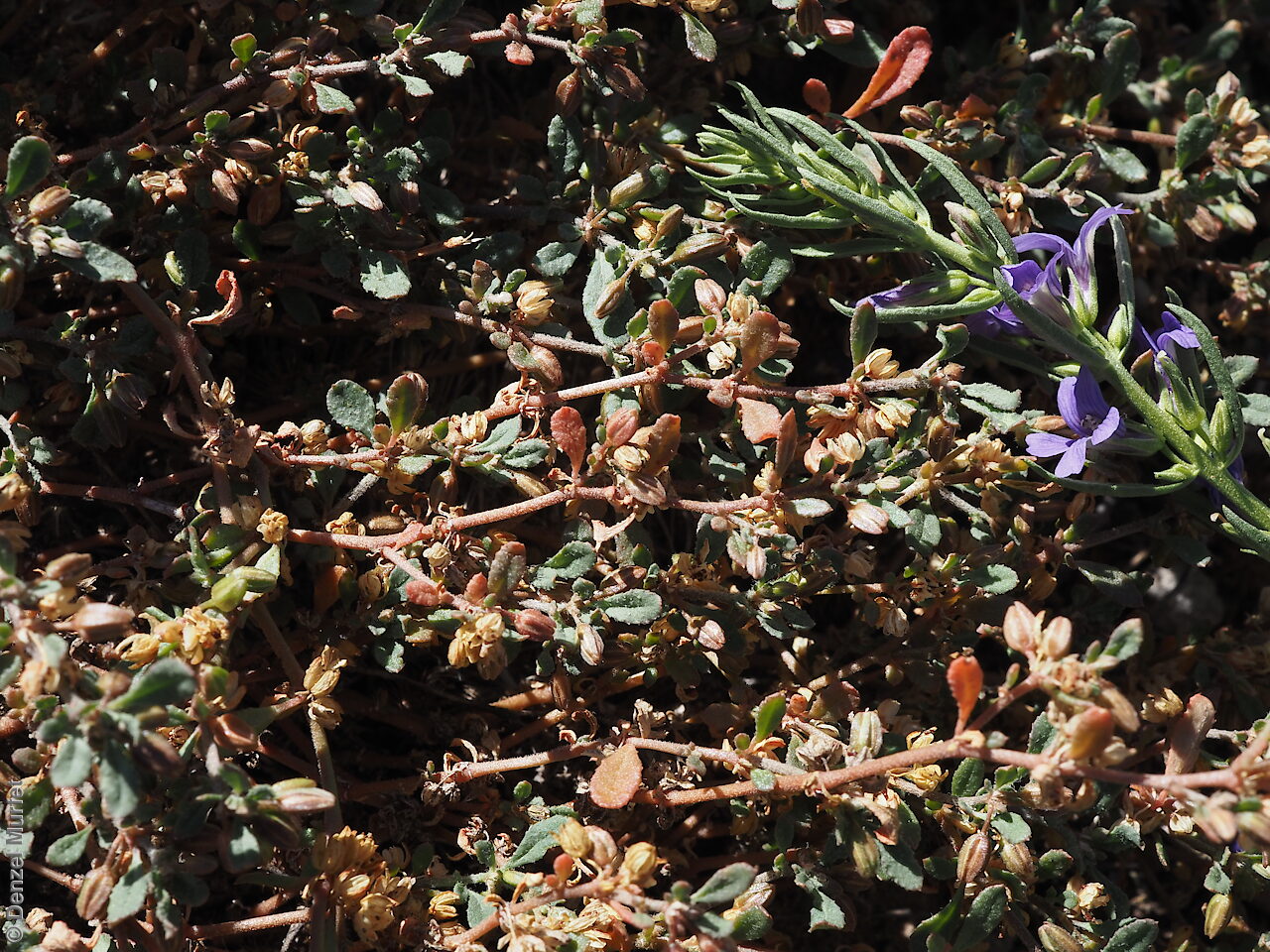
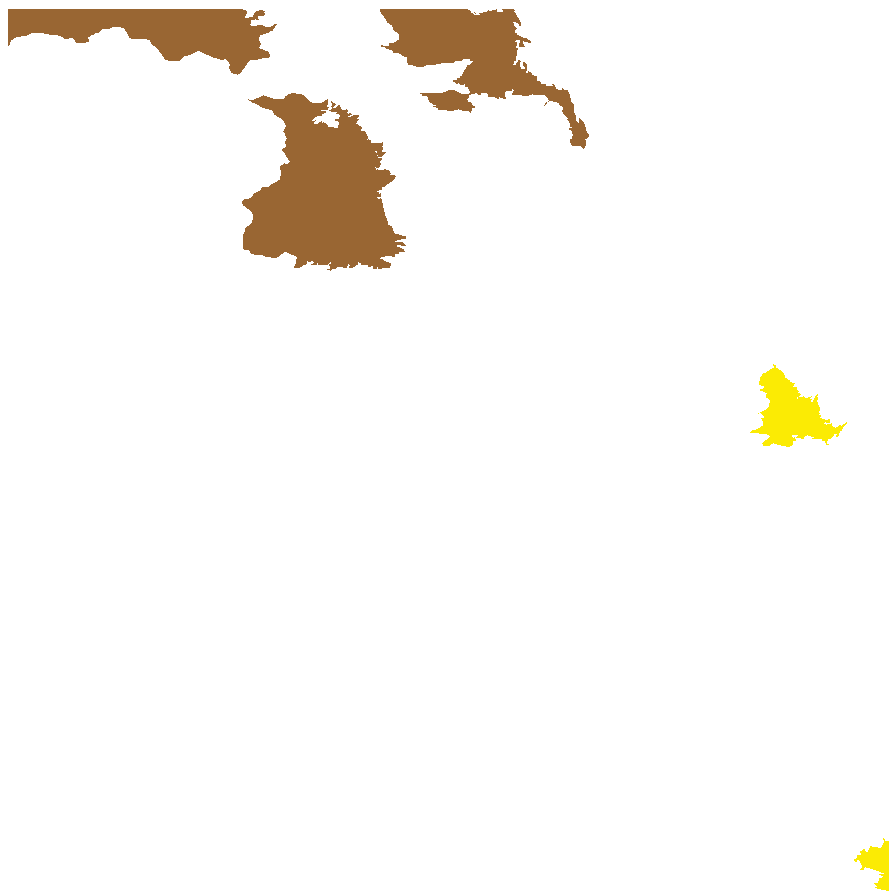
Found in three disjunct locations in South Australia, in the far north, eastern and Murray River, growing in beds of ephemeral watercourses. Also found in all mainland States. Native. Uncommon in South Australia. