









Botanical art
Prior names
Ptilotus gaudichaudii ssp. gaudichaudii
Ptilotus gaudichaudii var. gaudichaudii
Trichinium gaudichaudii
Trichinium corymbosum, nom.illeg., non (R.Br.)Spreng.(1
Common names
Yellow Ptilotus
Paper Fox-tail
Etymology
Ptilotus from the Greek 'ptilotos' meaning feathered or winged; referring to the hairy flowers. Gaudichaudii named after Charles Gaudichaud-Beaupre (1789-1854), a French botanist who sailed on Freycinet expedition (1817-20) to Australia and named a few Australian genus.
Distribution and status
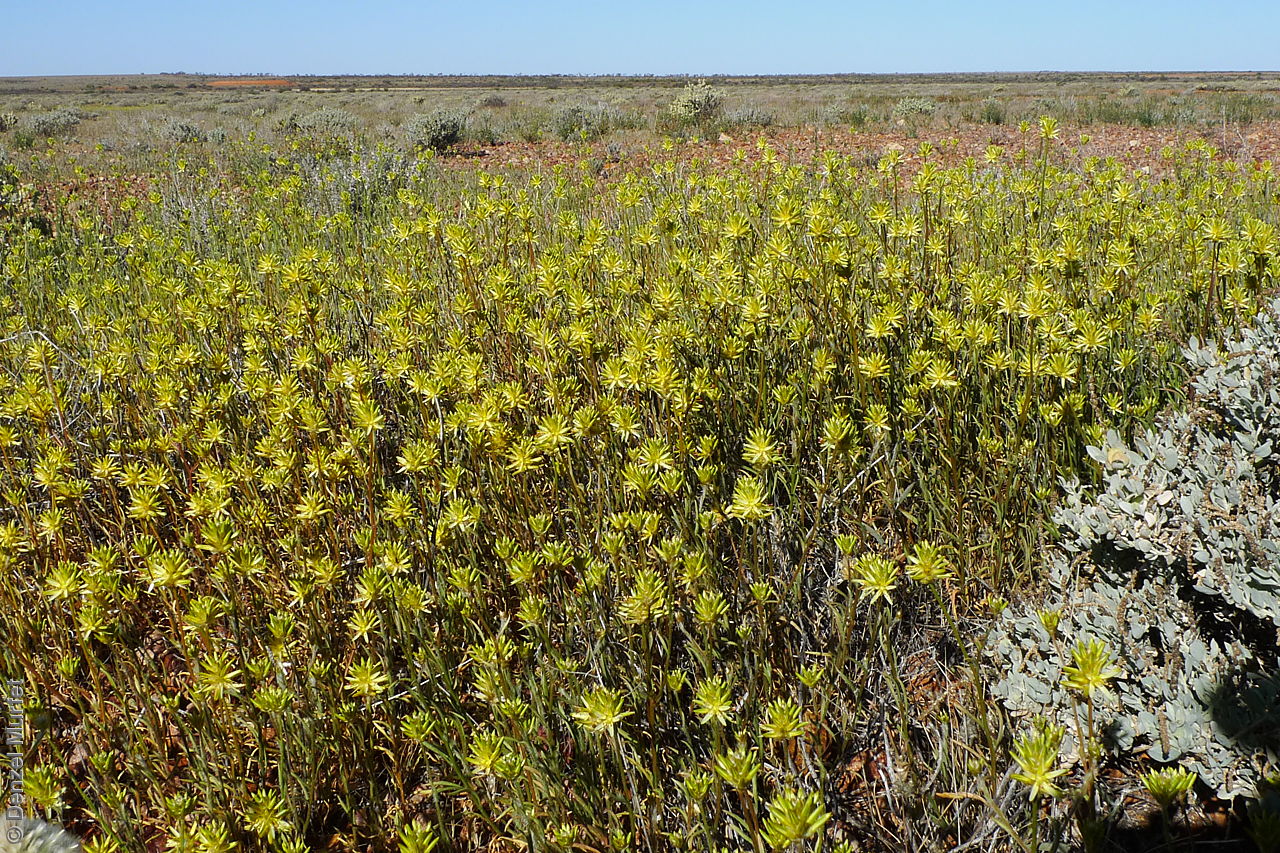
Found in the central and western parts of South Australia, growing on dunes, plains or creek banks, in red or brown sand, loam or clay-loam, in open mulga (Acacia aneura) woodland, chenopod shrubland or Triodia communities. Also found in Western Australia and Northern Territory. Native. Common in South Australia. Common in the other states.
