









Botanical art
Prior names
Brachycome campylocarpa
Etymology
Brachyscome from the Greek 'brachys' meaning short and 'kome' meaning hair; referring to the short bristles or hairs of the pappus. Campylocarpa from the Greek 'capylos' meaning curved, bent and 'carpos' meaning fruit; alluding to its bent fruit.
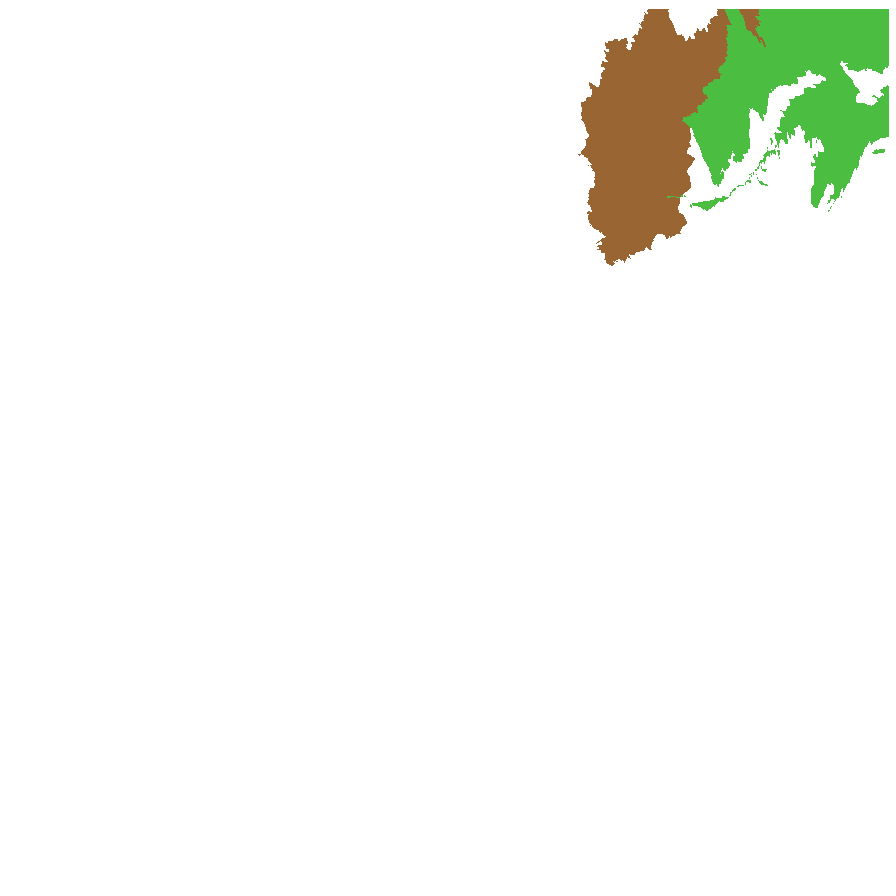
Distribution and status
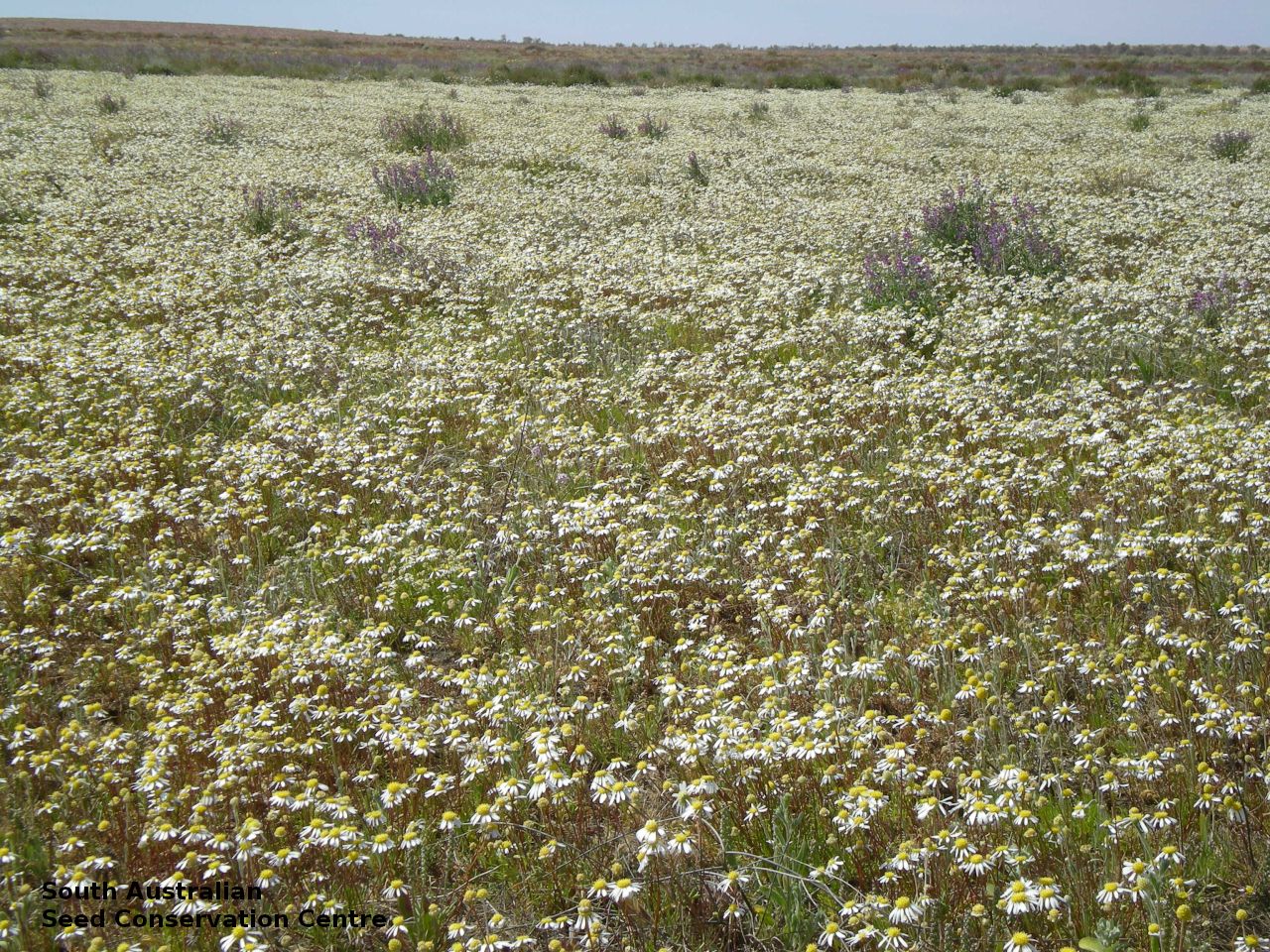
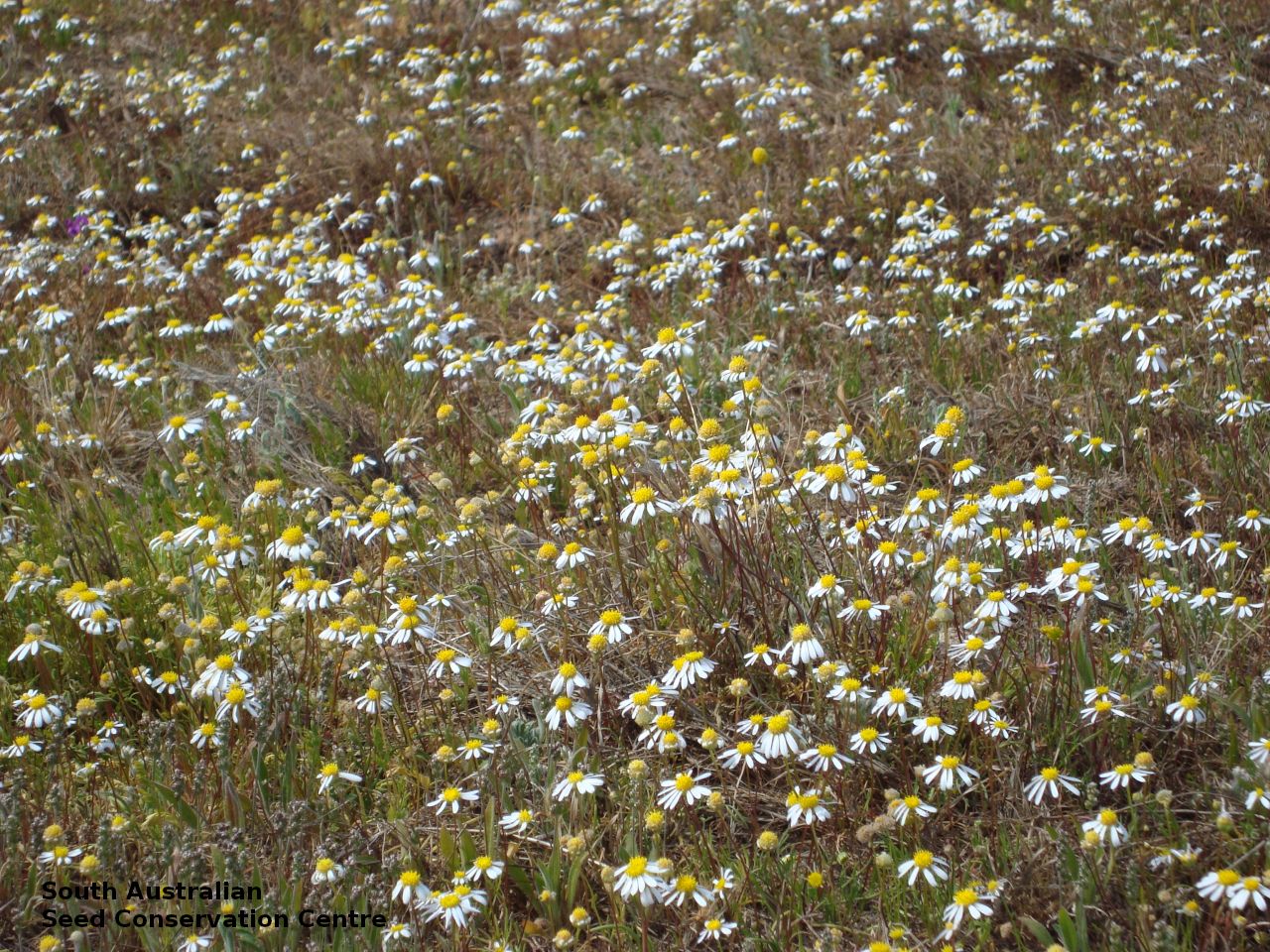
Found in the central and northern parts of South Australia, in depressions between sand dunes and on flood plains. Also found in Queensland. Native. Common in South Australia. Uncommon in Queensland.