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: North Western, Lake Eyre, Eastern, Murray, South Eastern
NRM regions: Alinytjara Wilurara, South Australian Arid Lands, South Australian Murray-Darling Basin, South East
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
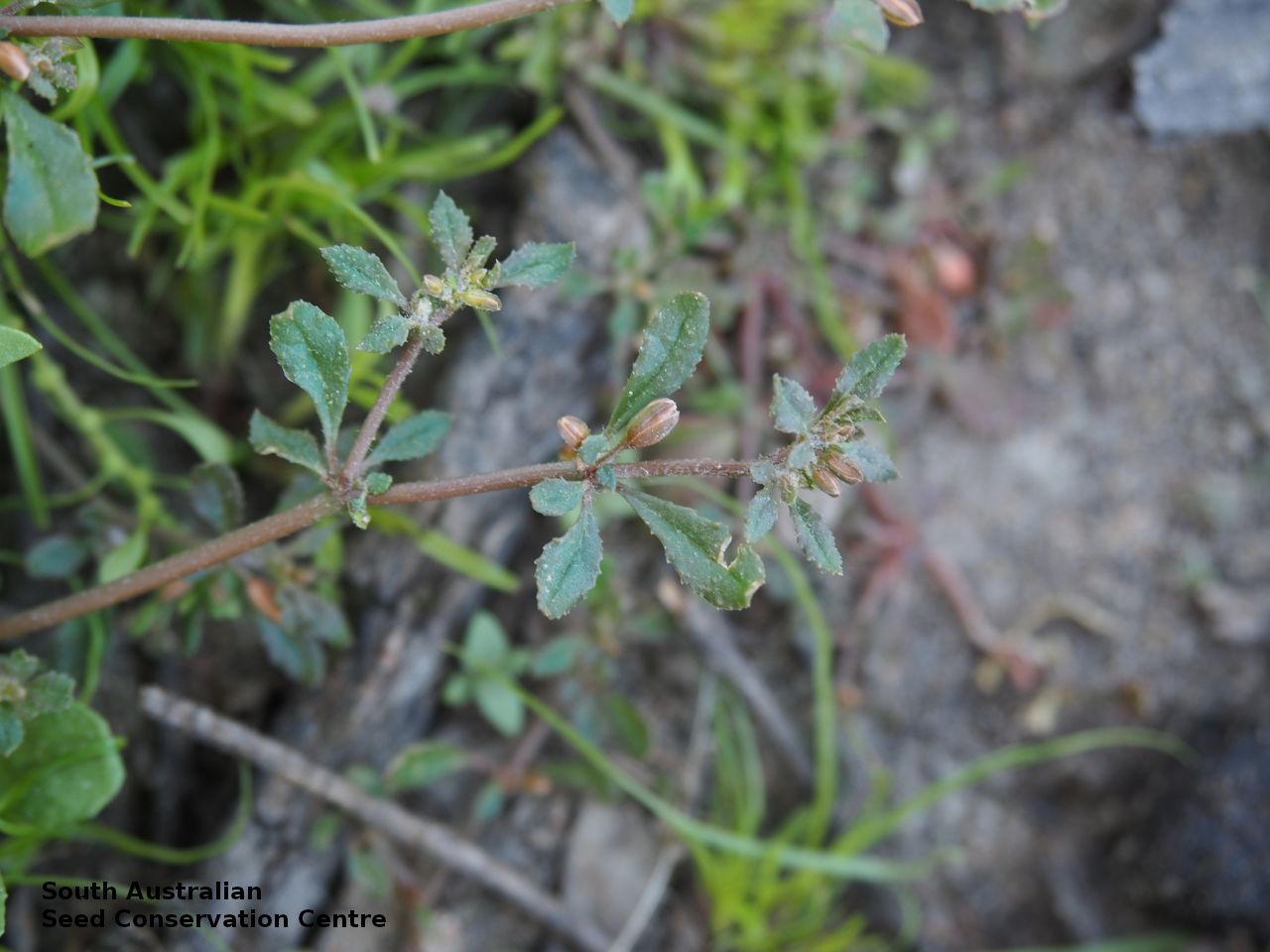
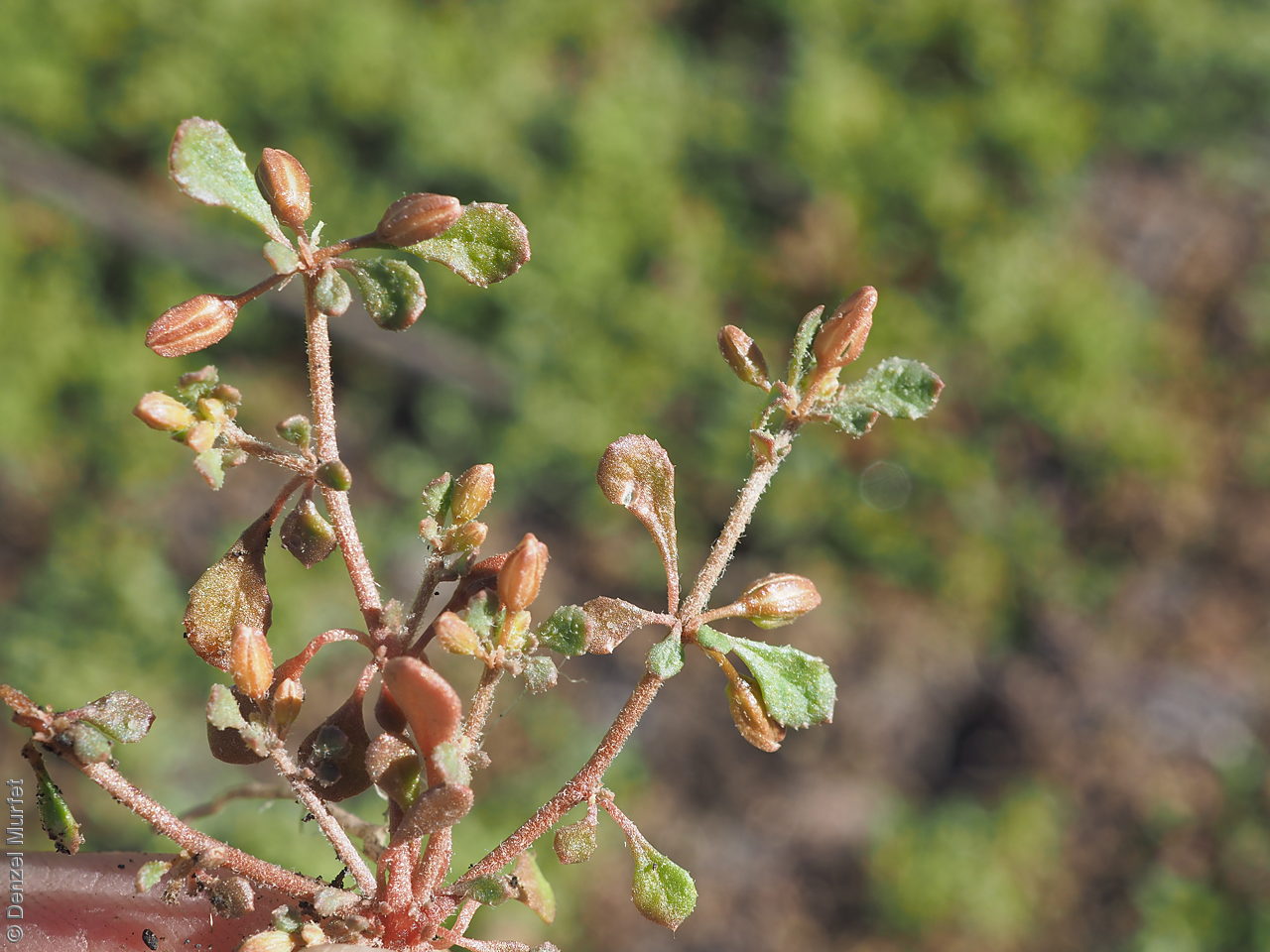
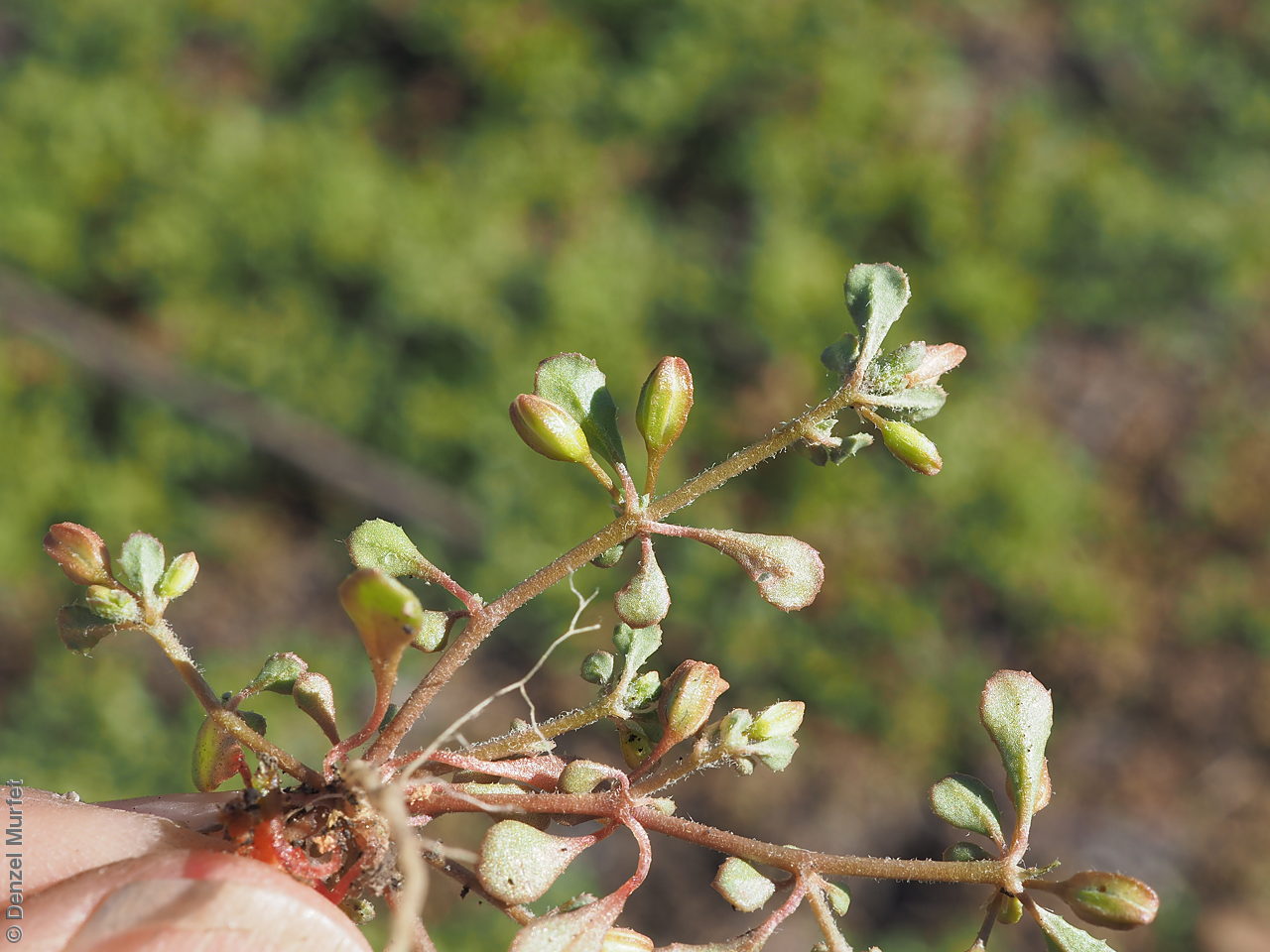
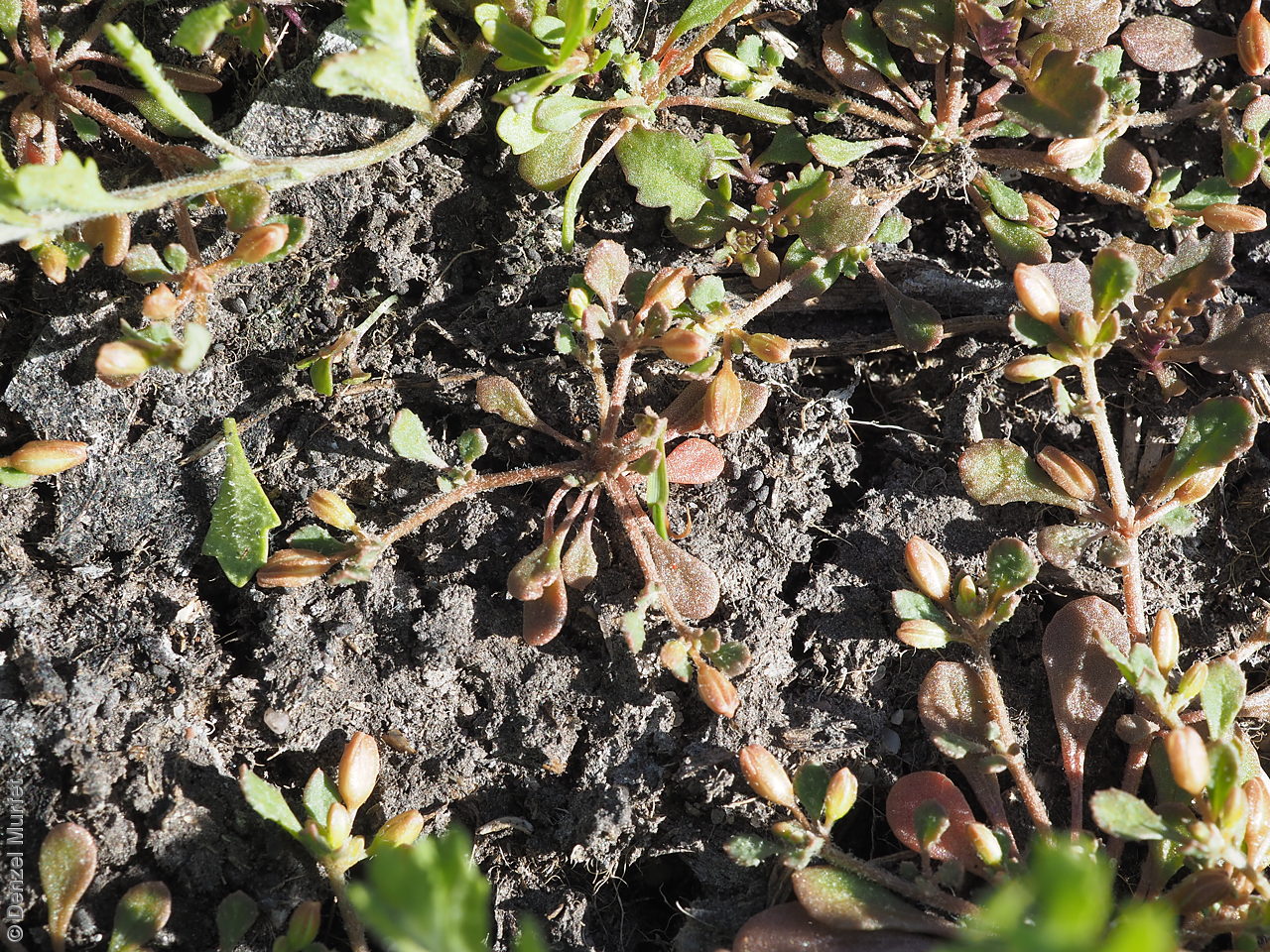
Plant description
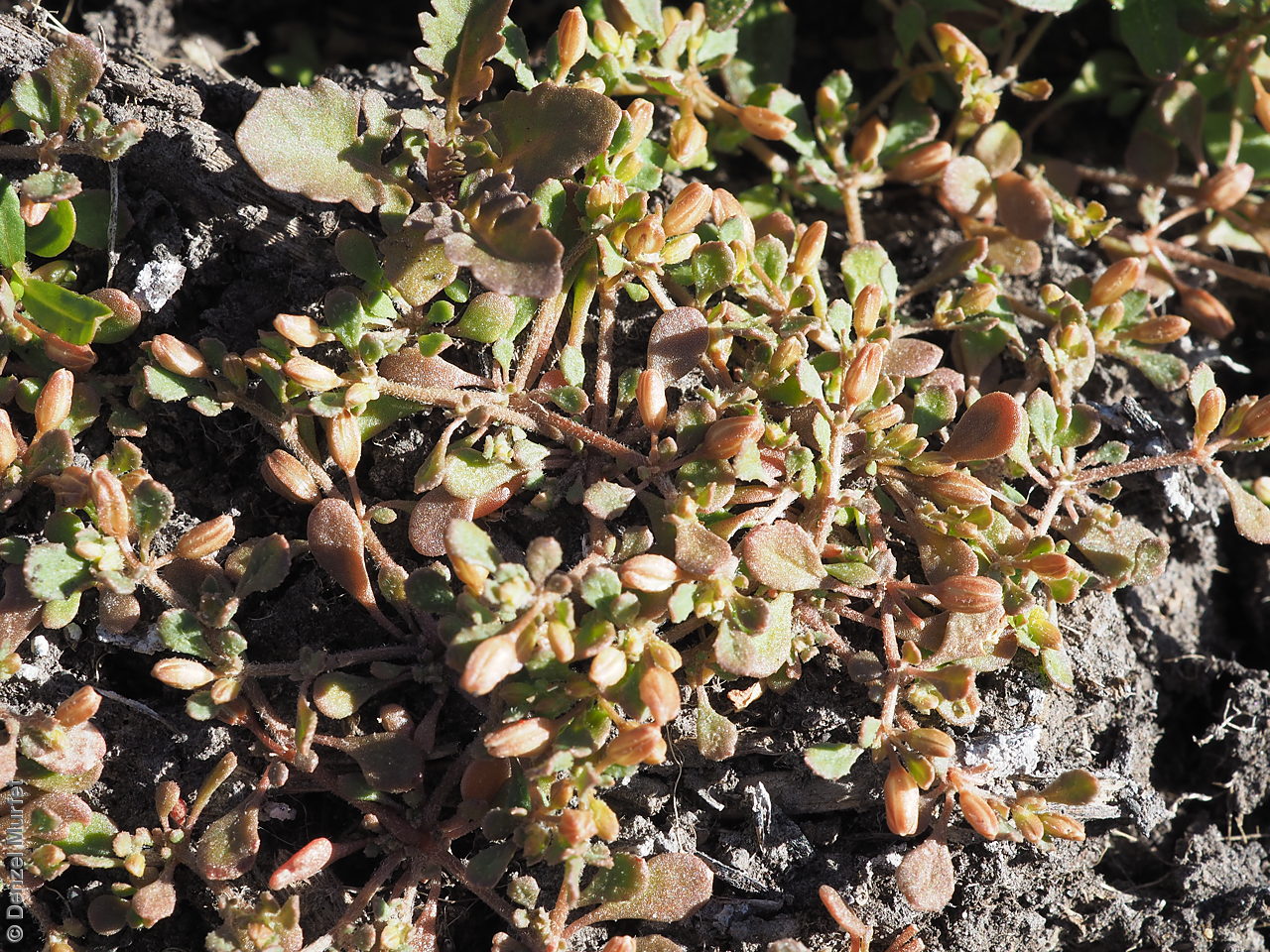
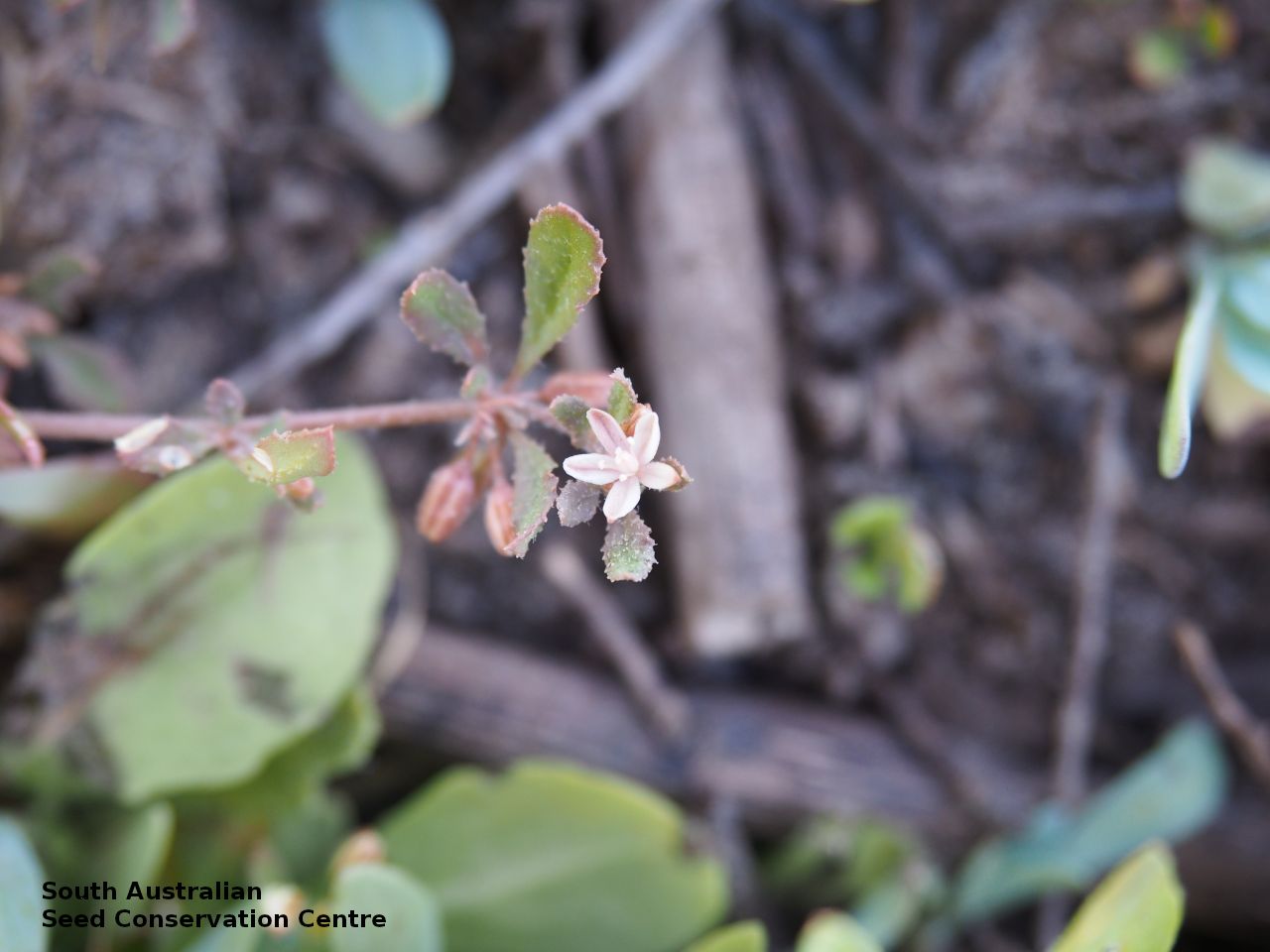
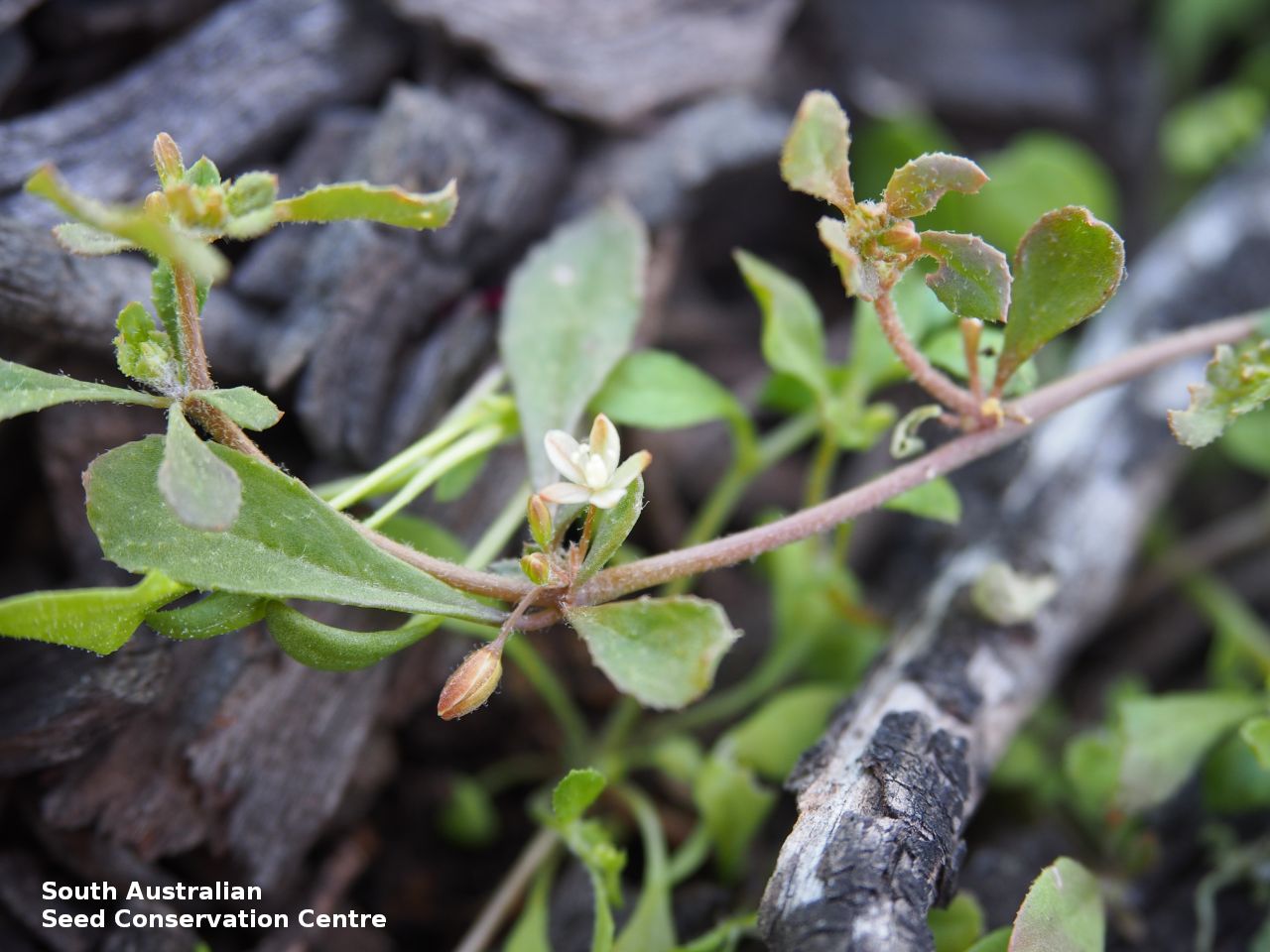