Herbarium regions: North Western, Lake Eyre, Nullarbor, Gairdner-Torrens, Eyre Peninsula
NRM regions: Alinytjara Wilurara, Eyre Peninsula, South Australian Arid Lands
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
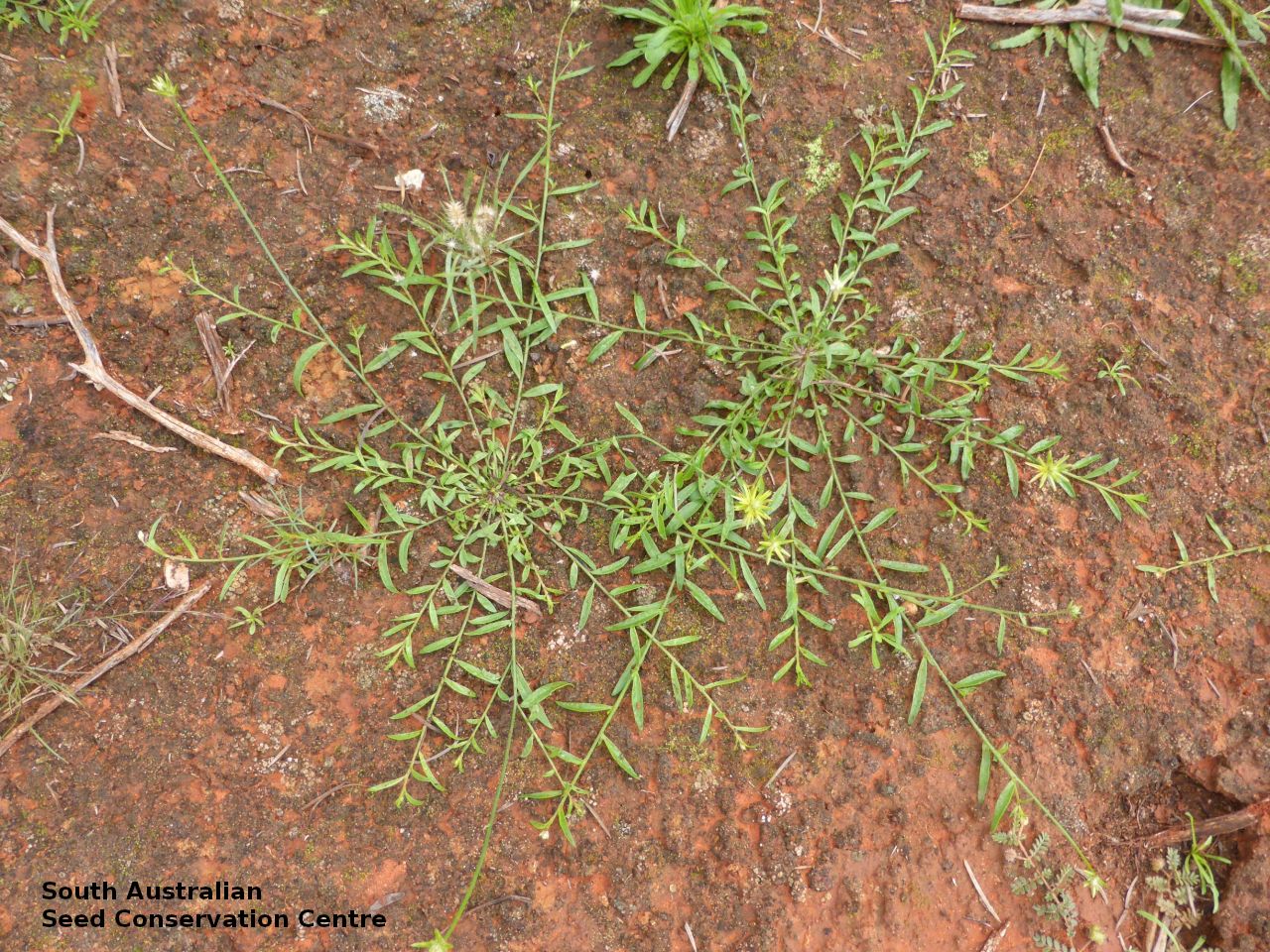
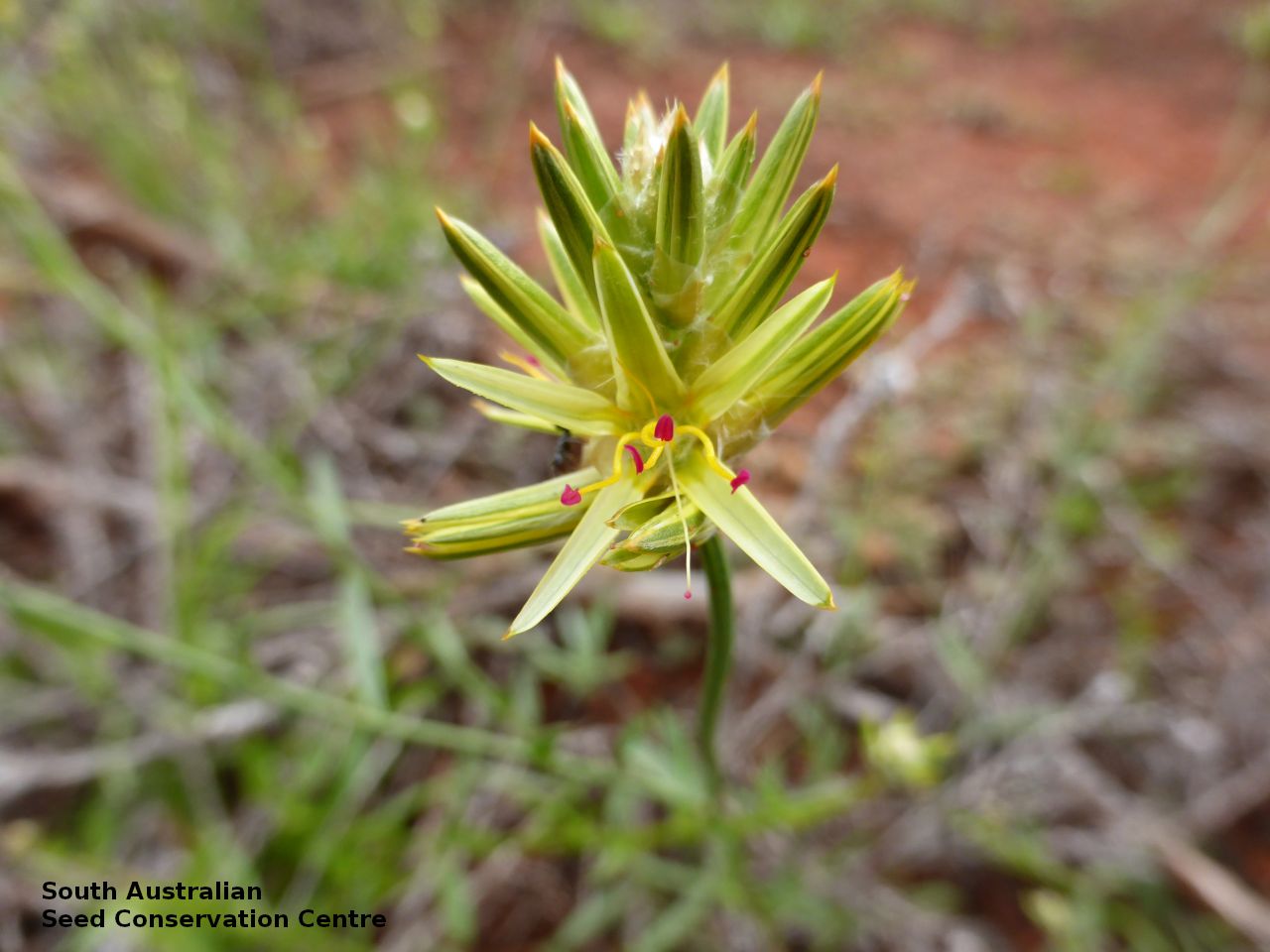
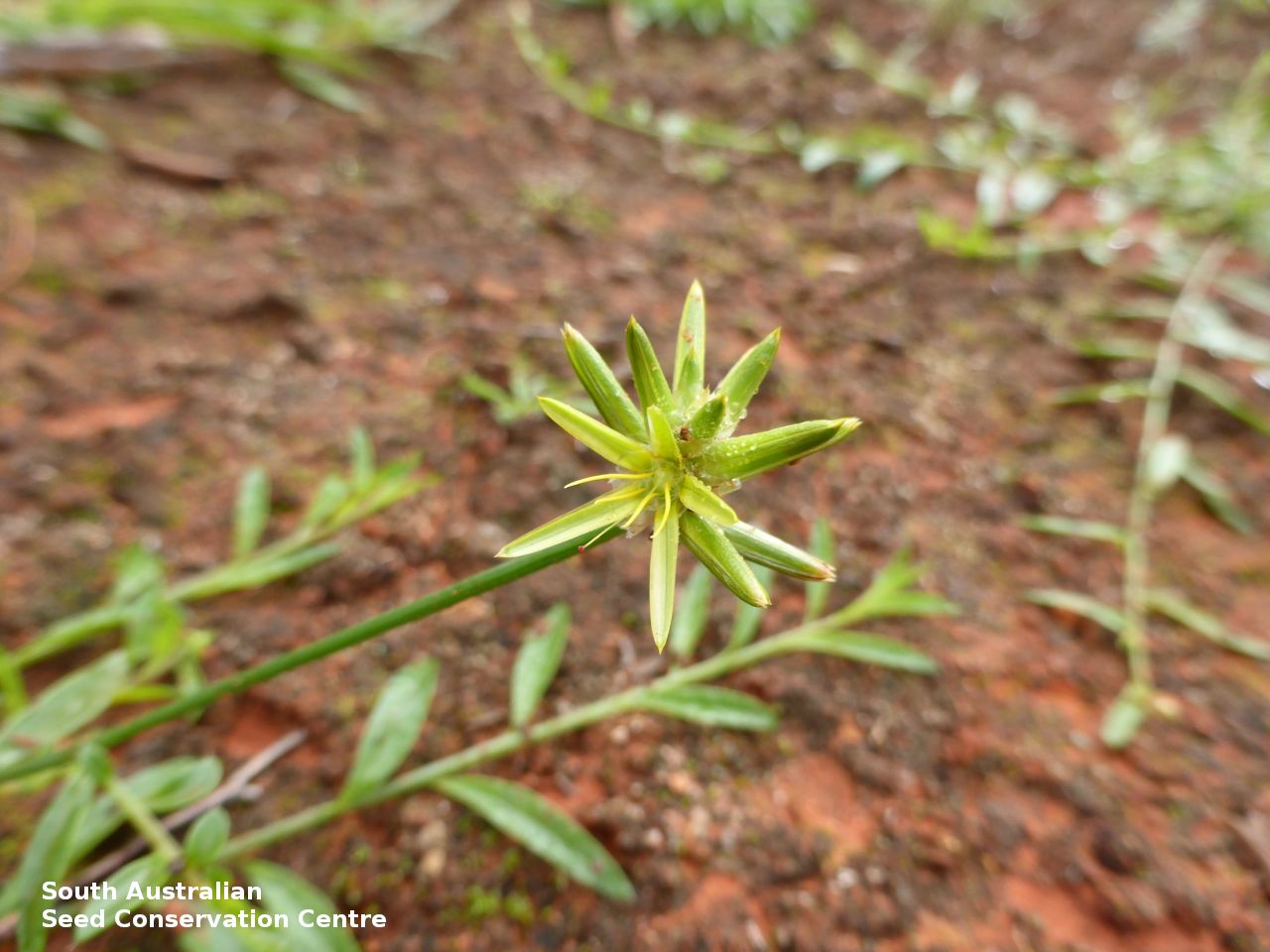
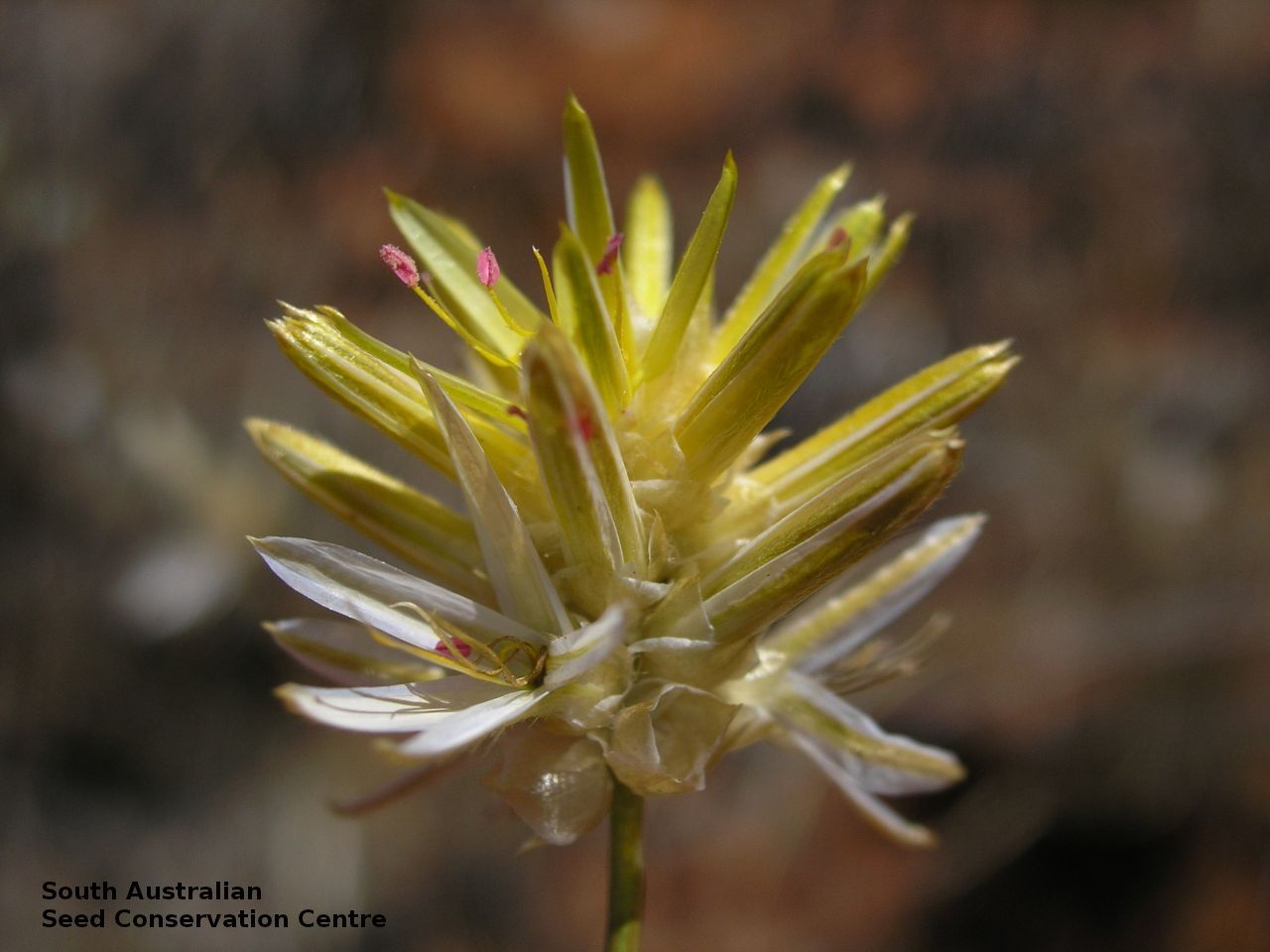