Herbarium regions: Lake Eyre, Flinders Ranges
NRM region: South Australian Arid Lands
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
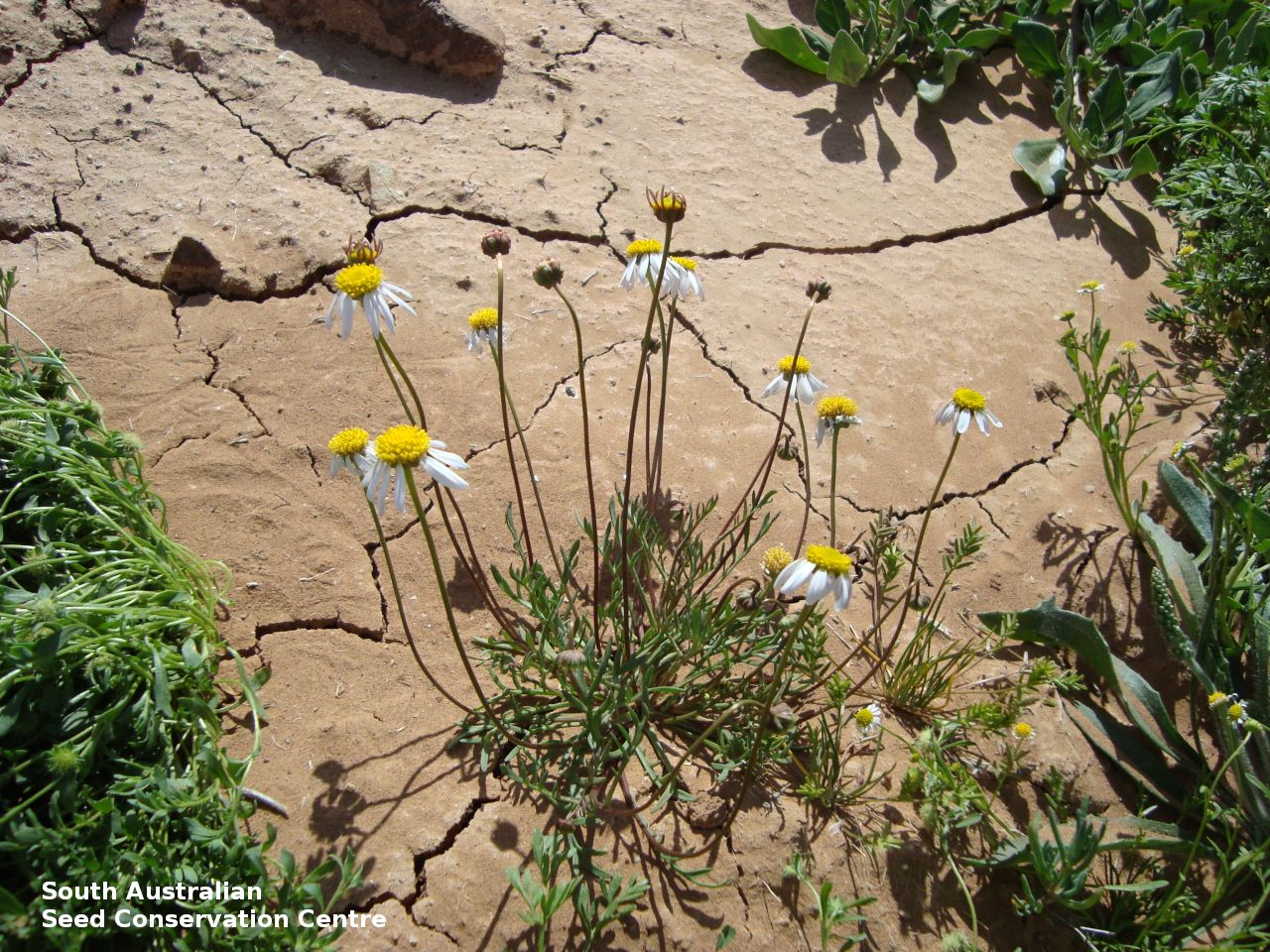
