






















Botanical art
Prior names
Cynoglossum drummondii
Cynoglossum australe var. drummondii
Etymology
Cynoglossum from the Greek 'kynoglosson', name of a plant used by Dioscorides, from the Greek 'kynos' meaning a dog and 'glossa' meaning a tongue, alluding to the shape and texture of the leaves. Australe means of or from the south, referring to the distribution of the species in Australia.
Distribution and status
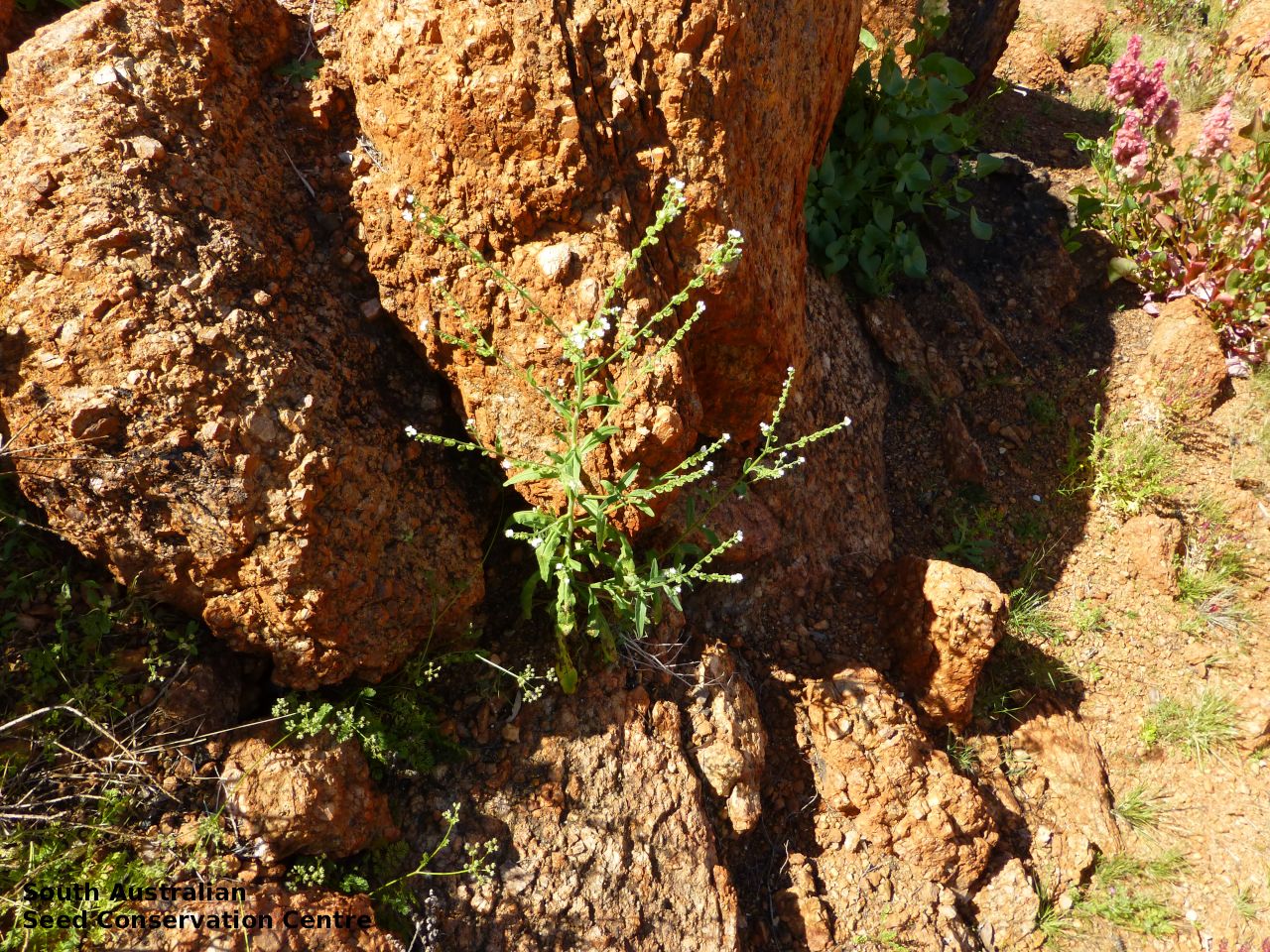