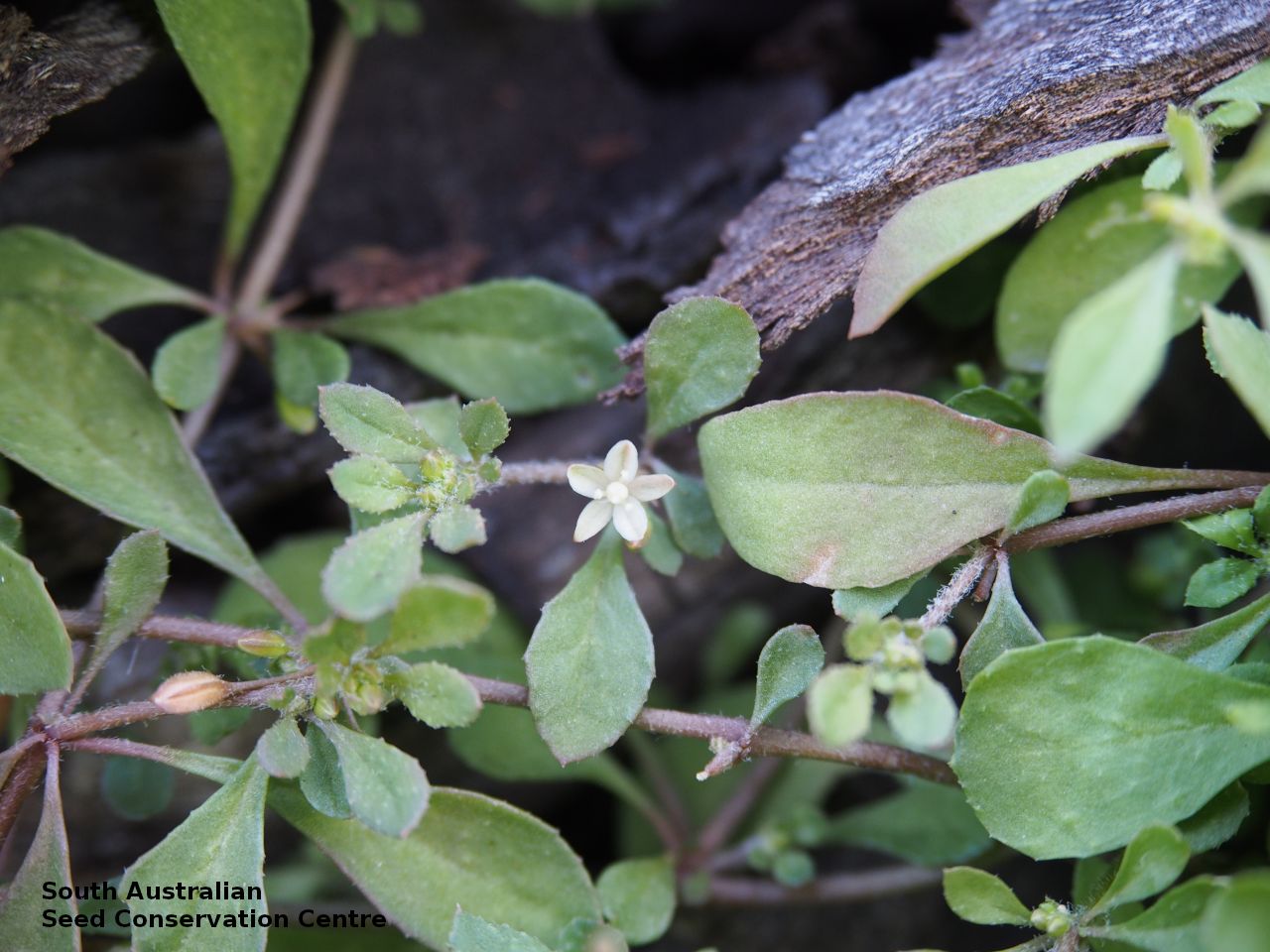
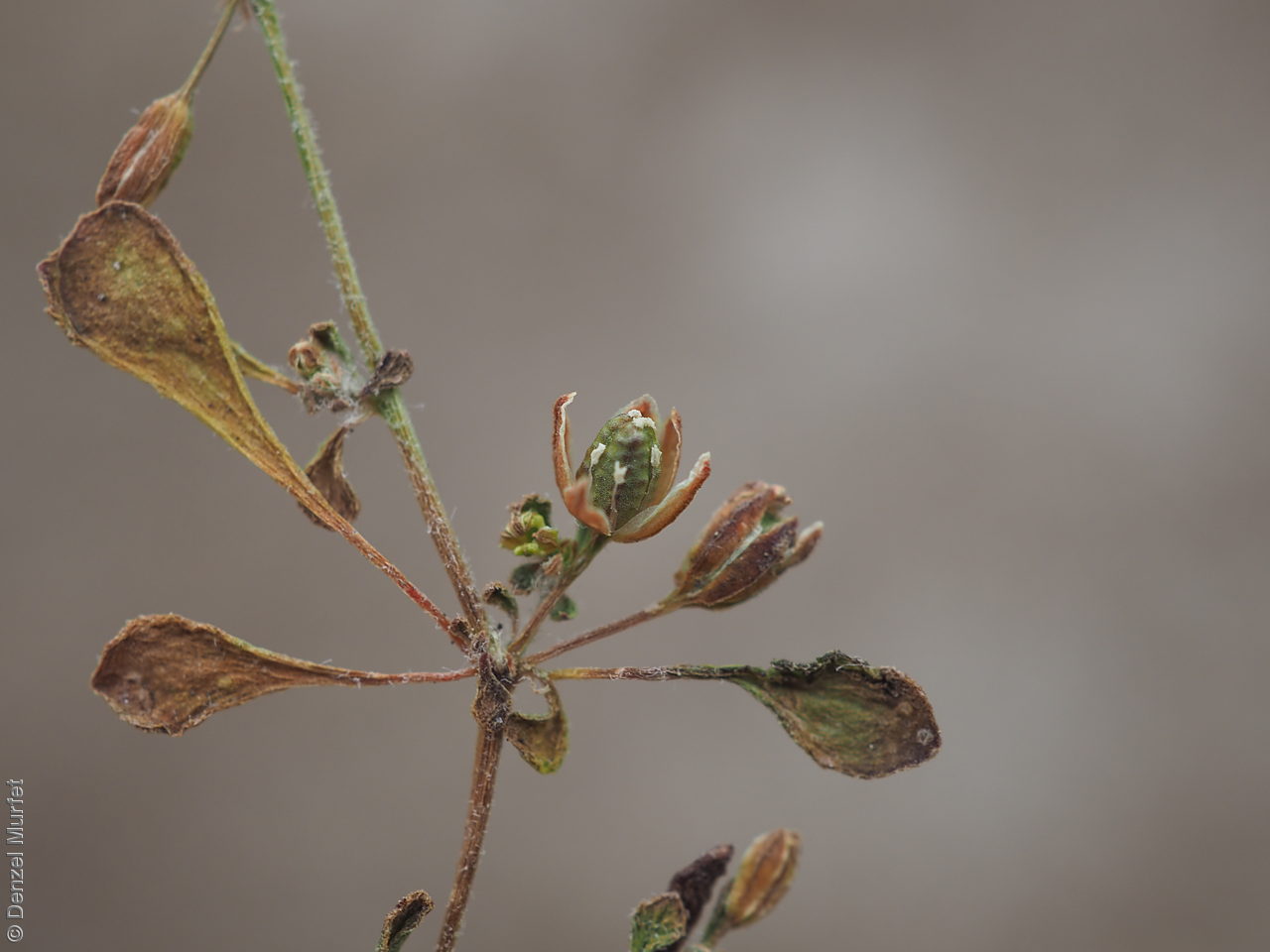
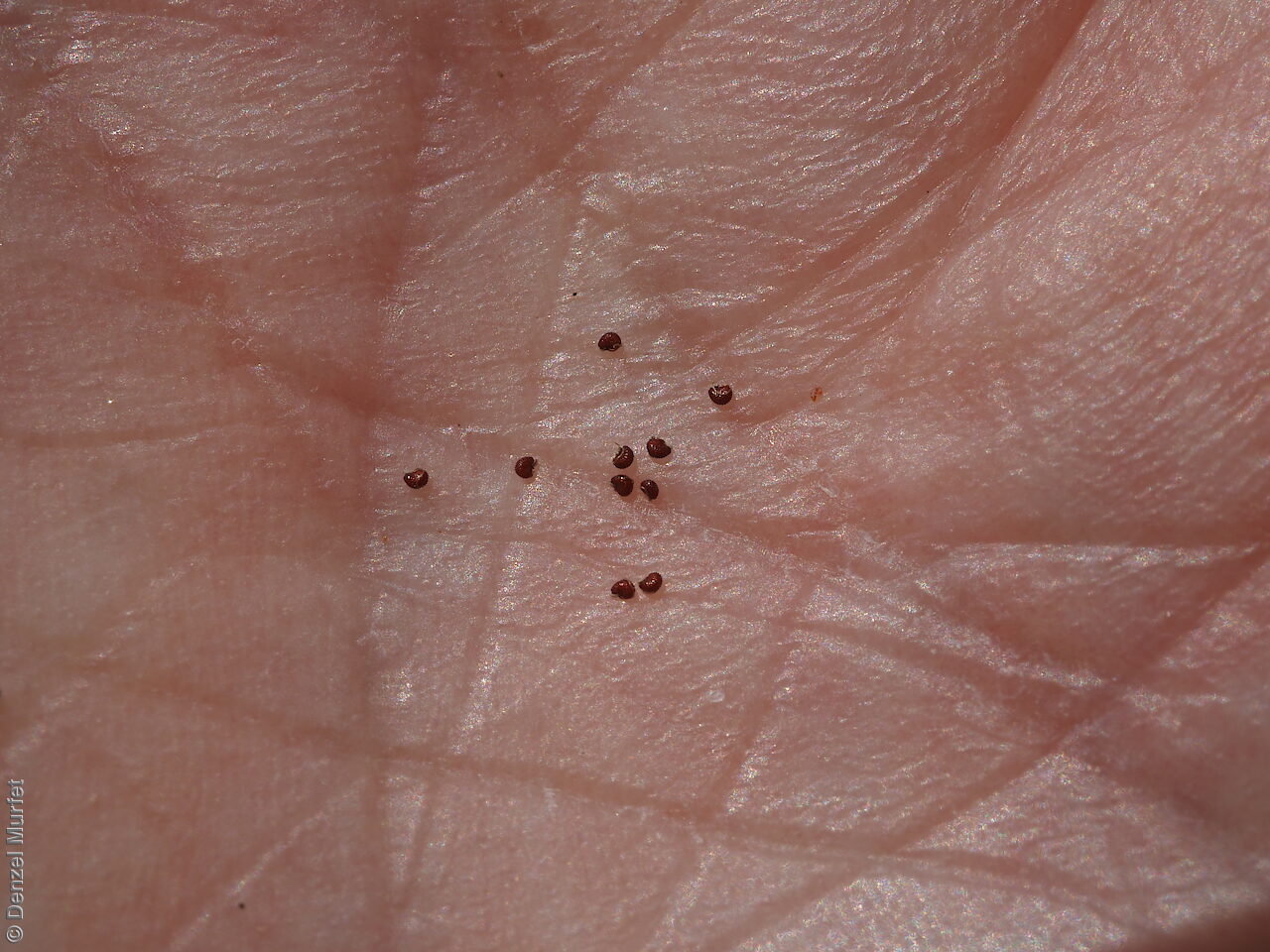
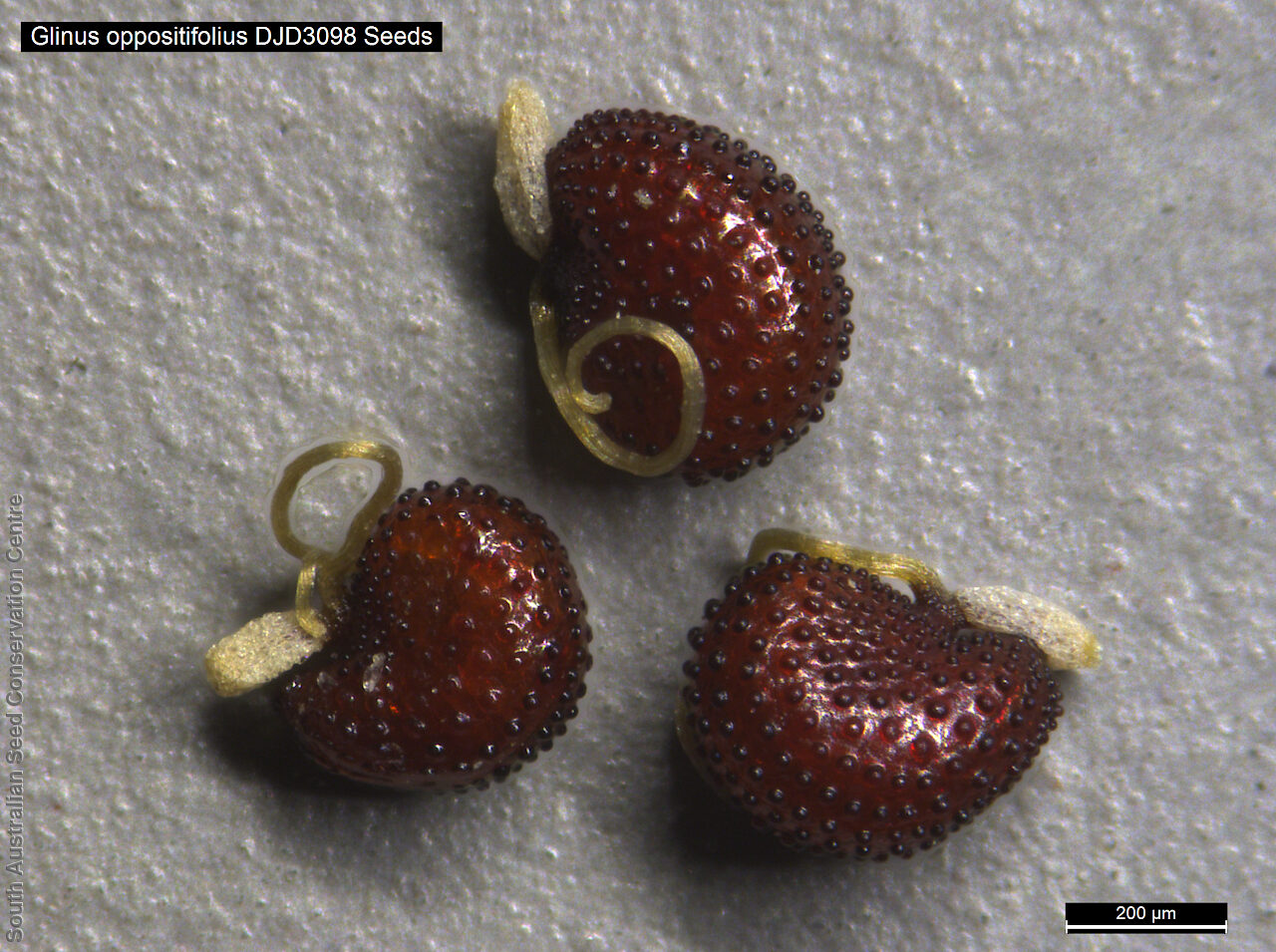
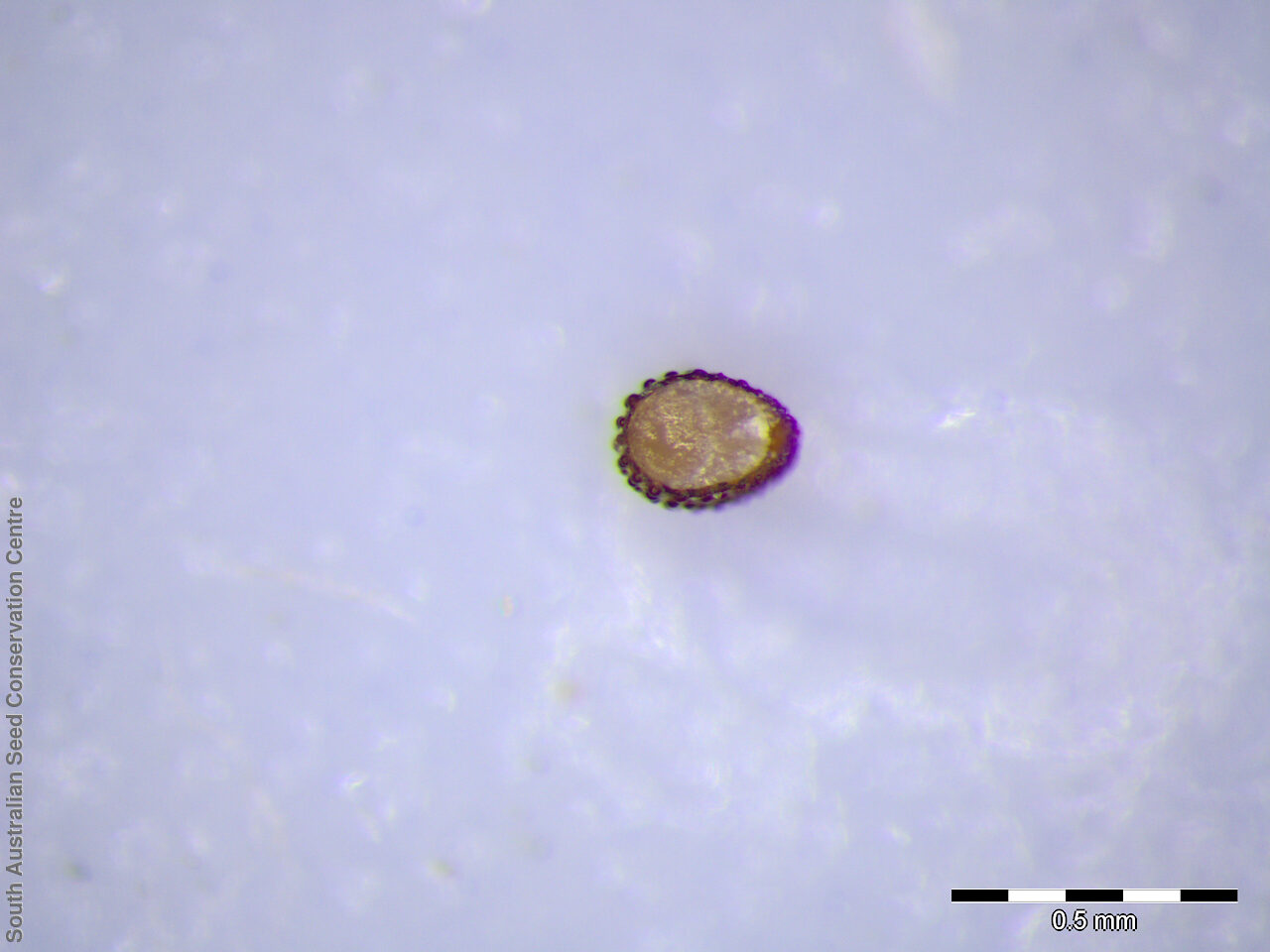
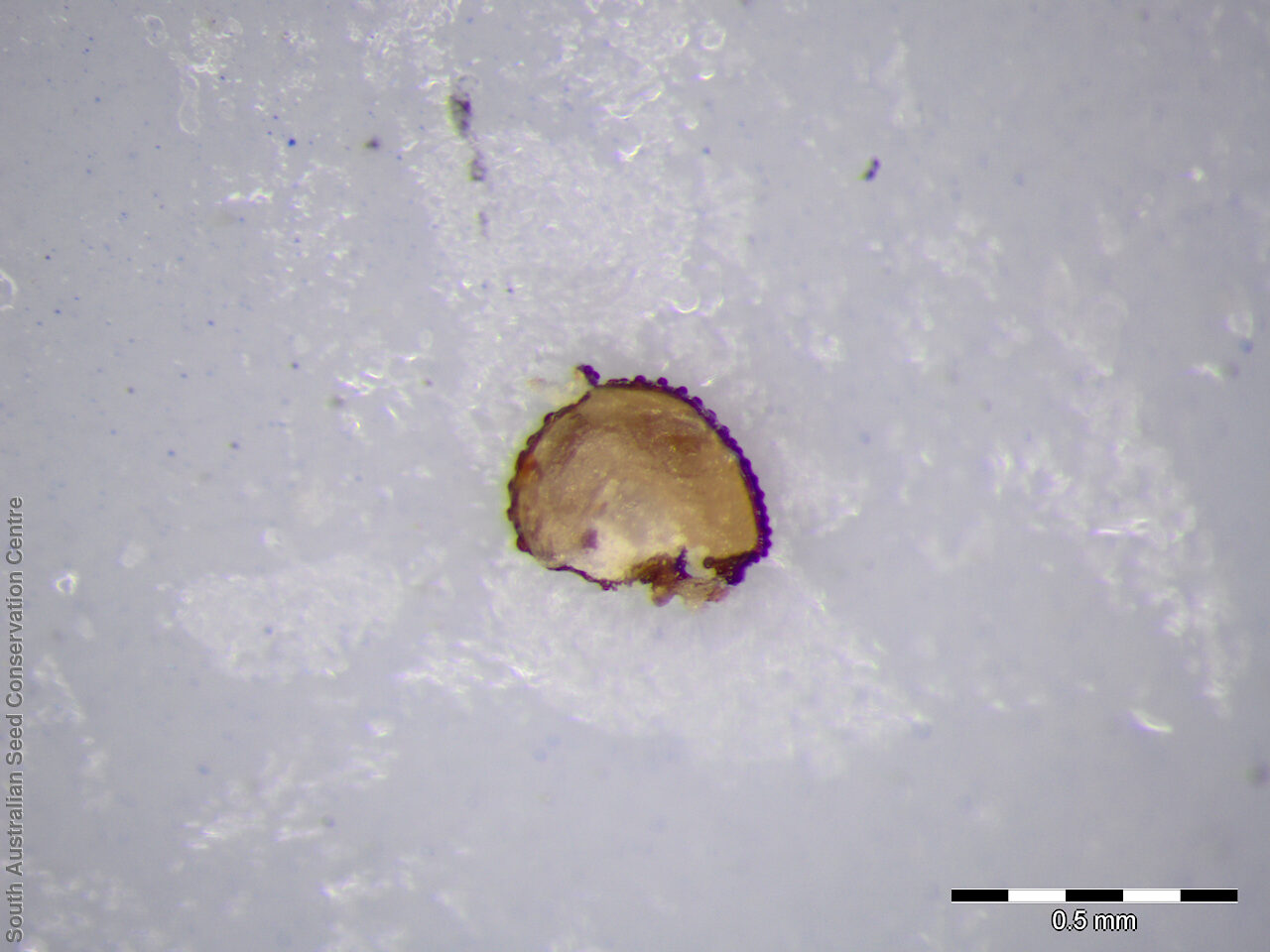
Prostrate annual to 50 cm in diameter. Leaves opposite and/or alternate, obovate to oblanceolate, to 30 mm long, glabrous. Flowers in leaf-opposed clusters of 3-6; perianth-segments to 5 mm long, white or pinkish inside. Flowering between January and July. Fruits are brown capsules enclosed in the perianth with 3-valves. Seeds are brown reniform seed to 0.5 mm long and 0.4 mm wide, with tuberculate surface. Seed embryo type is peripheral.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between April and August. Collect capsules that are maturing, turning brown and contain hard, brown seeds inside. Place the capsules in a tray and leave to dry for one to two weeks. Then rub the capsules gently by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Be careful as the seeds are very small. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. This species has physiological dormancy and can be difficult to germinate.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA | 31,000 (0.51 g) | 30+ | 11-Jan-2012 | MJT361 Murray | 1-Nov-2012 | 100% | -18°C |
| BGA | 34,000 (0.68 g) | 5-Feb-2015 | DJD3098 Murray | 1-Jan-2016 | 70% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.