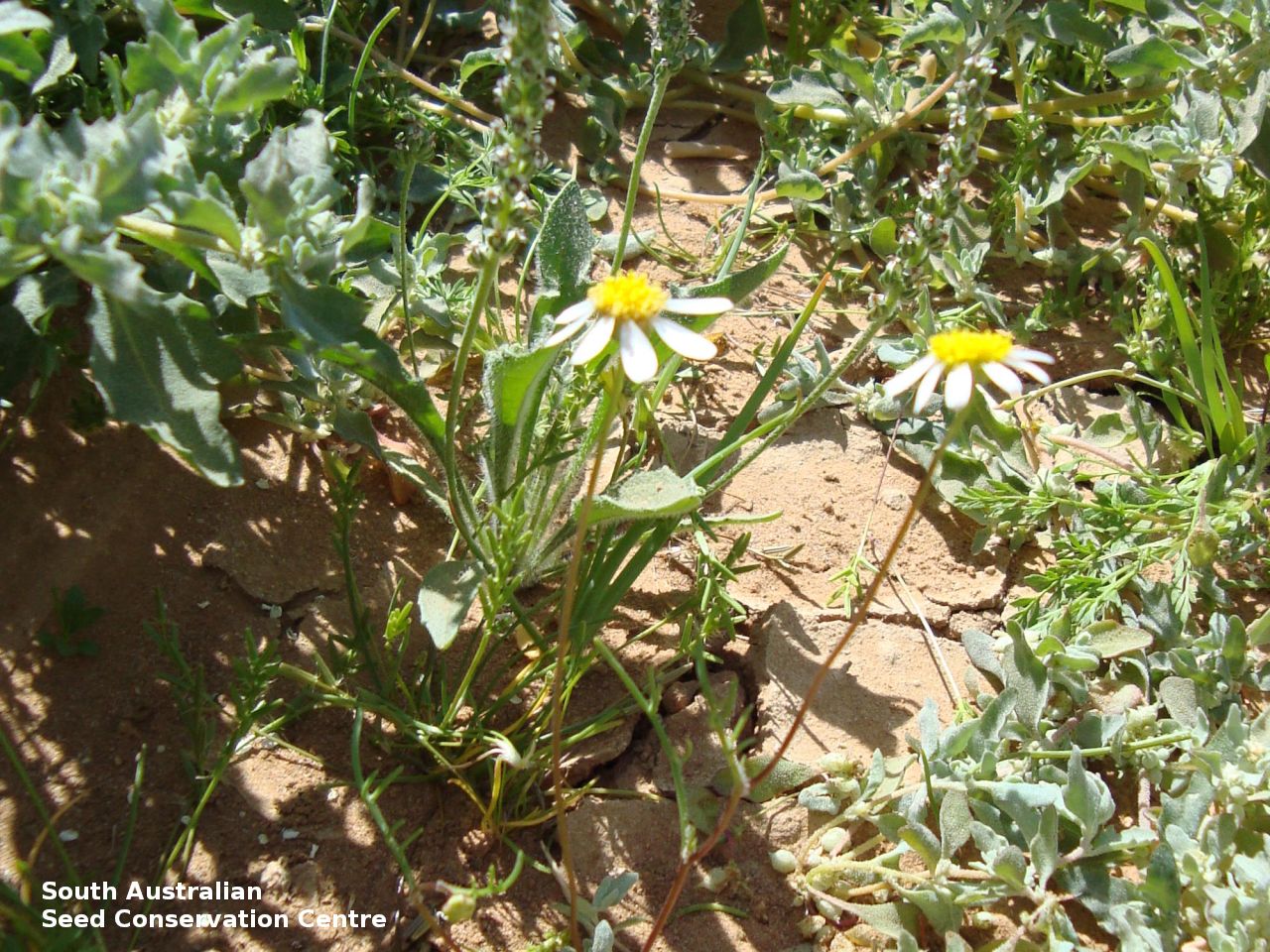
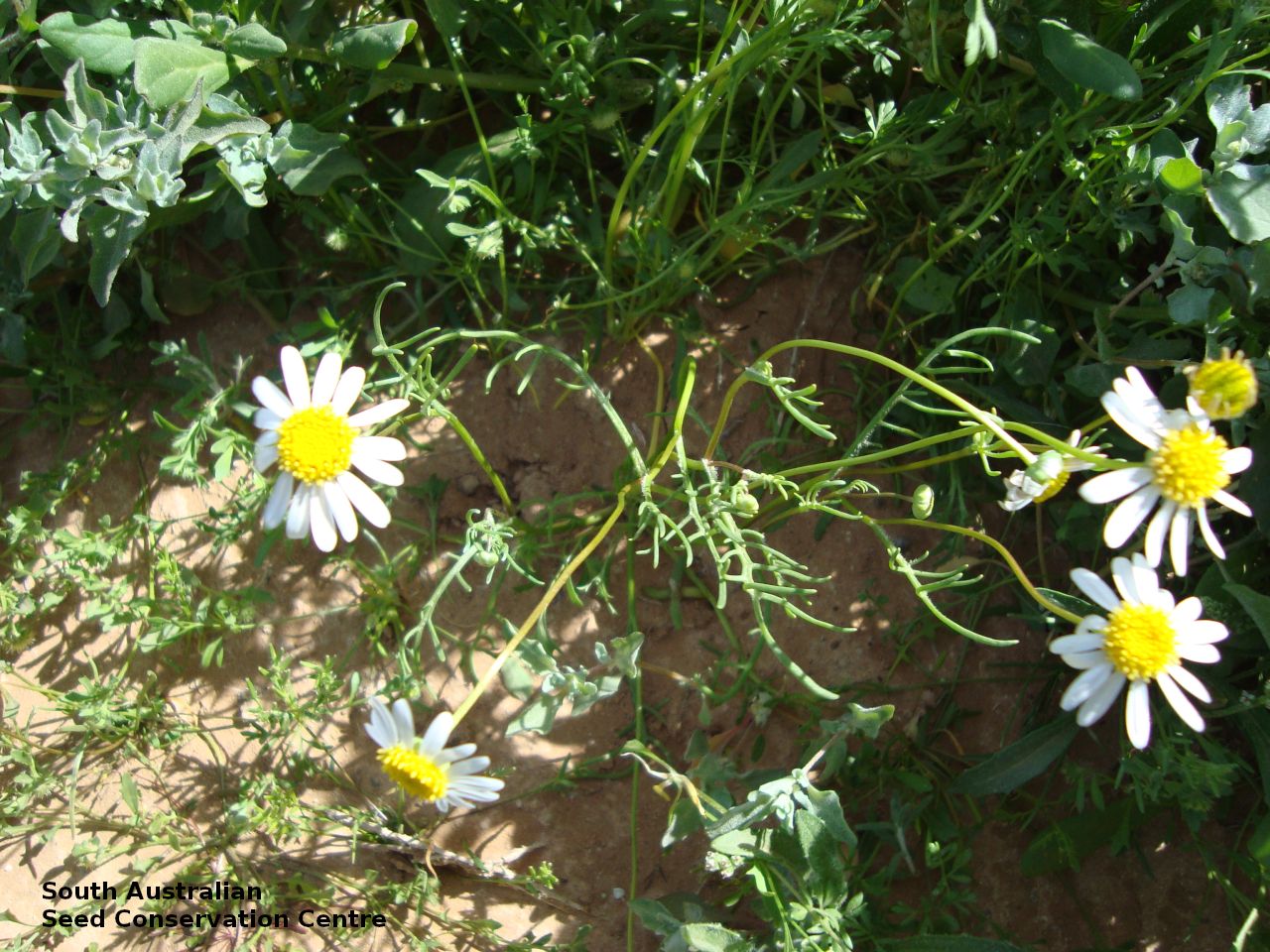
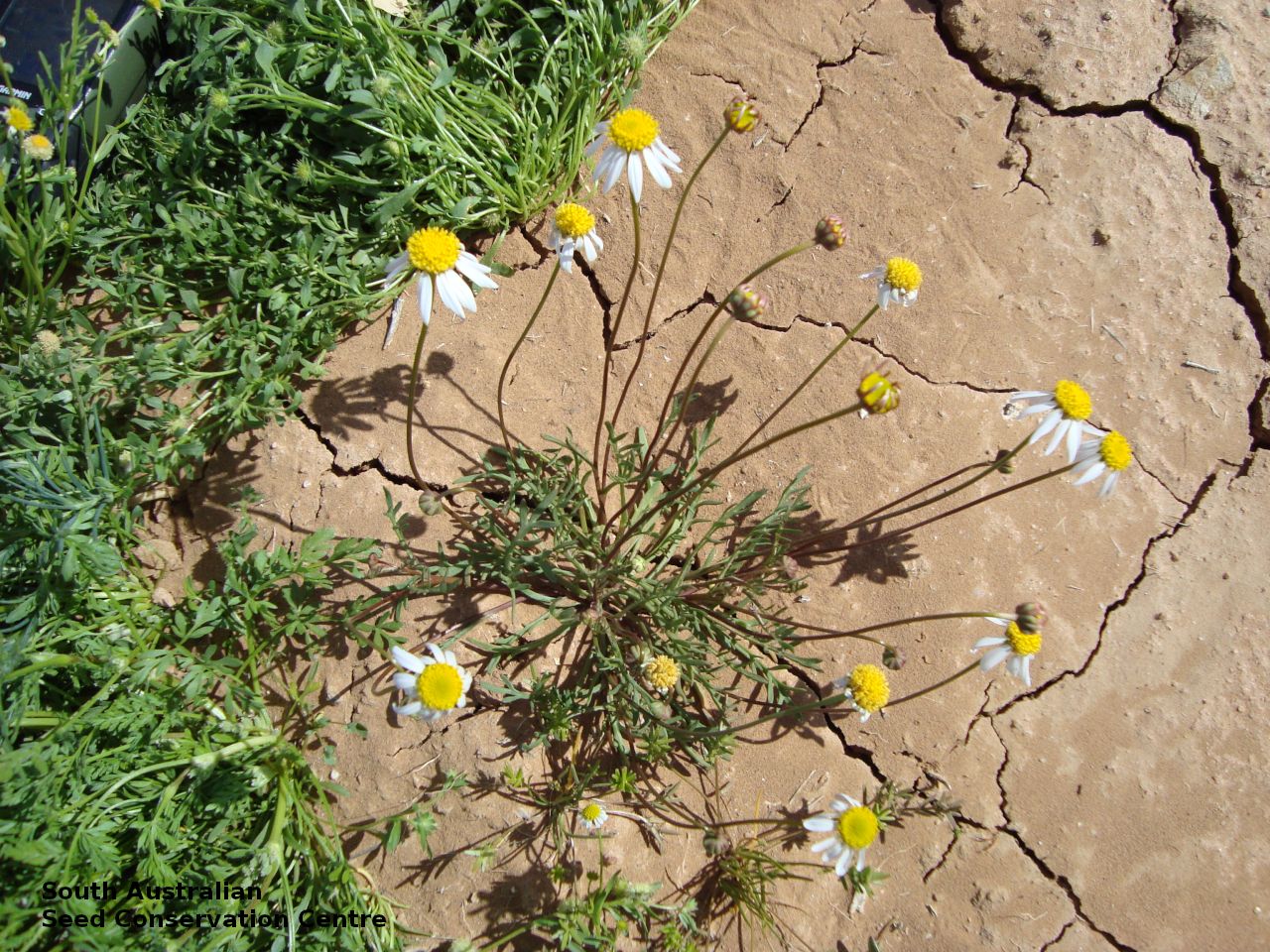
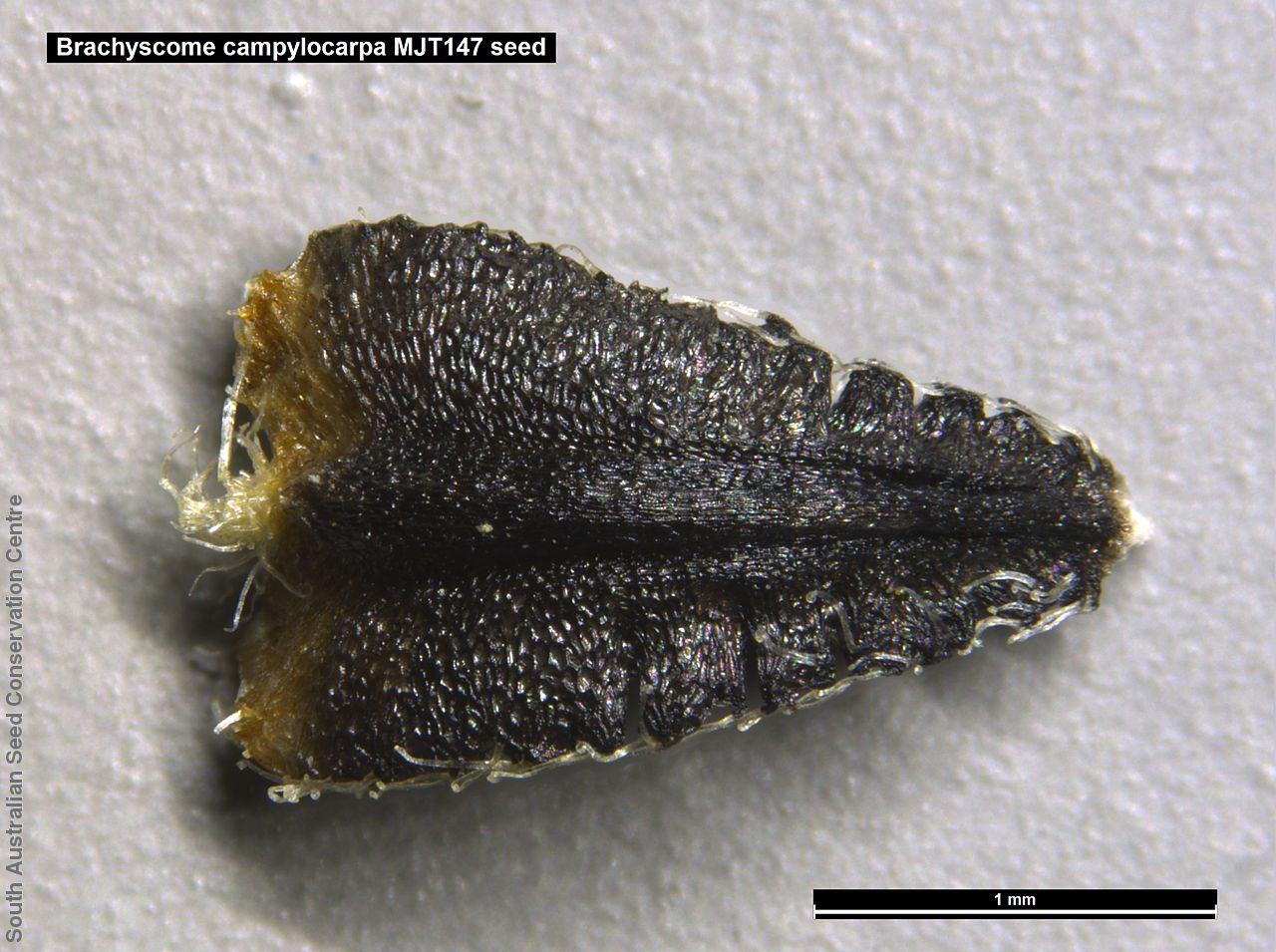