Found in the far north-west and southern parts of South Australia growing in various communities from sclerophyll forest and woodland to sand dunes, also invades disturbed sites. Also found in all States. Native. Common in South Australia. Uncommon in Western Australia and Tasmania. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: North Western, Lake Eyre, Flinders Ranges, Eastern, Eyre Peninsula, Murray, Yorke Peninsula, Southern Lofty, Kangaroo Island, South Eastern, Green Adelaide
NRM regions: Adelaide and Mount Lofty Ranges, Eyre Peninsula, Kangaroo Island, Northern and Yorke, South Australian Arid Lands, South Australian Murray-Darling Basin, South East
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
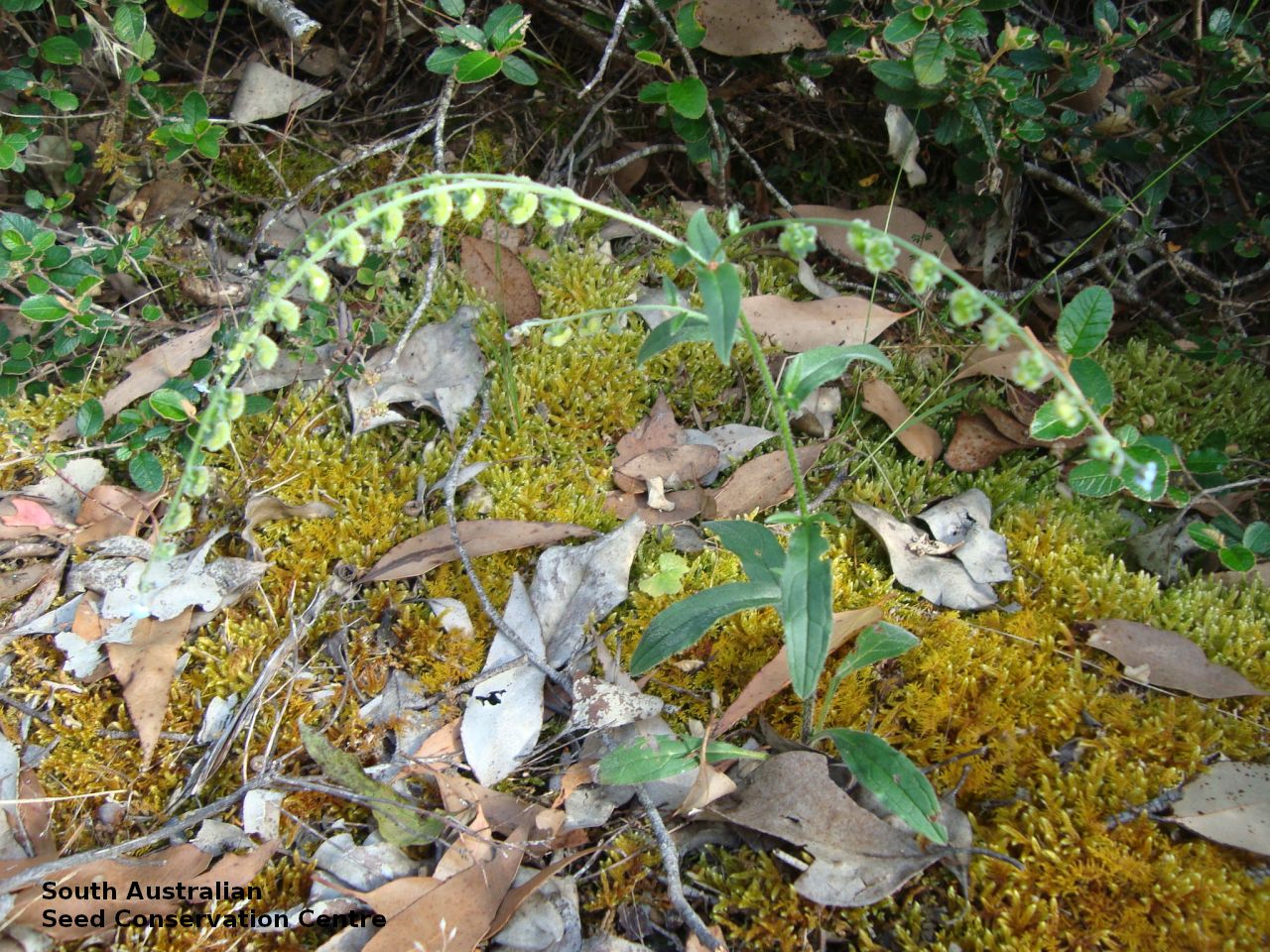
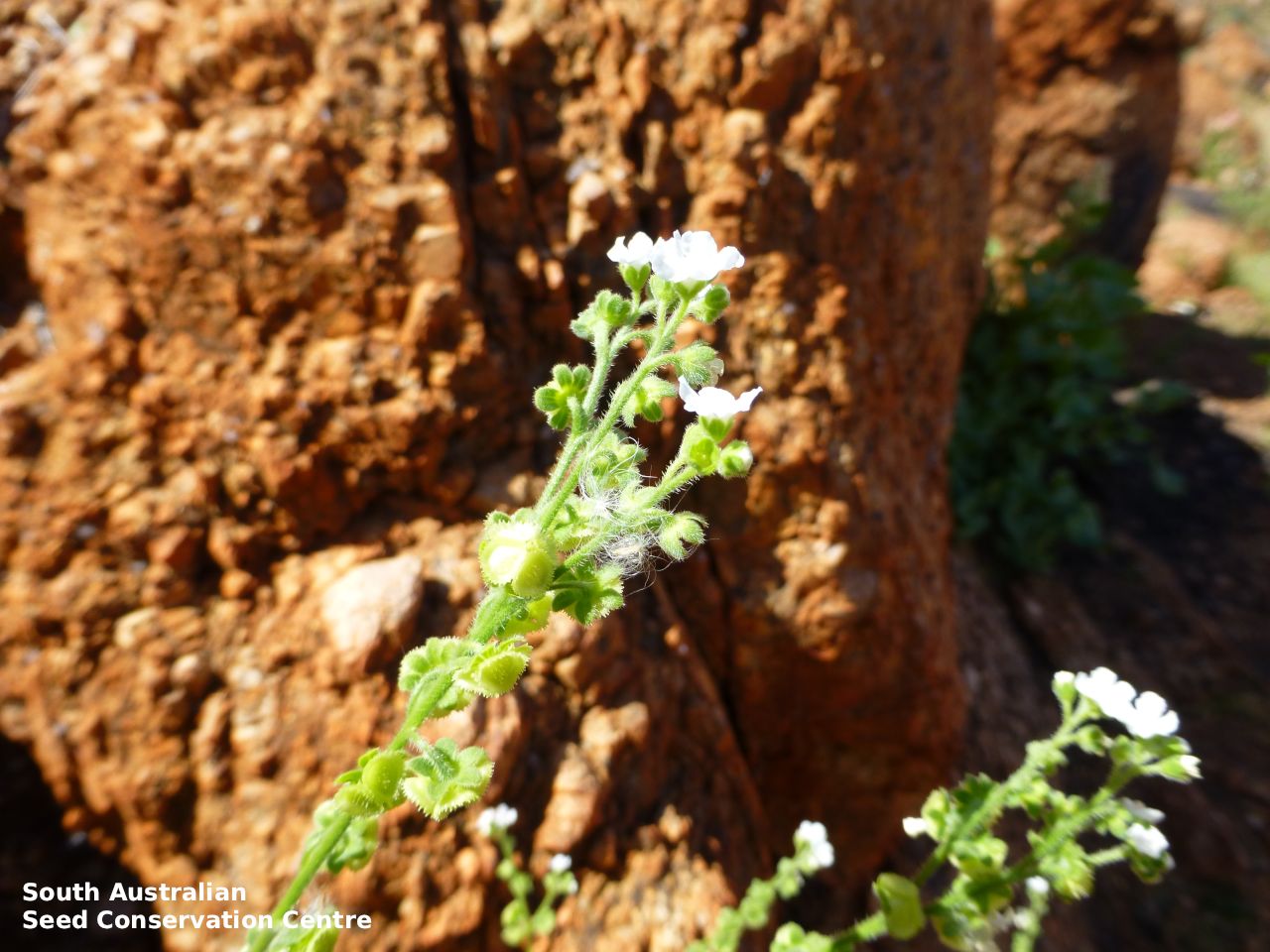
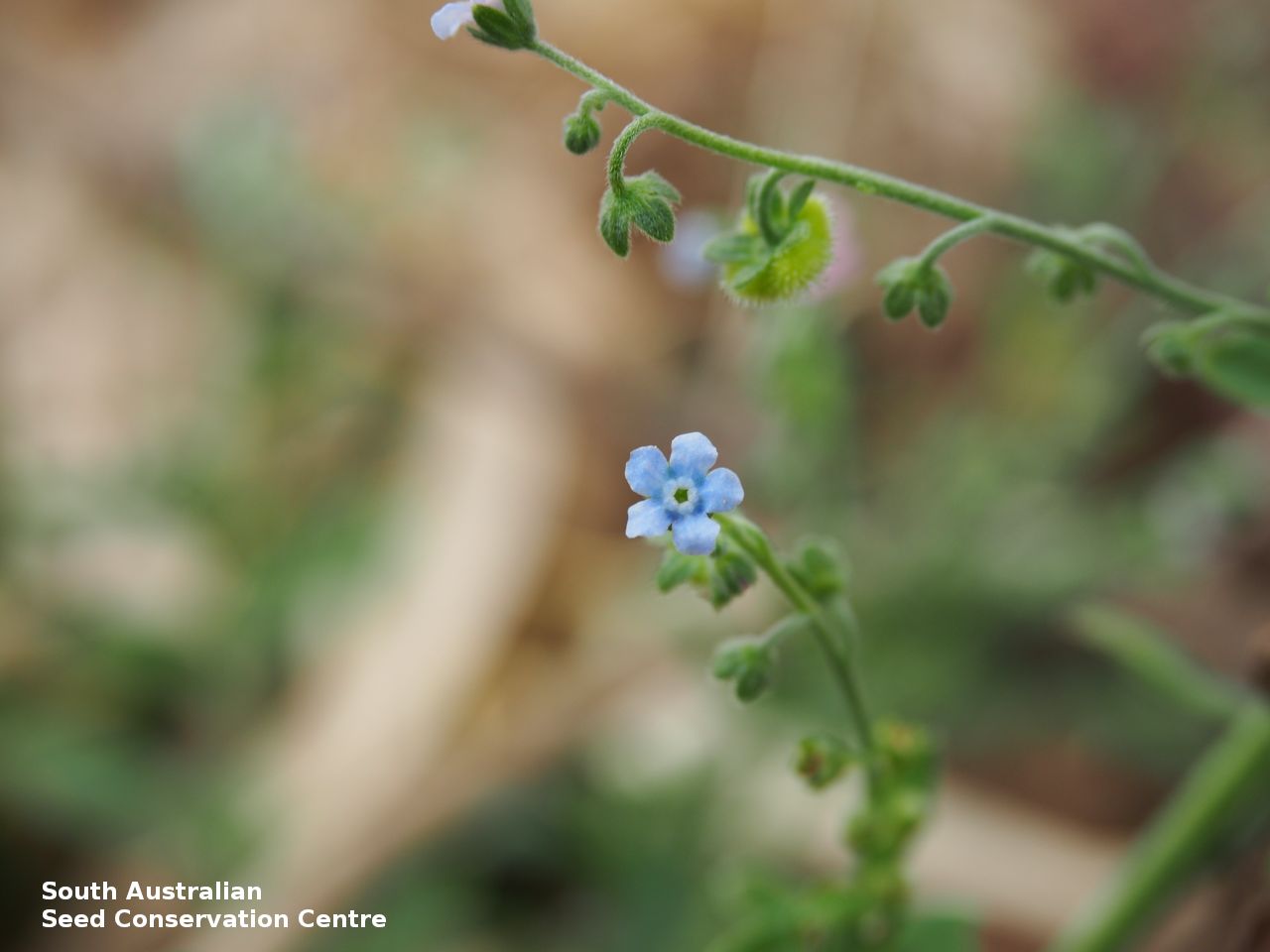
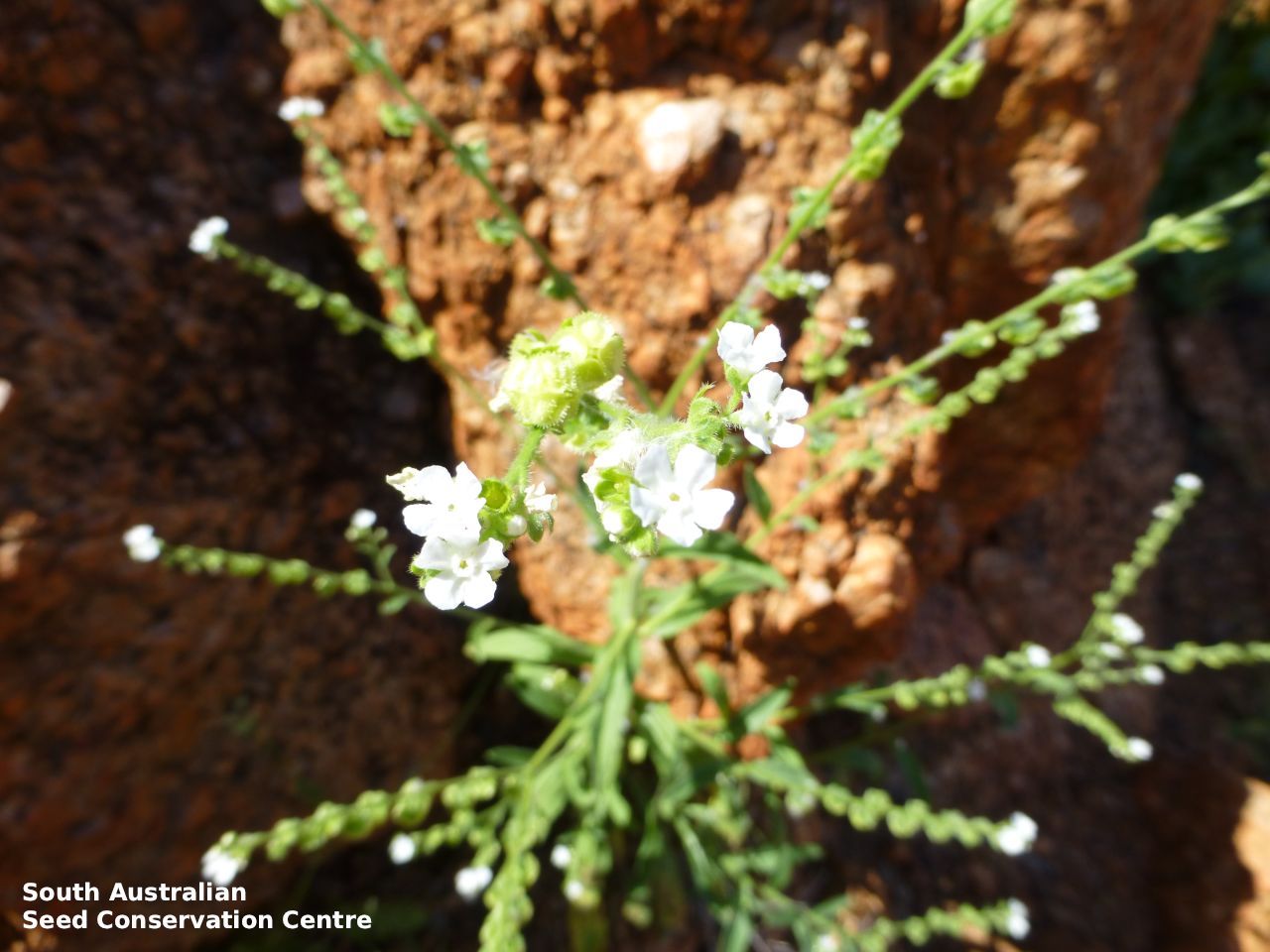