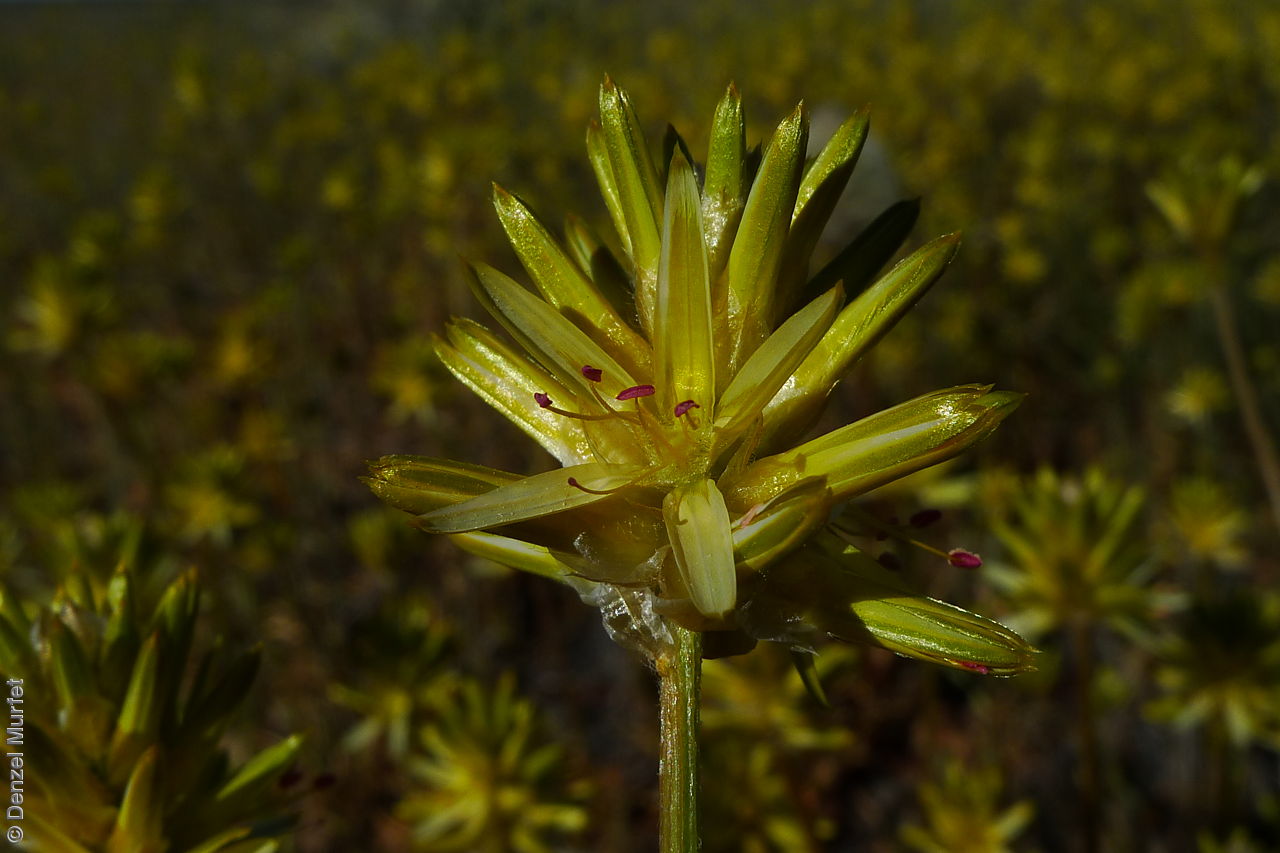
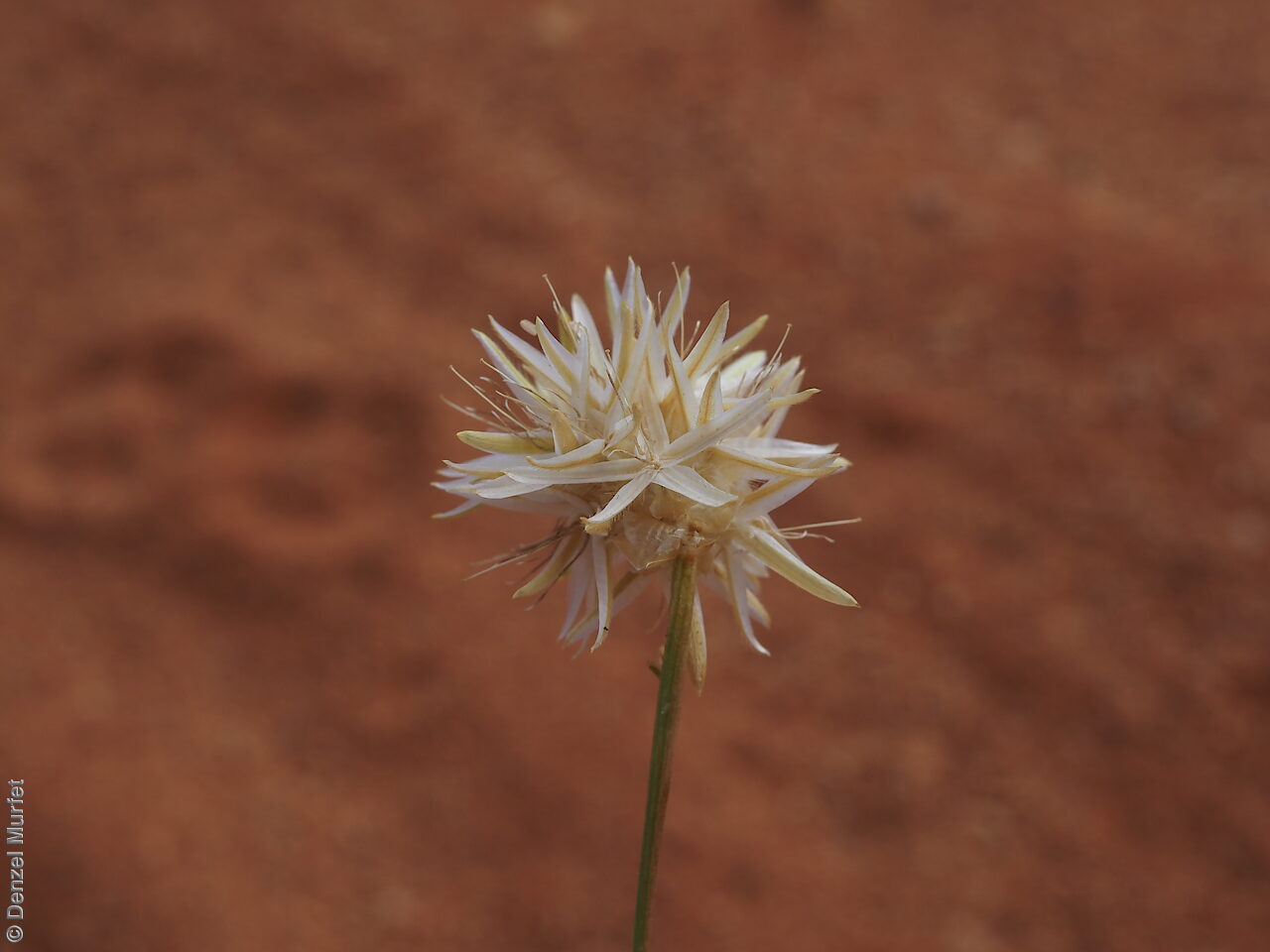
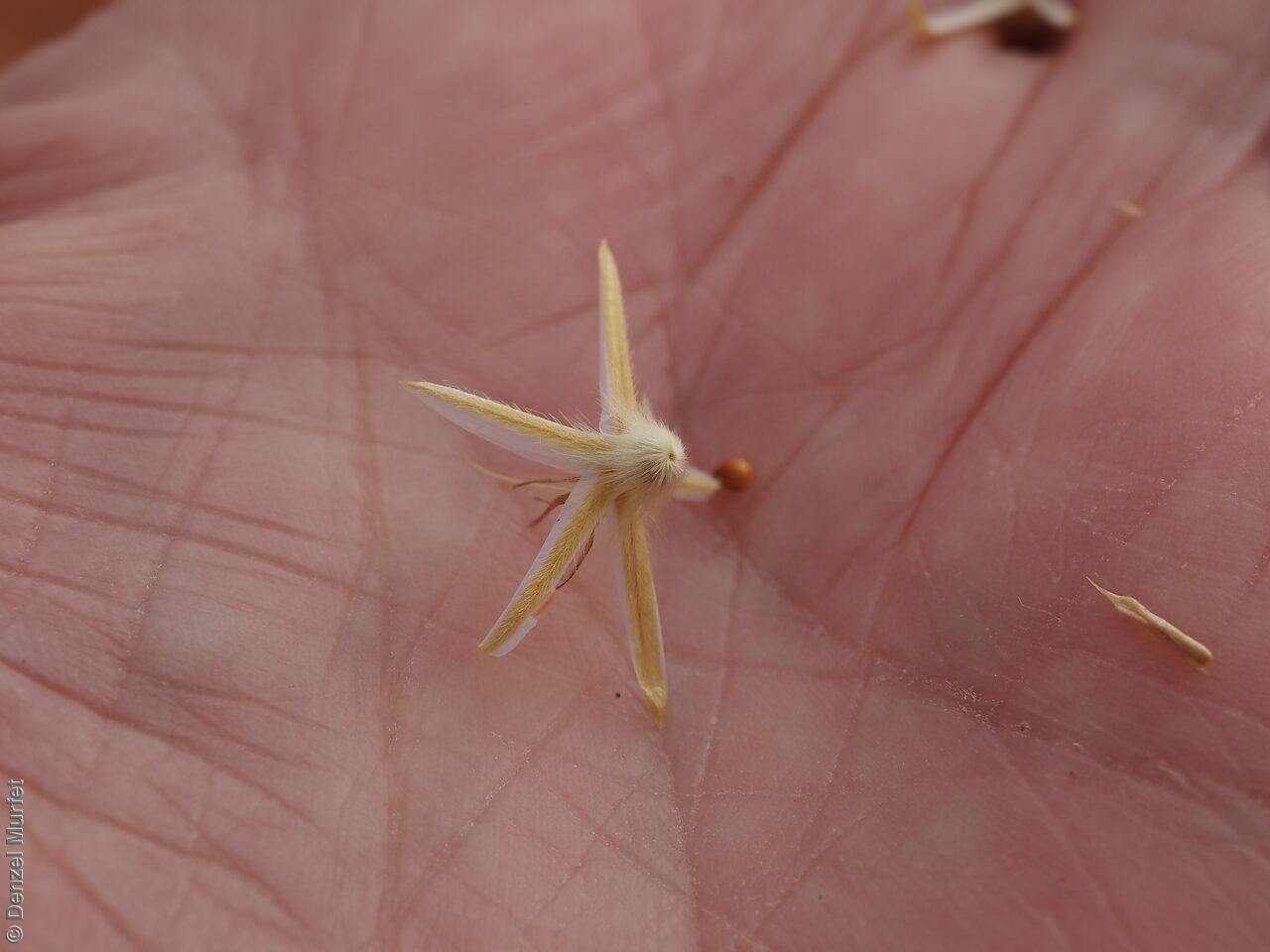
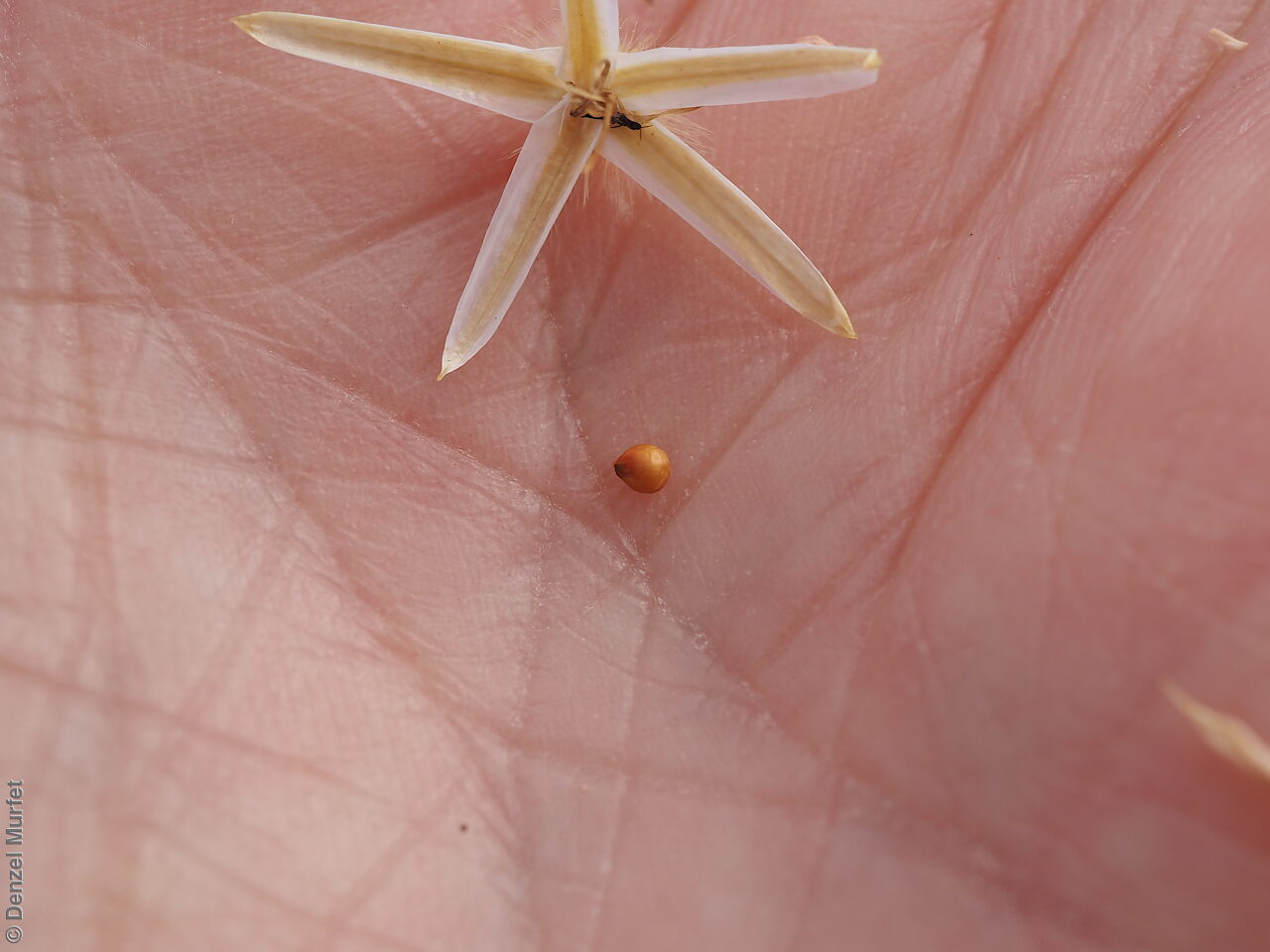
Erect herbs to 70 cm high with stems and leaves sparsely hairy. Leaves narrowly obovate or narrowly elliptic, rarely subspathulate or ovate, basal leaves usually withered and senescent