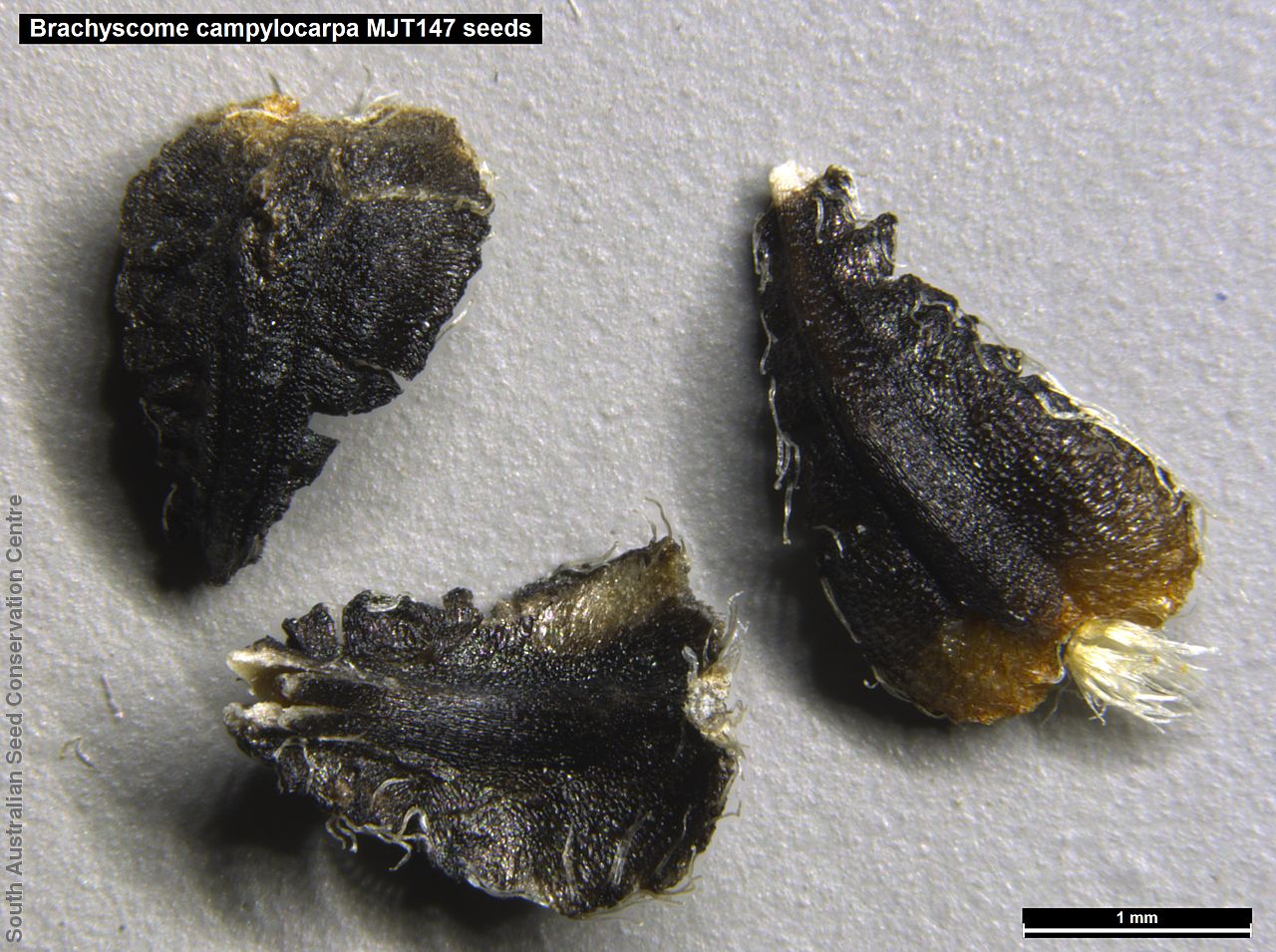
Branching annual herb to 40 cm high with hairless and relatively thick stems. Basal leaves are pinnate or entire. Stem leaves are pinnate to 11 cm long and reducing in size up the stem. Large daisy with white ray florets. Flowering between August and September. Fruits are large brown daisy heads. Seeds are black wedge-shaped curved seed to 3 mm long and 1.5 mm wide, with lobed margins and dense hairs at one end and scattered hairs along the margin. Seed embryo type is spatulate fully developed.