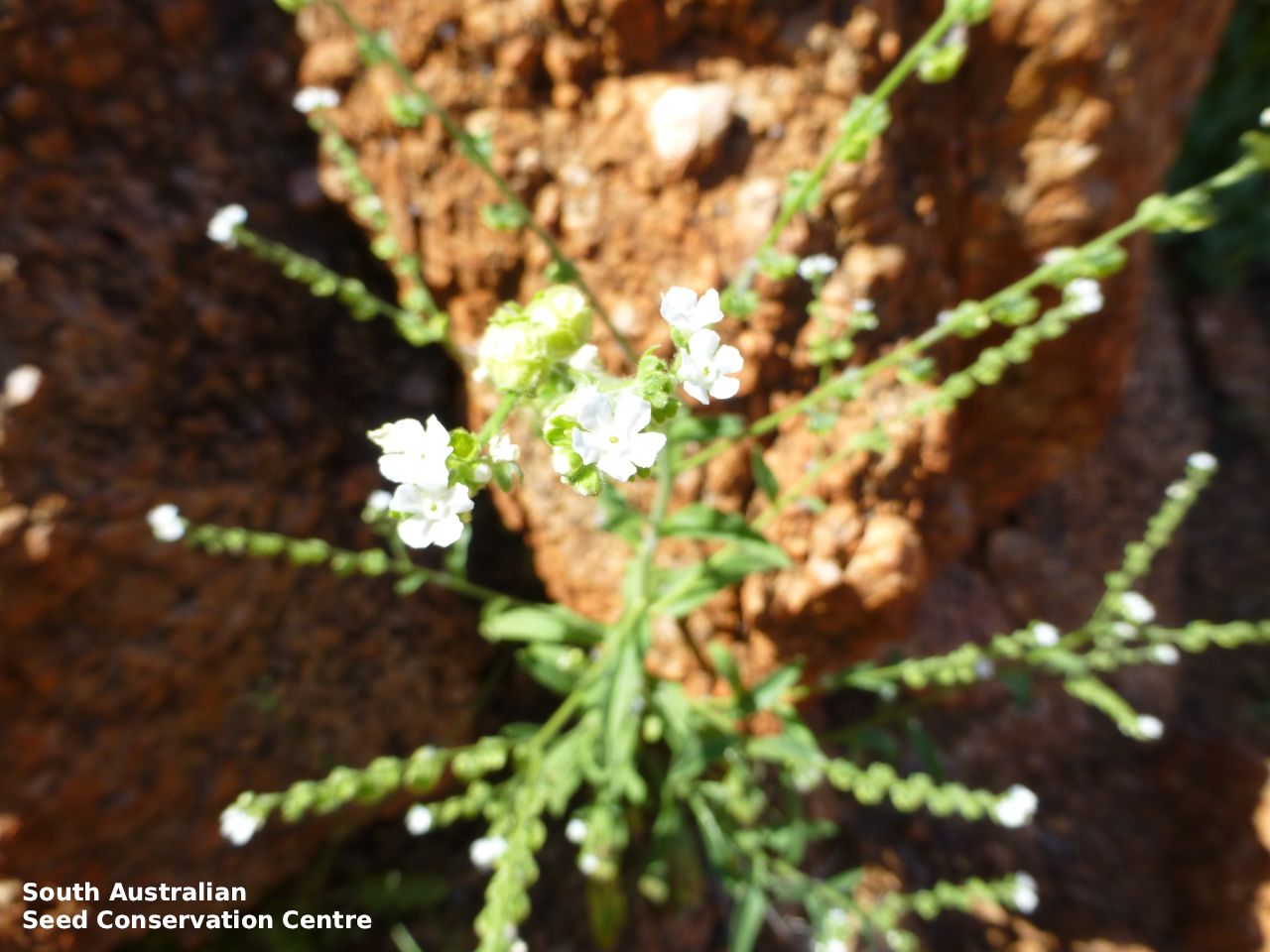
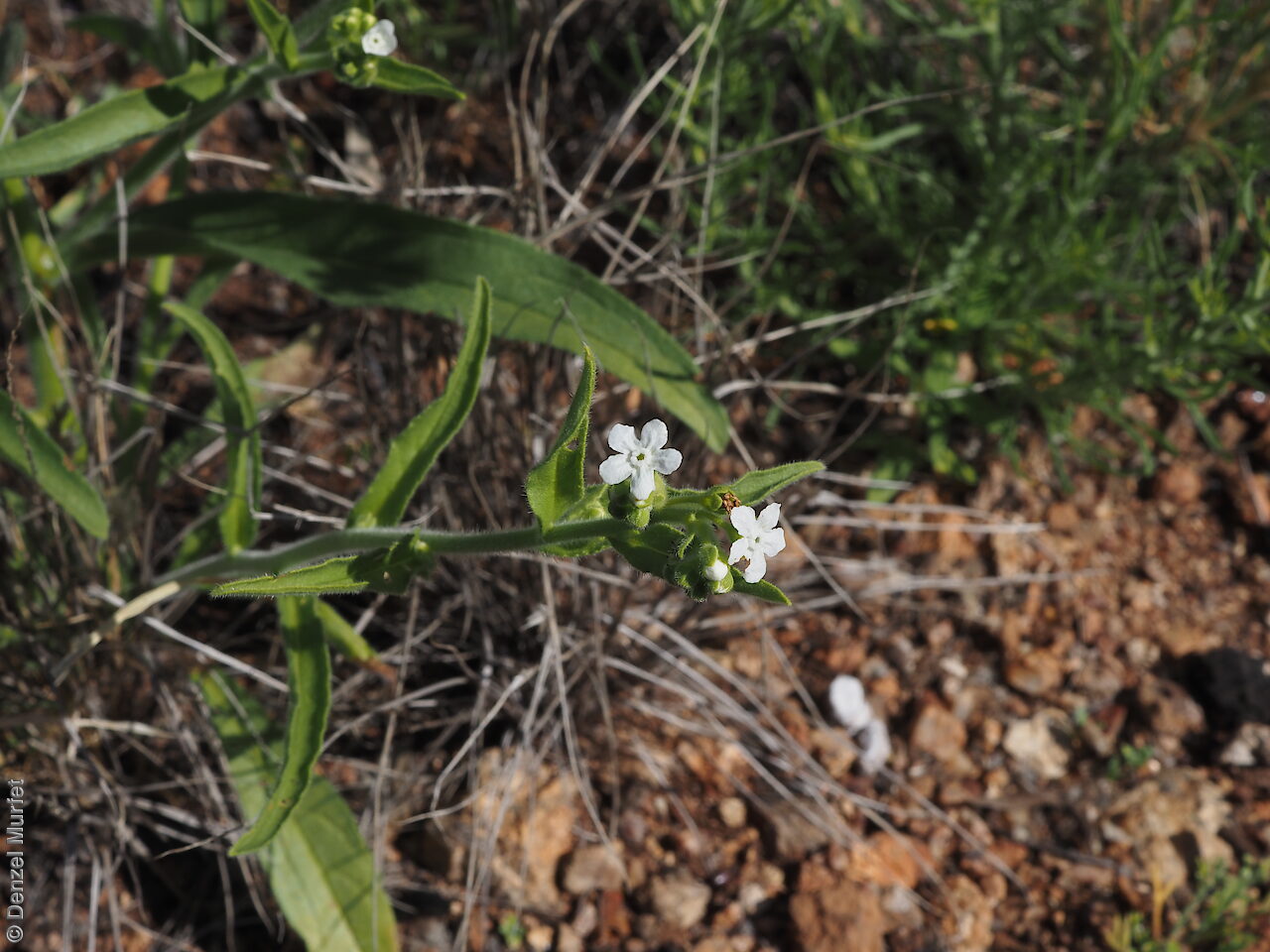
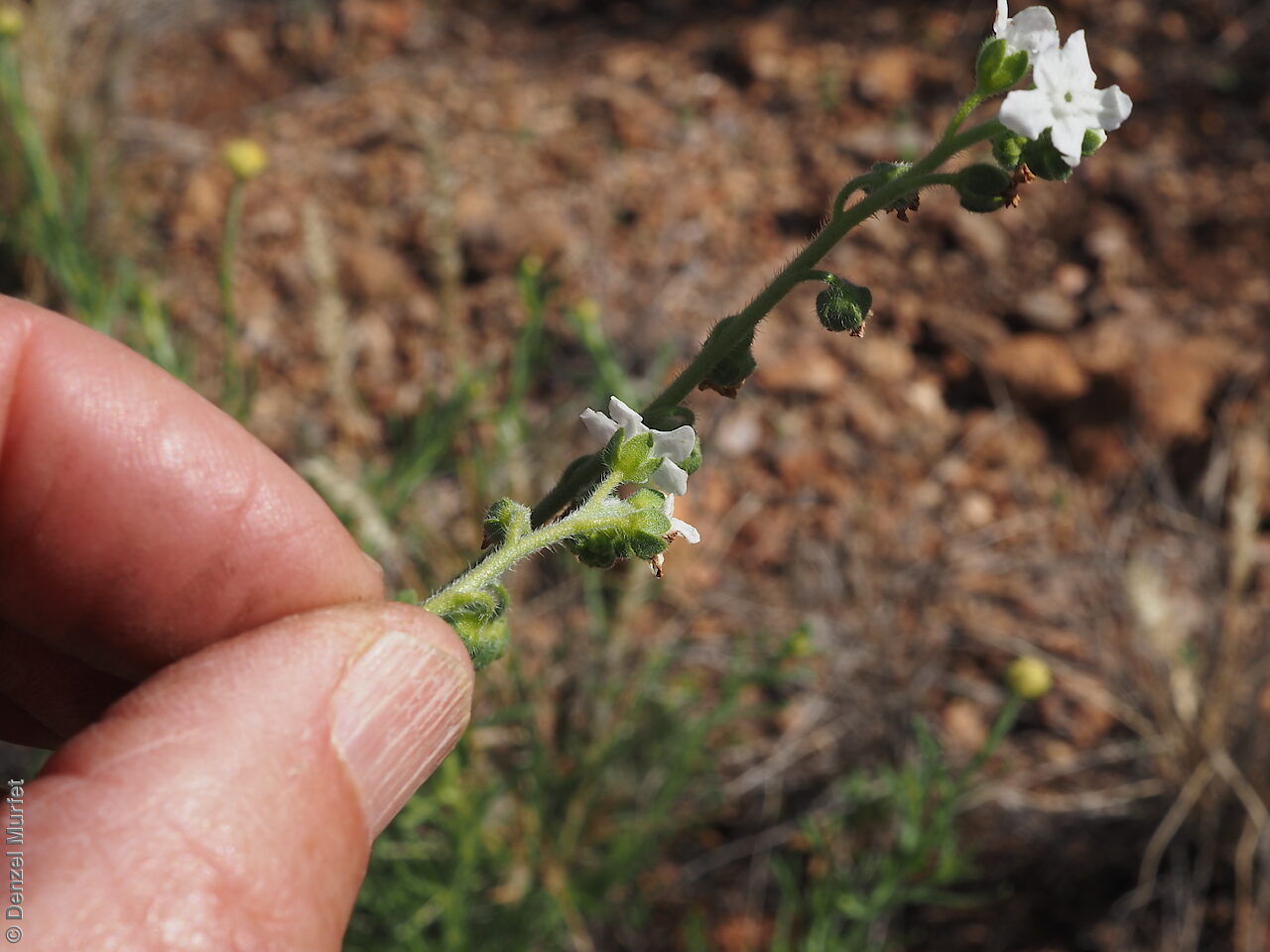
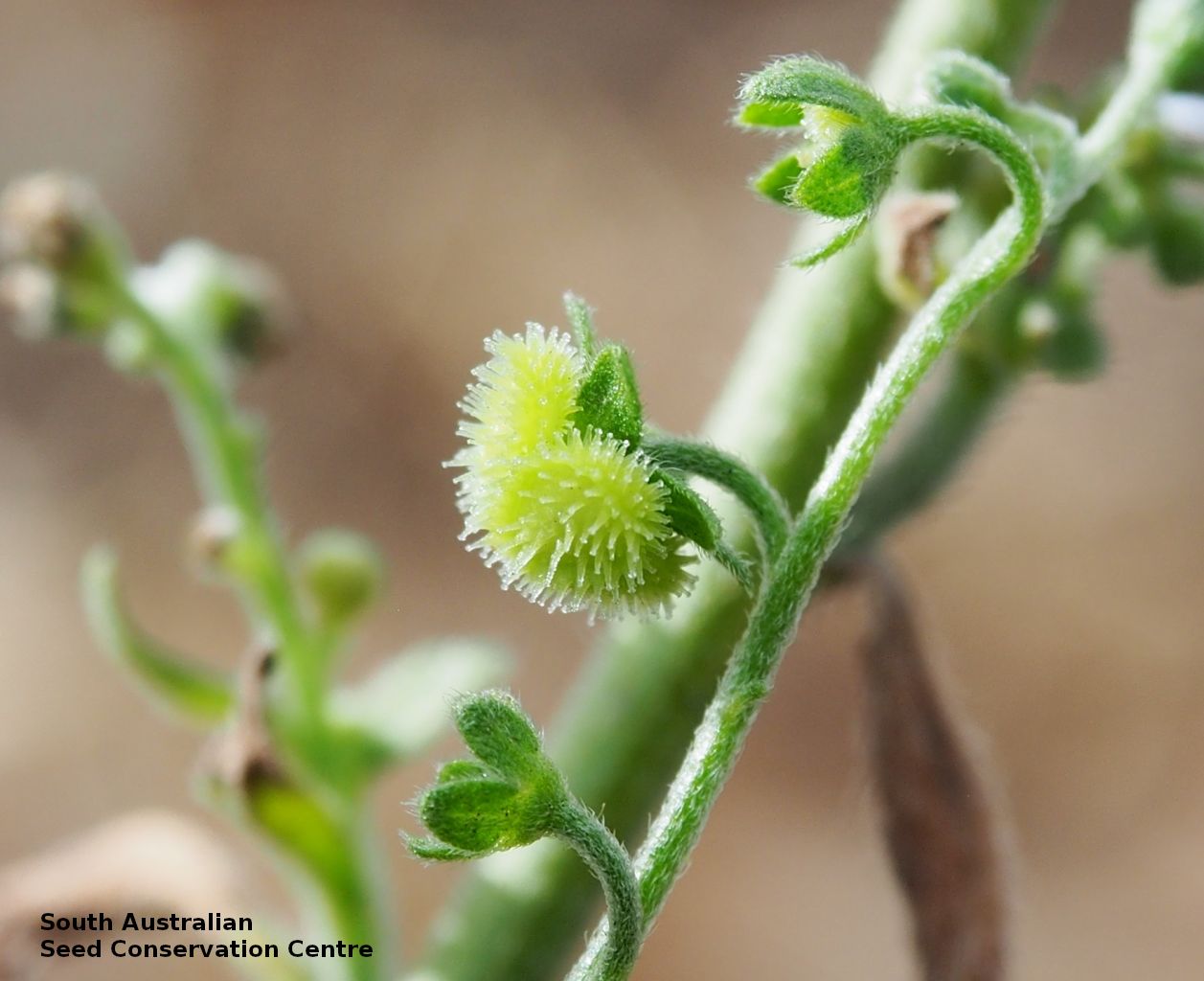
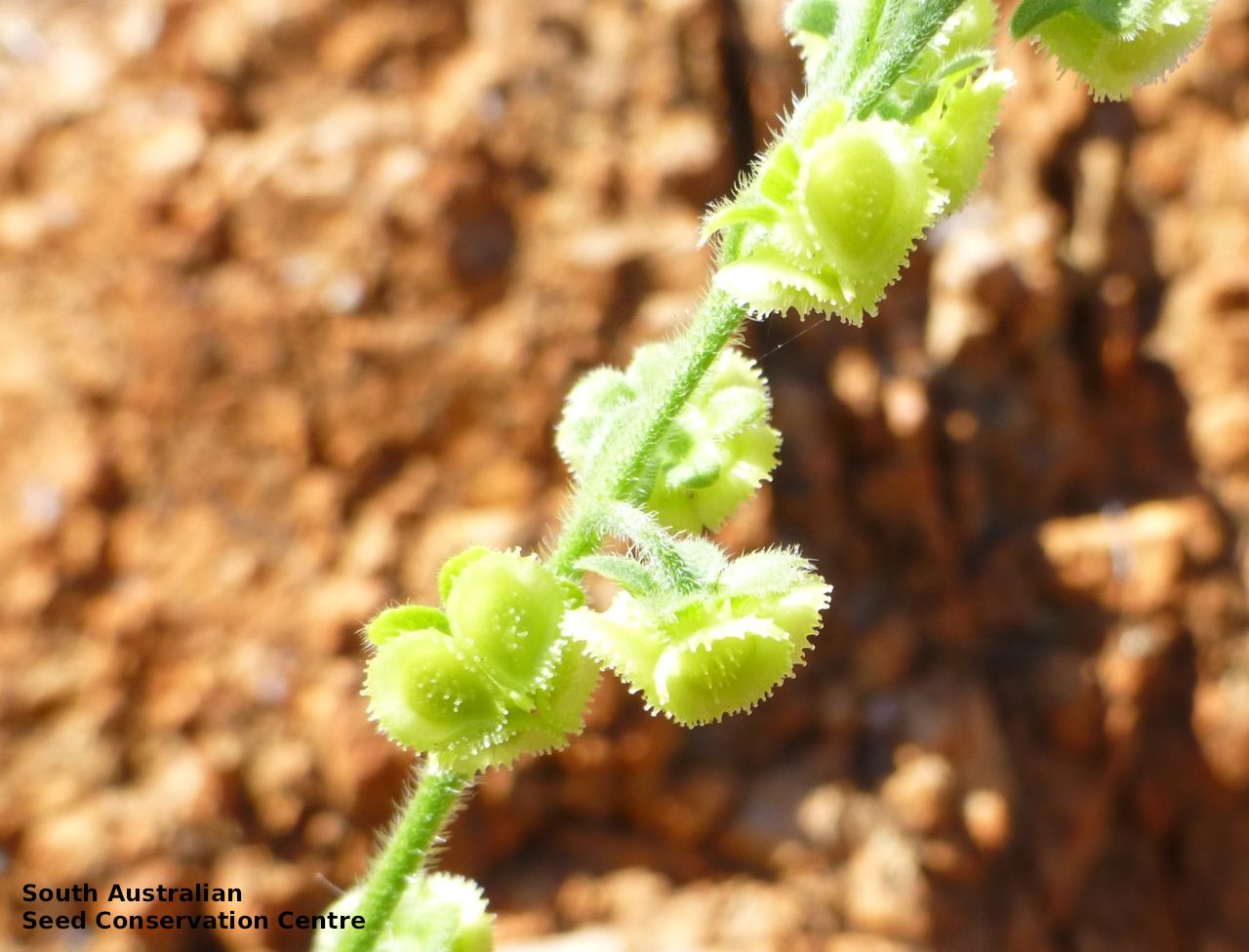
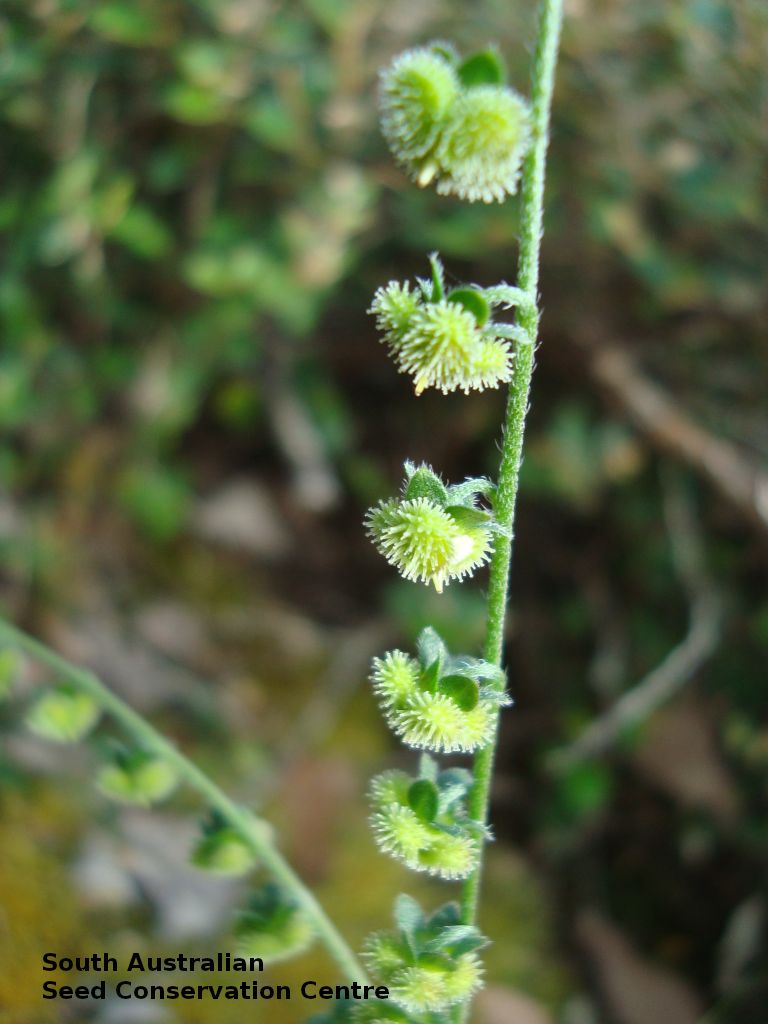
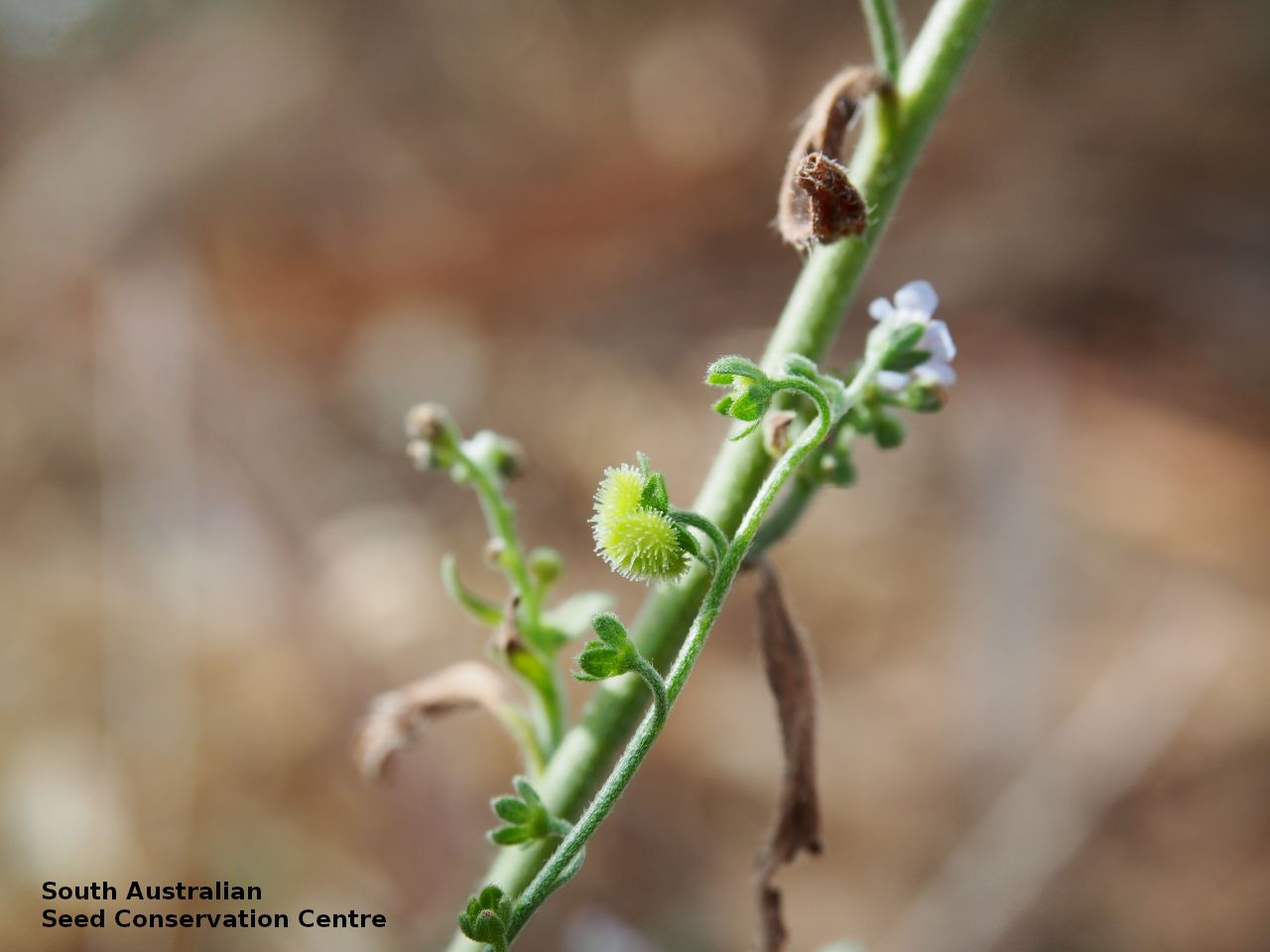
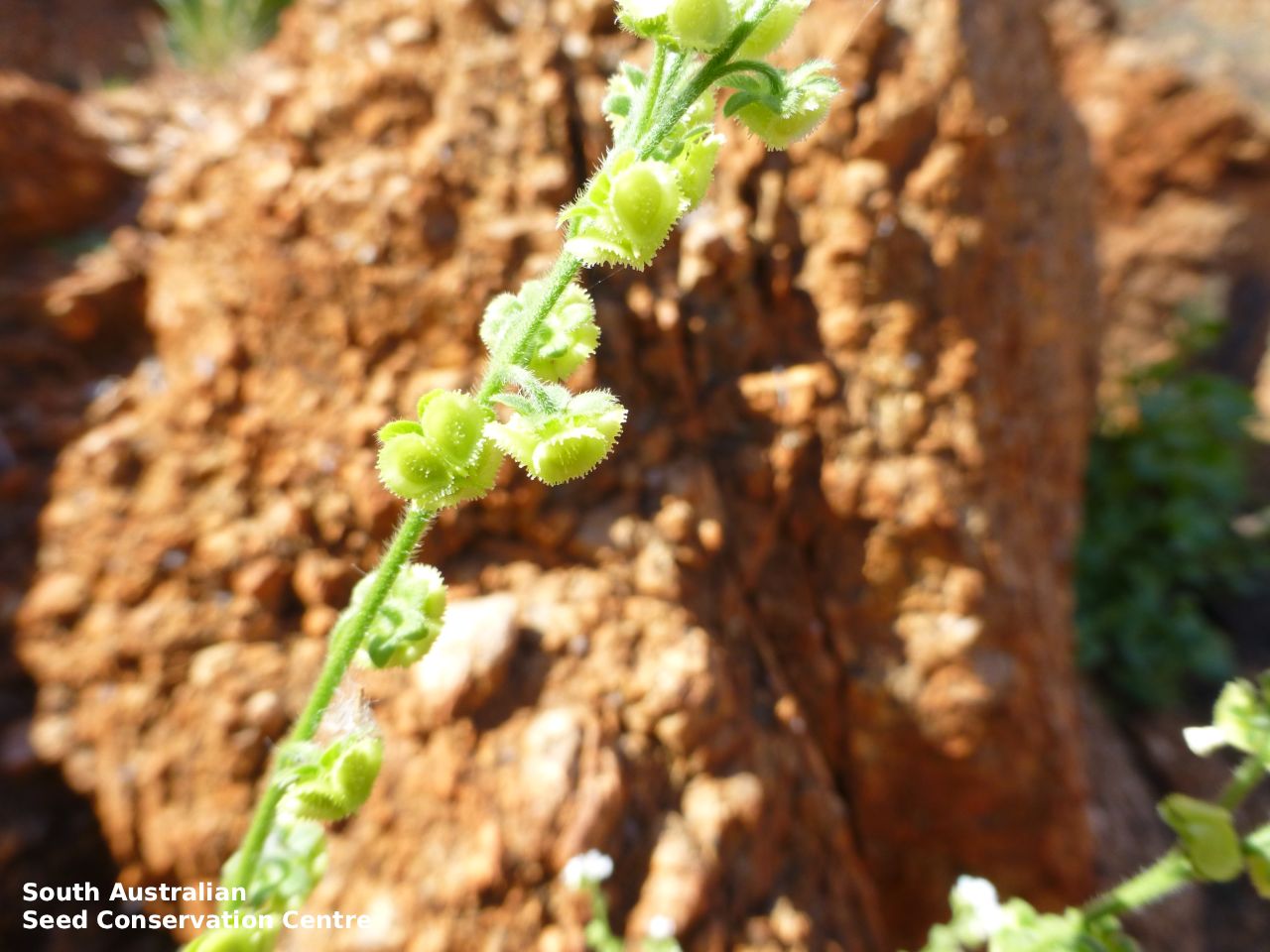
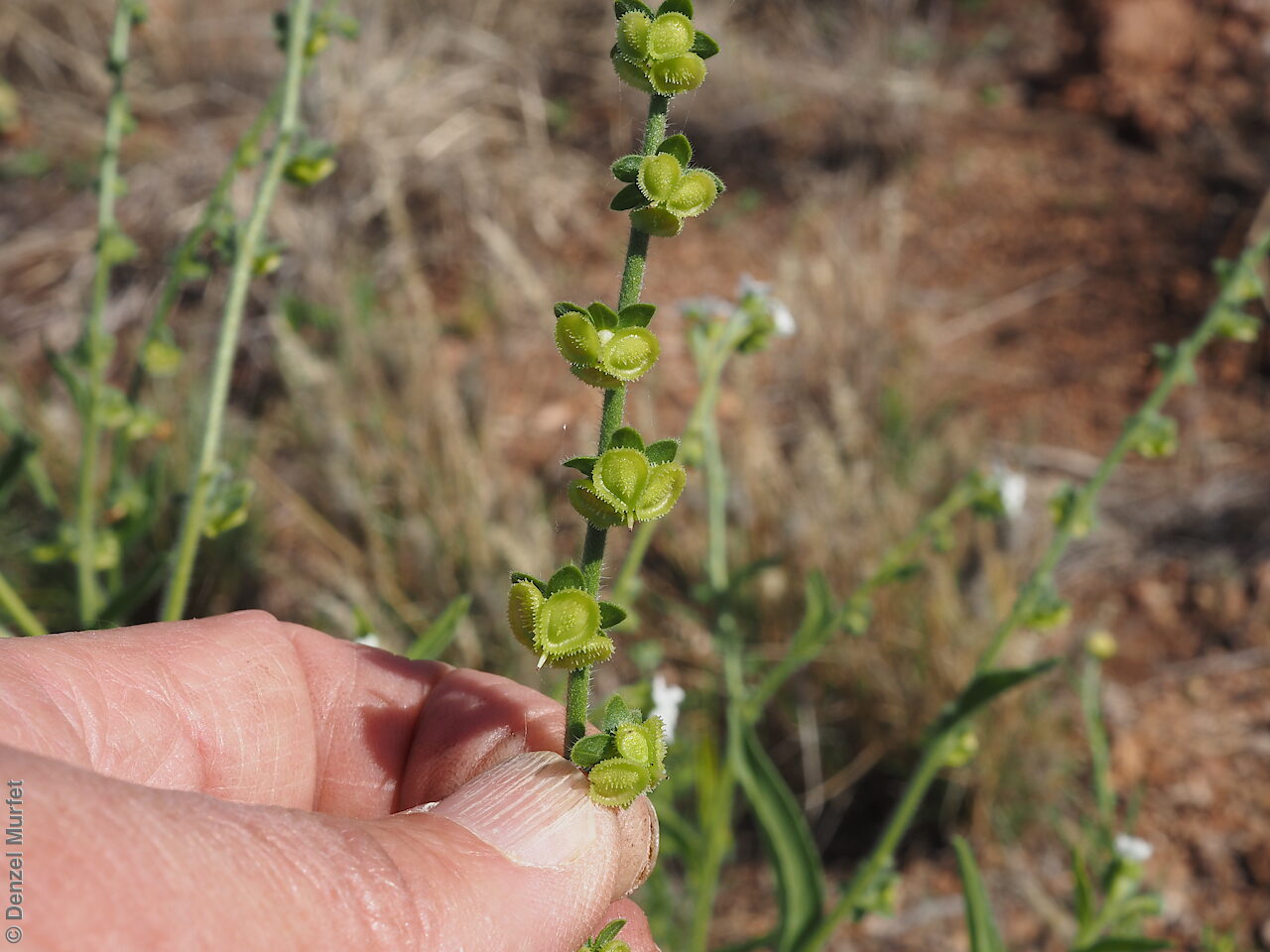
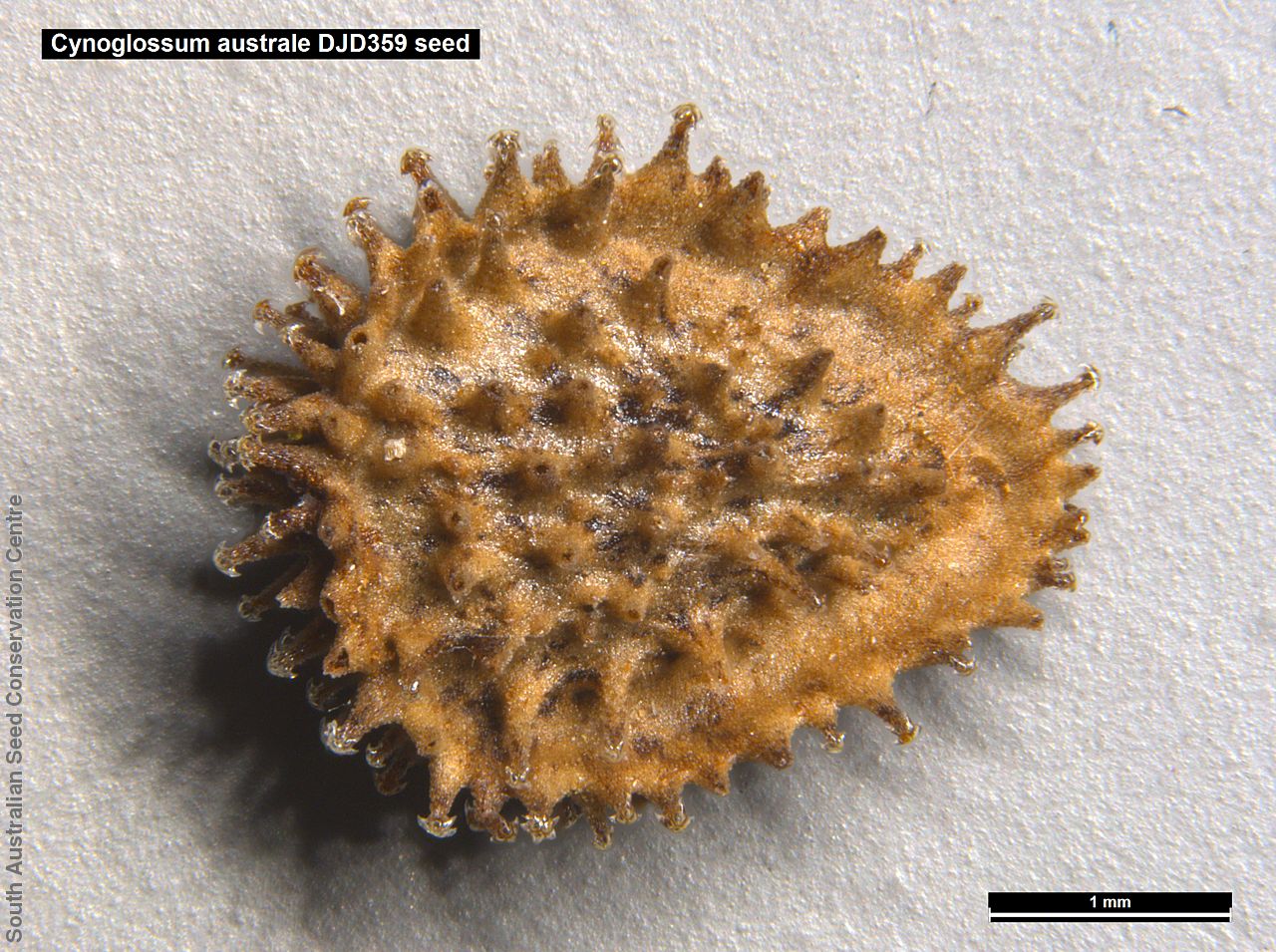
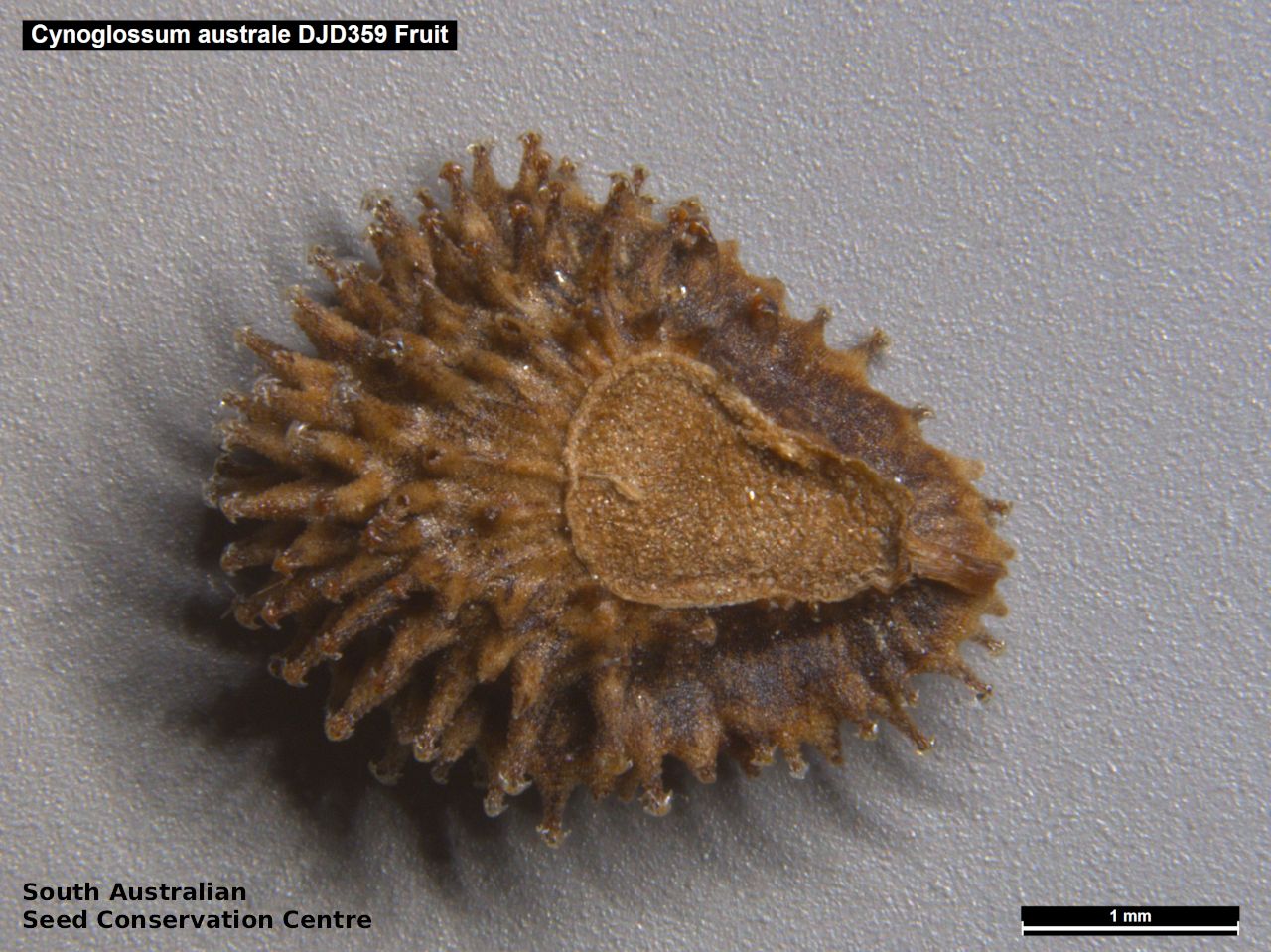
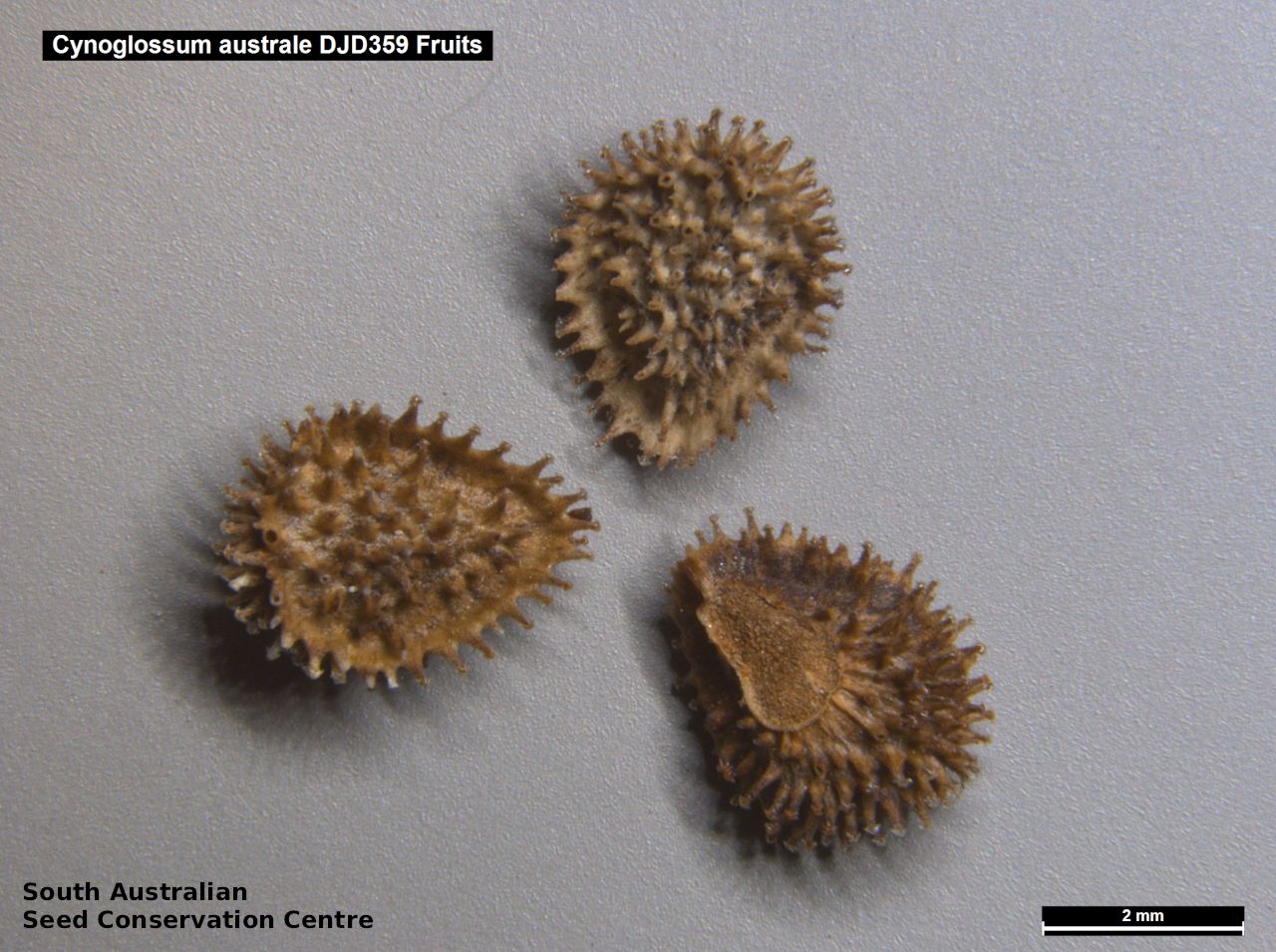