by anthesis, to 65 mm long and 8 mm wide, stem leaves to 47 mm long and 5 mm wide. Inflorescences terminal, globose, shortly cylindrical, or hemispherical to 3 cm long with 35 yellow flowers, with hairs at the base. Flowering between April and November. This subspecies is distinguish from the other subspecies found in South Australia by having perianth 10-15 mm long and style 7-10.5 mm long while P. modestus (formally P. gaudichaudii ssp. parviflorus) has perianth 7.5-9 mm long and style 4.5-5 mm long. Fruits are yellow-brown globular or cylindrical head containing numerous long papery and hairy fruits, each containing one seed. Seeds are orange-brown reniform seed. Seed embryo type is peripheral.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between September and January. Be very careful when collecting this species as the fruits contain fine hairs that may cause an allergic reaction for some people. Collect the fruit heads when dried to a pale straw colour. Each fruit should come off the head easily when fingers are rubbed up the stem. Collect more fruits than required as not all fruits will have a viable seed. Be very careful when cleaning this species as the fruits contain fine hairs that may cause an allergic reaction for some people. To clean, rub the fruit heads gently to dislodge the seed at the base of each fruit. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Seed viability is usually high but seed availability tend to be low. Seeds are non-dormant, viable seed should germinate readily.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 8,100 (40.8 g) 8,100 (40.8 g) | 100+ | 28-Oct-2004 | MOL4641 Gairdner-Torrens | 28-Mar-2006 | 40% | -18°C |
| BGA | 4,600 (23.6 g) | 50 | 18-May-2007 | RJB72089 North Western | 19-Sep-2008 | 60% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.