Seed collection and propagation
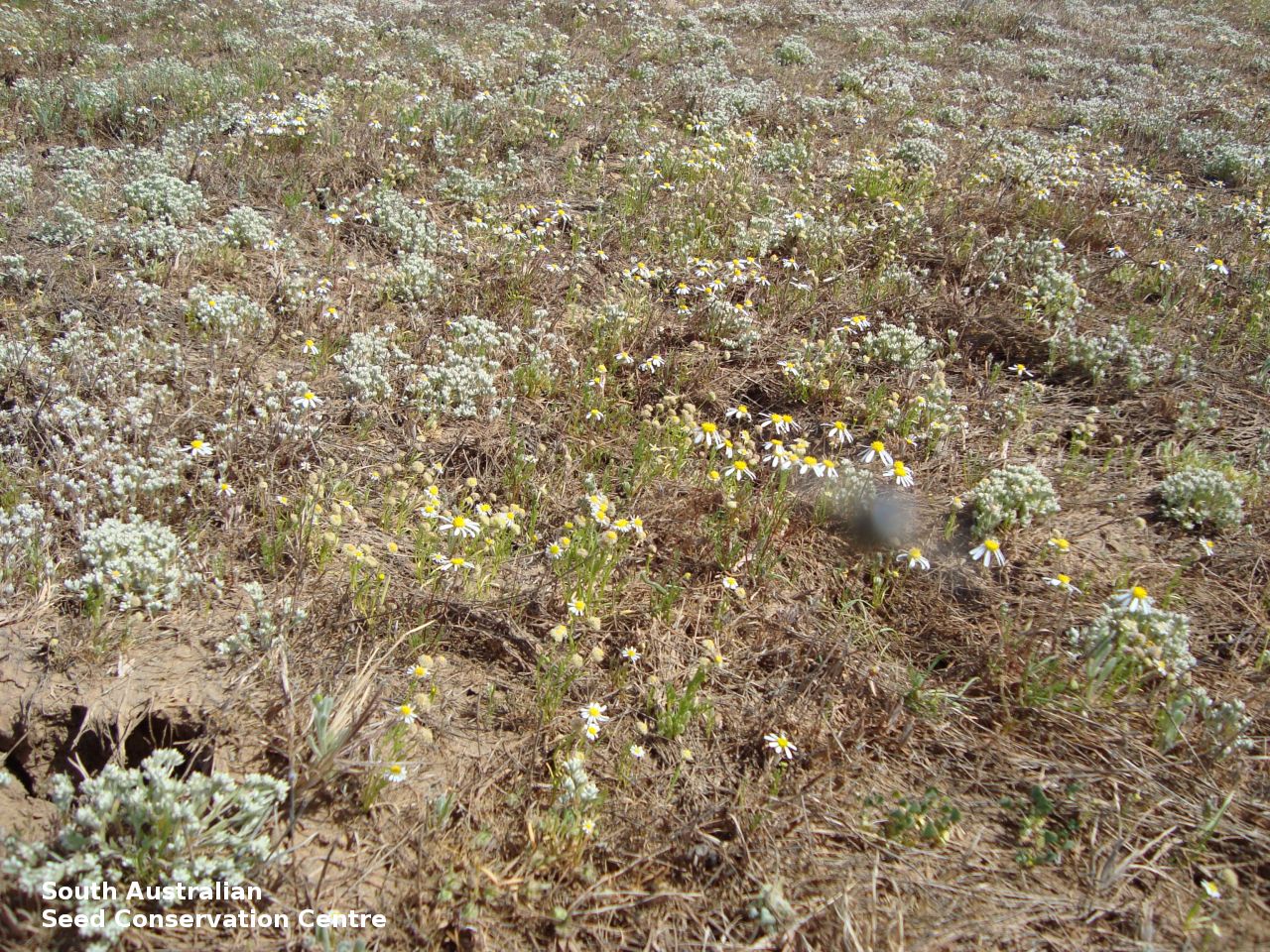
Collect seeds between October and December. Pick heads that are maturing, drying off, with brown seeds that dislodge easily. Place the seed-heads in a tray and leave to dry for a week. Then gently rub the heads by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. From one collection, the seed viability was average to high, at 80%. This species has physiological dormancy that needs to be overcome for the seed to germinate. Winter conditions produce high germination. Germination is increased with 250 mg/L gibberellic acid added to water agar. Dormancy can be alleviated with after-ripening at 30 oC or stratification at 15 oC
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 16,000 (7.1 g) 16,000 (7.1 g) | 200+ | 22-Oct-2007 | MJT147 Lake Eyre | 1-Jun-2010 | 80% | -18°C |
| BGA | 96,000 (40.65 g) | 25-Sep-2008 | MJT191 Lake Eyre | 1-Jan-2012 | 90% | -18°C | |
| 200+ | 25-Sep-2008 | MJT191 Lake Eyre | 1-Nov-2017 | 90% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.