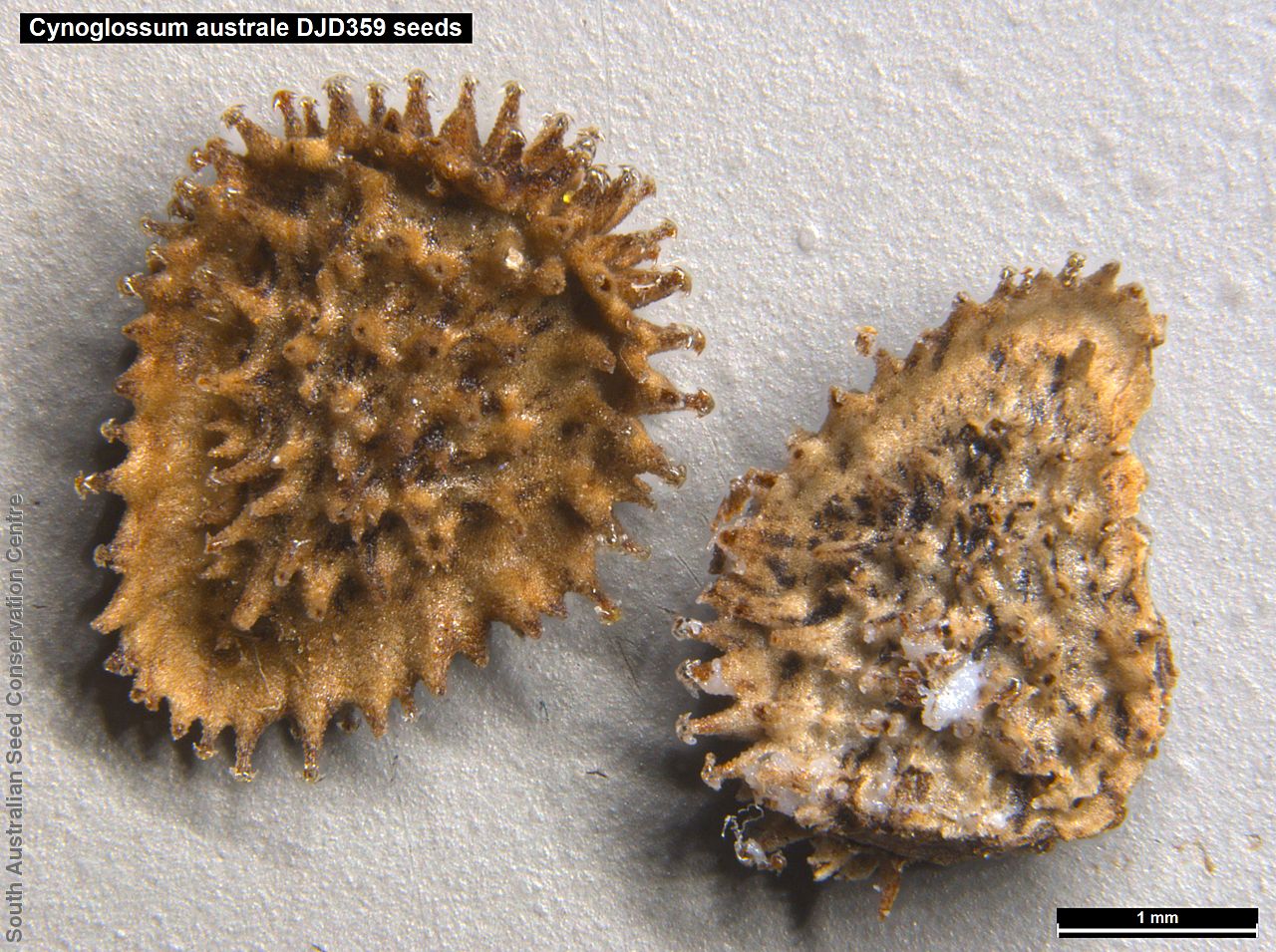
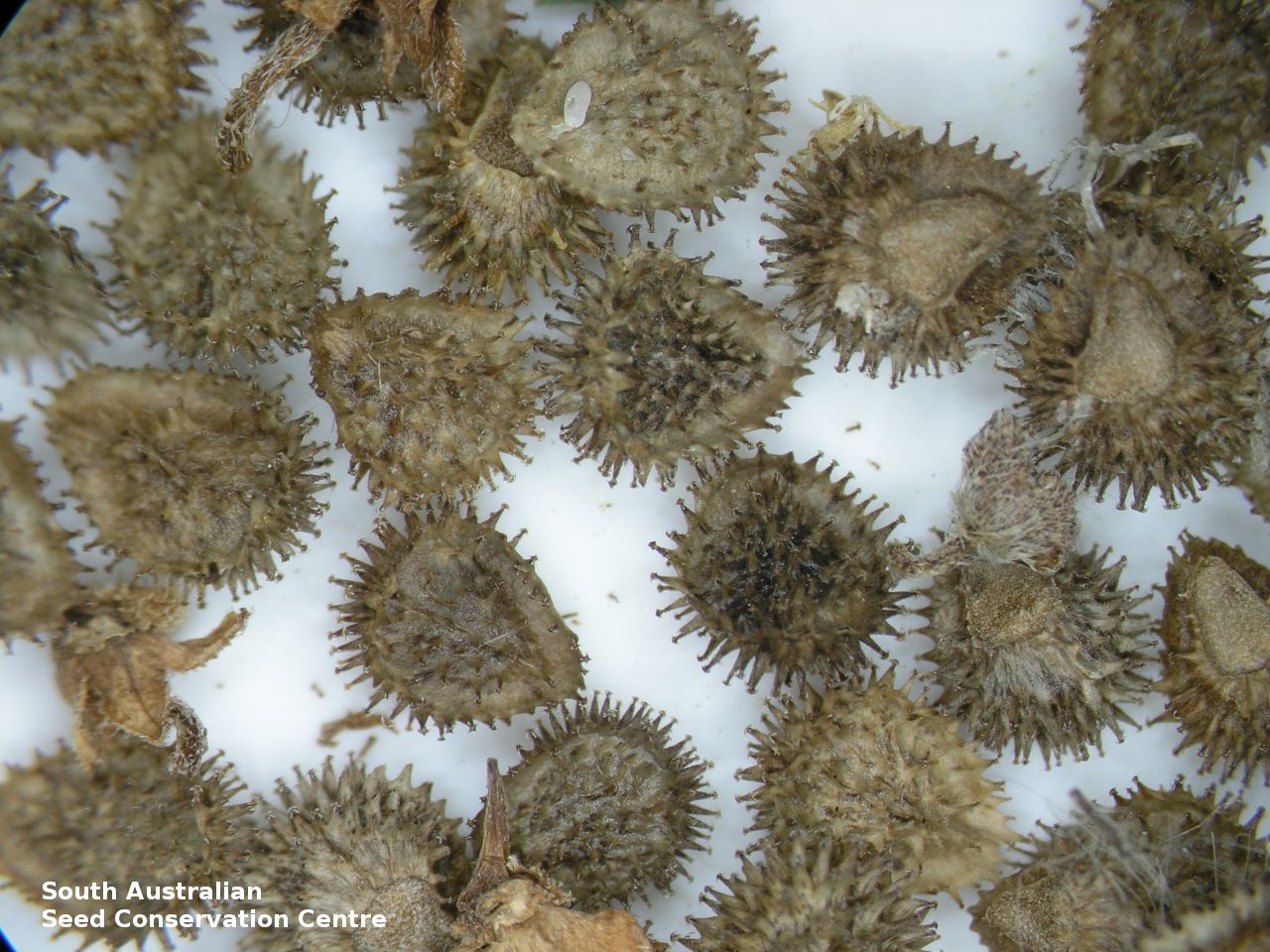
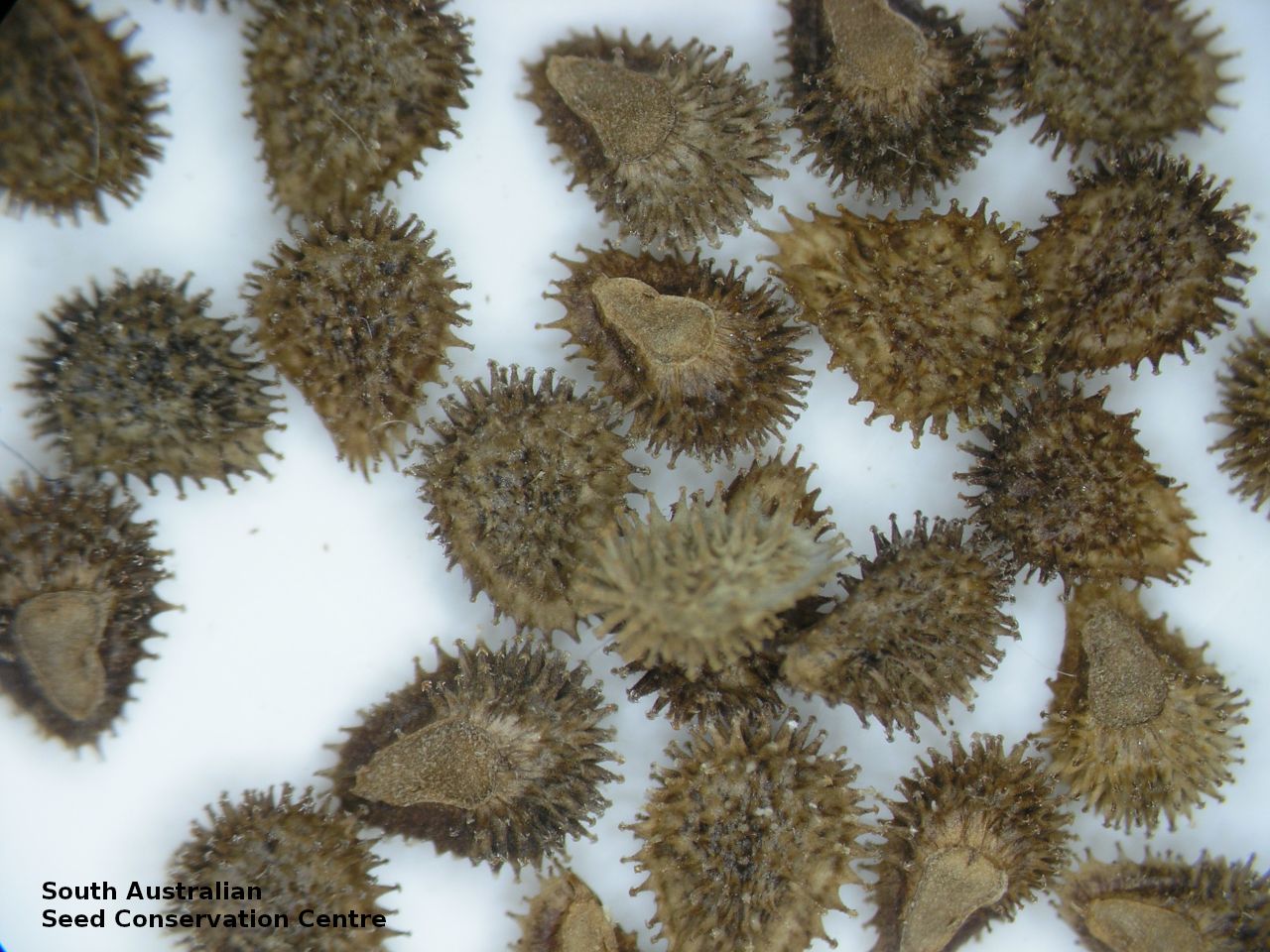
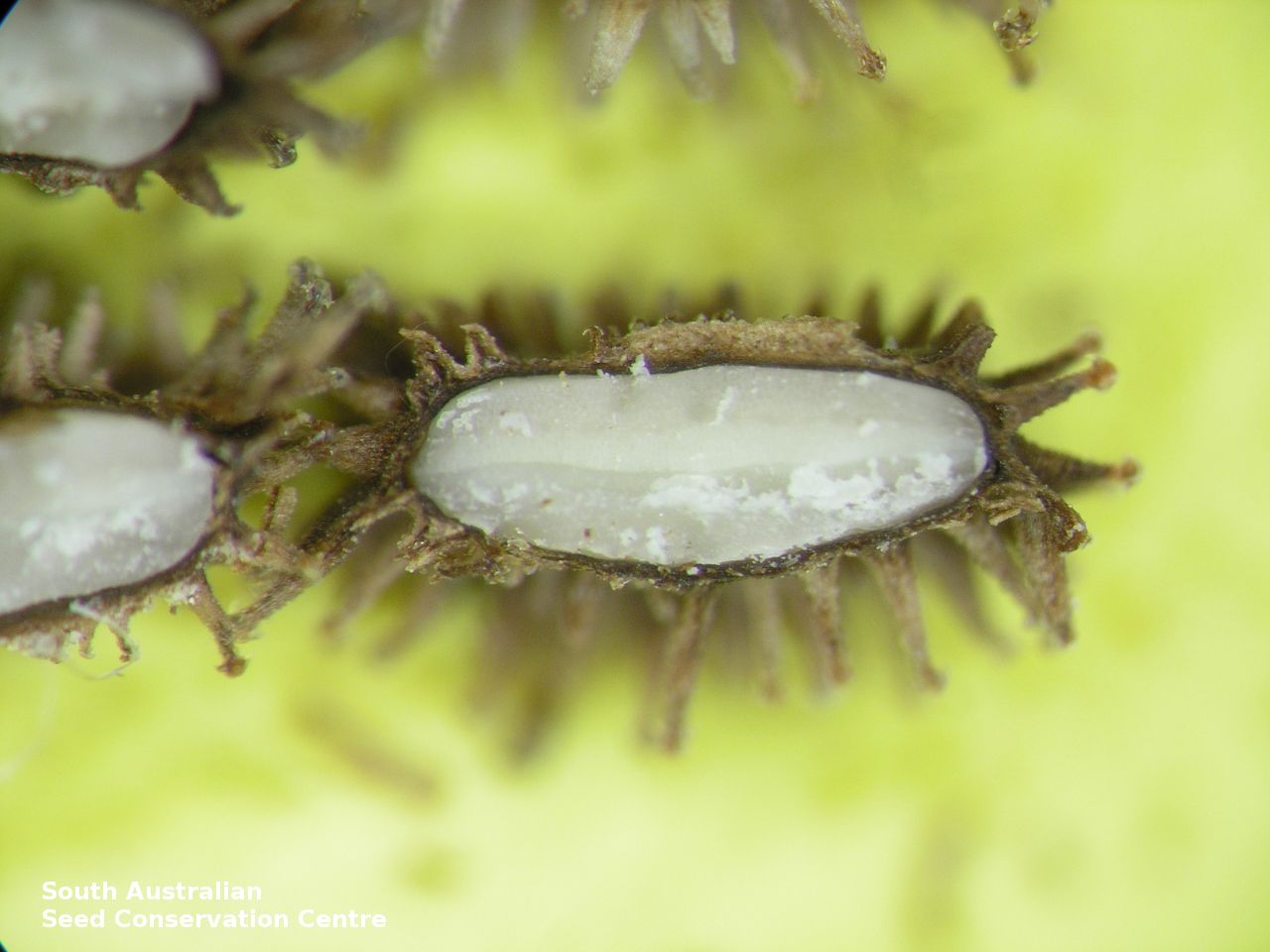
Annual herb to 60 cm high with one to usually several erect stems from the basal rosette, with a tap root, covered with spreading to appressed hairs. Leaves densely clustered, oblanceolate, subpetiolate but with a short sheath in the basal rosette; becoming widely spaced, lanceolate and sessile below the inflorescence, to 25 cm long and 4 cm wide; pointed, rarely with undulate margins. Flower-spike terminal with pedicellate funnel-shaped, blue flowers. Flowering between July and November. Fruits are brown fruit cluster with up to four seeds hanging along fruiting spike. Seeds are brown ovoid to globose seed to 4 mm long and 2.5 mm wide covered in barbed spines to most of the surface. Seed embryo type is spatulate fully developed.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between December and February. Collect maturing fruits, those turning brown and contain a hard seed inside, by running your hands along the fruiting spike or break off the whole spike. Wear gloves as fruits can be prickly. Place the seeds/spikes in a tray and leave to dry for two weeks. No further cleaning is required if only seed collected. If seed spikes collected, use hand to strip off the mature seeds. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Seed viability is usually high. Seeds are non-dormant, viable seed should germinate readily.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 11,000 (44.72 g) 11,000 (44.72 g) | 50+ | 25-Jan-2006 | DJD359 Southern Lofty | 28-Jul-2006 | 100% | -18°C |
| BGA MSB | 9,000 (41.2 g) 9,000 (41.2 g) | 35+ | 24-Jan-2006 | KHB47 Southern Lofty | 28-Jul-2006 | 100% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.