




Botanical art
Prior names
Brachyscome leptocarpa
Brachycome leptocarpa
Brachycome debilis
Common names
Weak Daisy
Etymology
Brachyscome from the Greek 'brachys' meaning short and 'kome' meaning hair, referring to the tuft of short bristles or hairs of the pappus. Debilis from the Latin 'debilis' meaning weak, frail, small, alluding to its habit.
Distribution and status
Scattered records from the Flinders Ranges, southern Mount Lofty Ranges, Eyre Peninsula and the lower South-east in South Australia, growing in woodland in damp mossy hollows in rocks or in seepage areas. Also found in New South Wales and Victoria. Native. Rare in South Australia. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: Flinders Ranges, Eastern, Eyre Peninsula, Northern Lofty, Murray, Yorke Peninsula, Southern Lofty, South Eastern, Green Adelaide
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
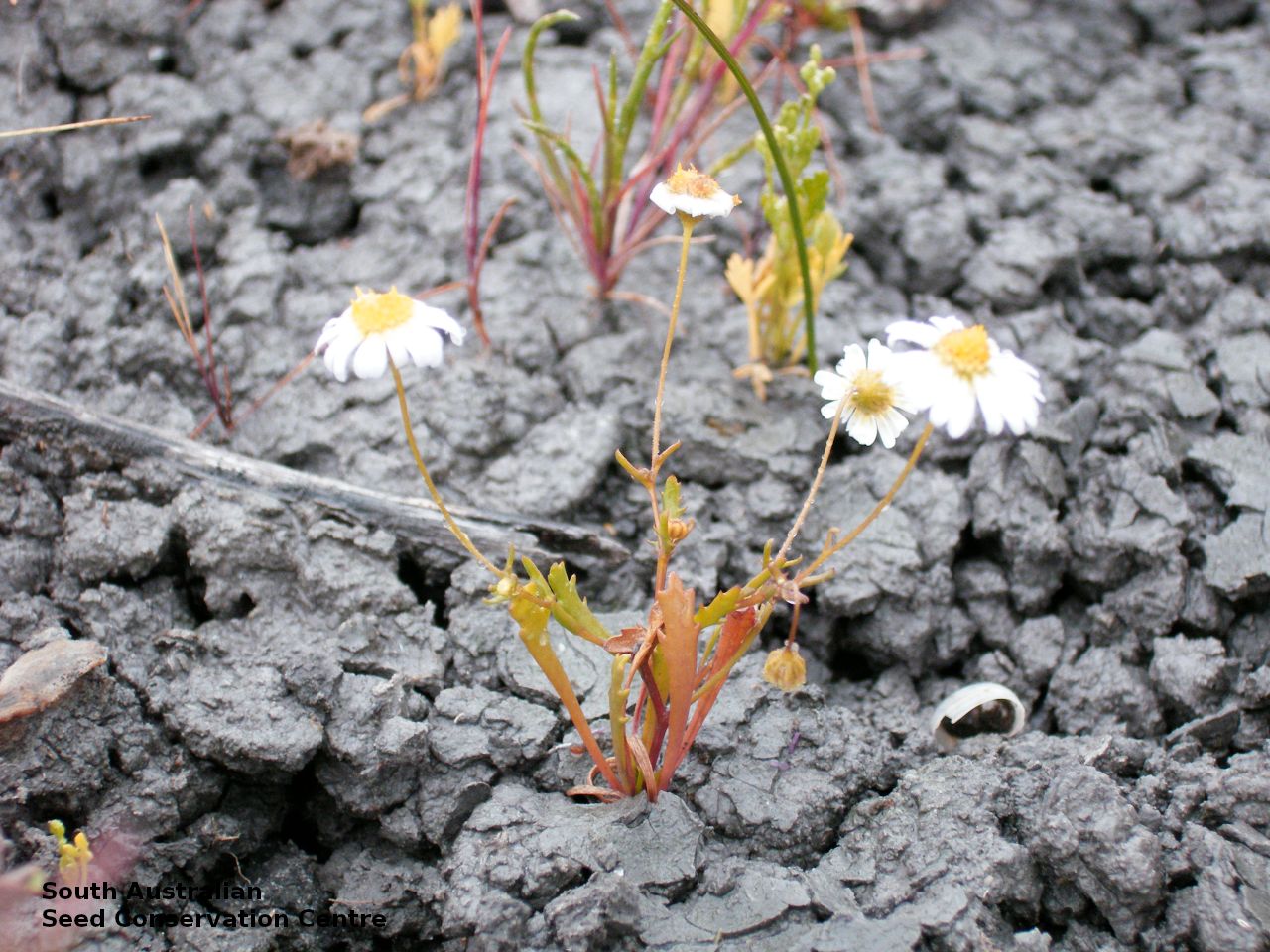
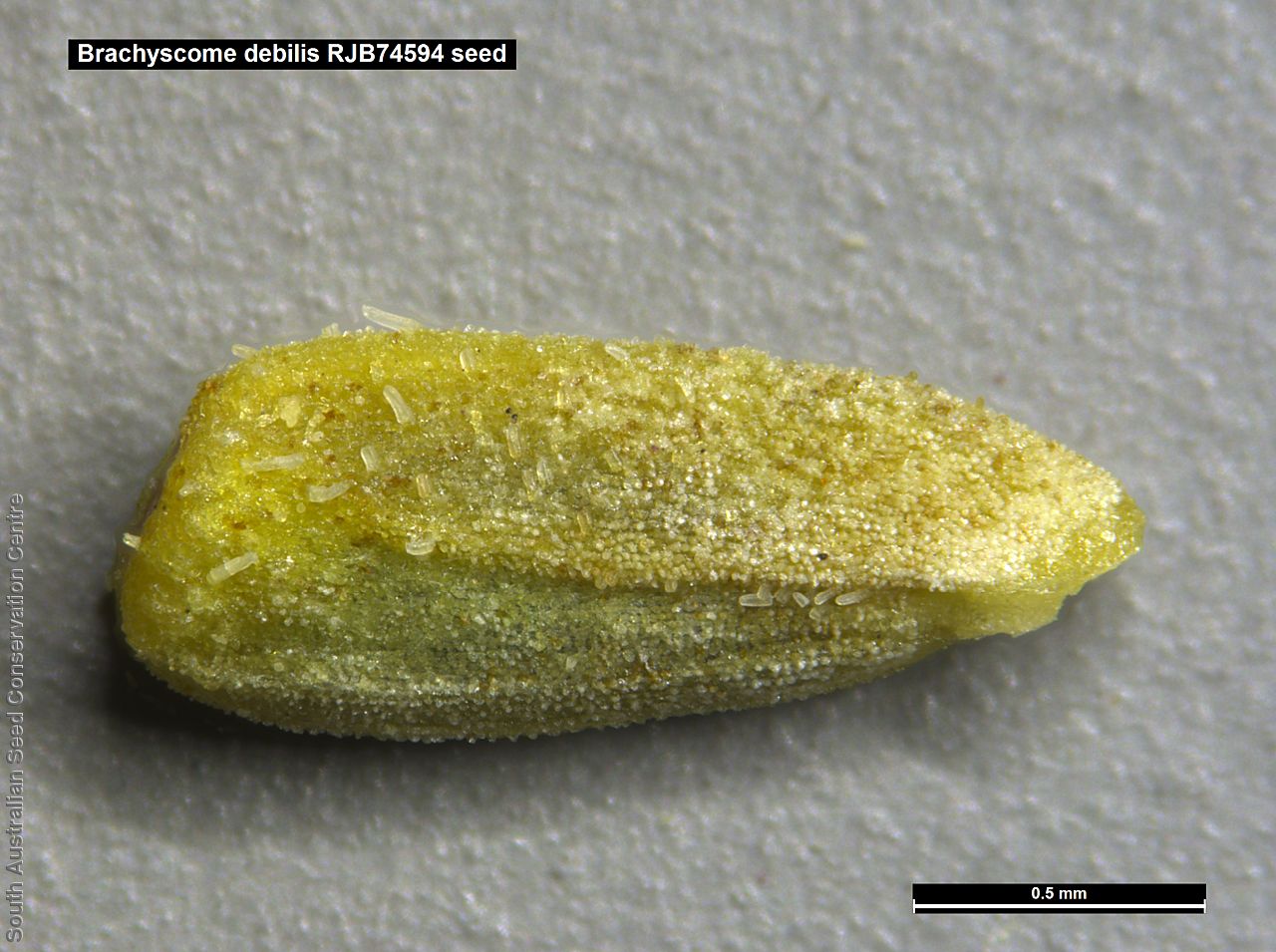
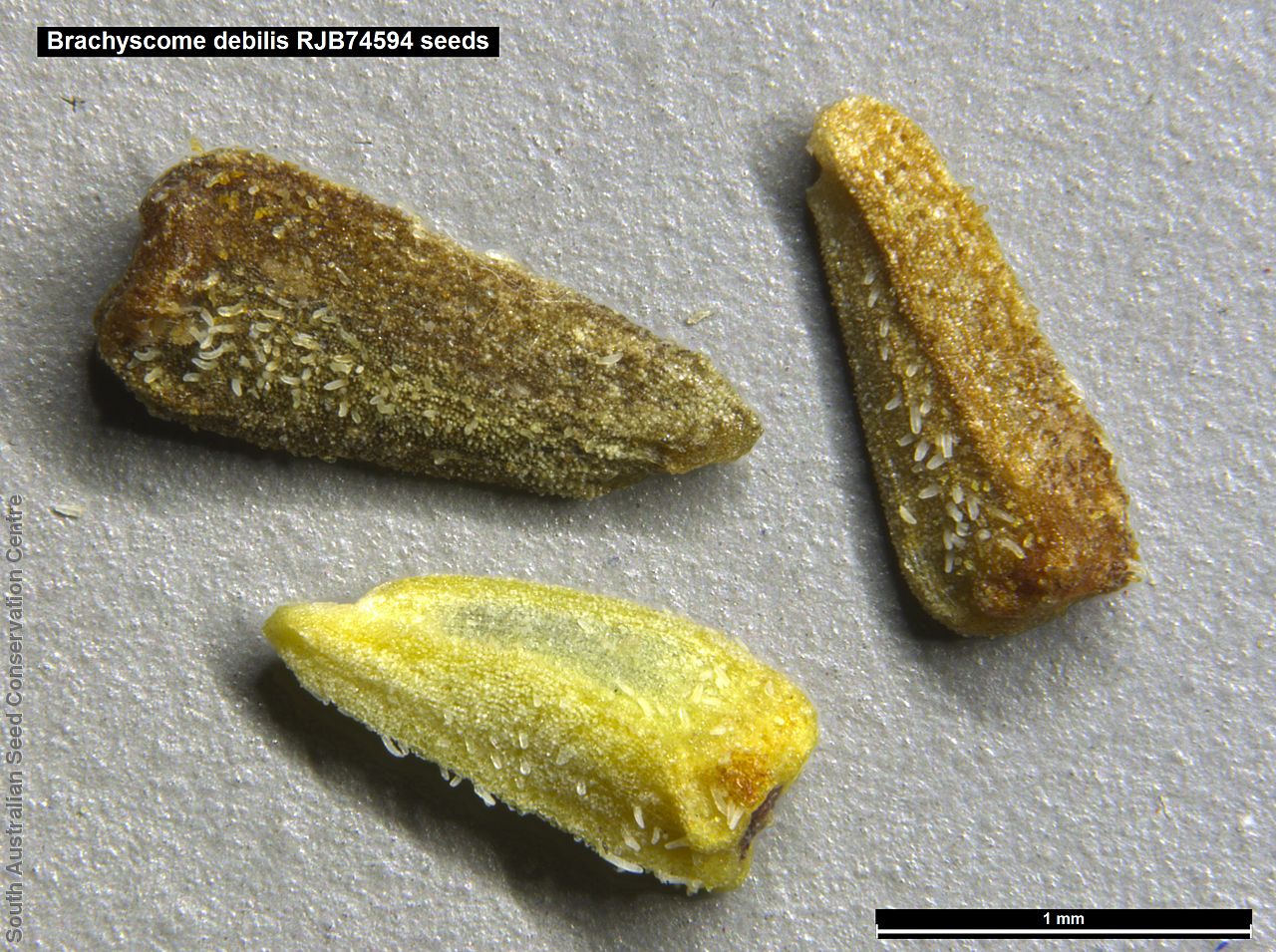
Annual or ephemeral herb to 12 cm high with ascending, sparsely pubescent stems. Basal leaves to 1 cm long, soon withering. Stem leaves with 3-7 linear lobe to 2 cm long, sparsely pubescent. Large white daisy appearing in spring but can flower all year, round depend on rainfall. Fruits are brown daisy-heads. Seeds are brown ovoid seed to 1.5 mm long and 0.5 mm wide. Seed embryo type is spatulate fully developed.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between January and December. Pick heads that are maturing, drying off, with brown seeds that dislodge easily. Place the seed-heads in a tray and leave to dry for a week. Then gently rub the heads by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Seed viability can be average. This species has physiological dormancy that need to be overcome for the seed to germinate.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 6,000 (1.33 g) 6,000 (1.33 g) | 30-Oct-2007 | RJB74594 South Eastern | 1-Jan-2012 | 60% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.