











Botanical art
Prior names
Trichodesma zeylanicum
Trichodesma sericeum
Pollichia zeylanica
Trichodesma zeylanicum var. sericeum
Trichodesma zeylanicum var. latisepaleum
Borago zeylanica
Common names
Cattle Bush
Camel Bush
Etymology
Trichodesma from the Greek 'thrix' or 'trikhos' meaning hair and 'desme' meaning a band or bundle; alluding to the twisted hairs or awns which terminate the anthers. Zeylanicum mean of or from Ceylon (Sri Lanka); probably referring to the location of the type specimen.
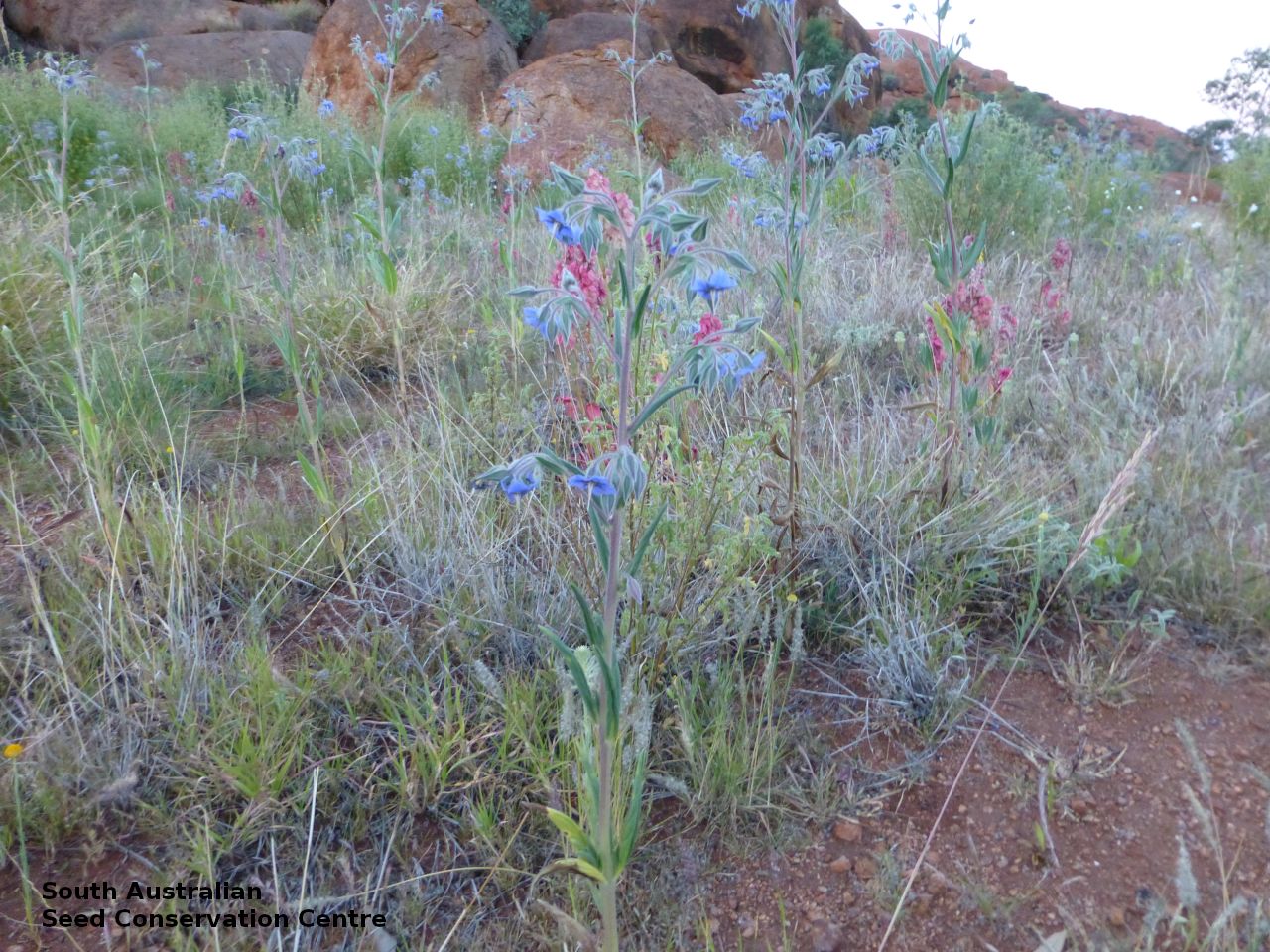
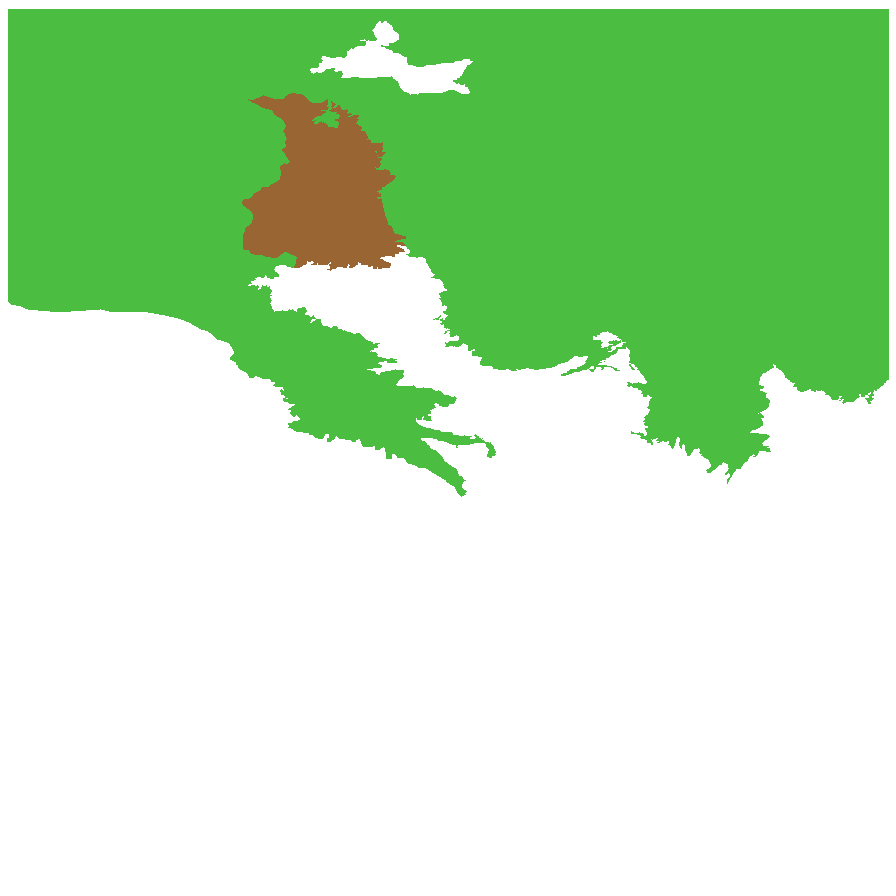
Distribution and status
Found in the northern half of South Australia, growing in sandy soils. Also found in Western Australia, Northern Territory, Queensland and New South Wales. Native. Common in South Australia. Common in the other states.
Herbarium regions: North Western, Lake Eyre, Gairdner-Torrens, Flinders Ranges, Eastern
NRM regions: Alinytjara Wilurara, South Australian Arid Lands
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
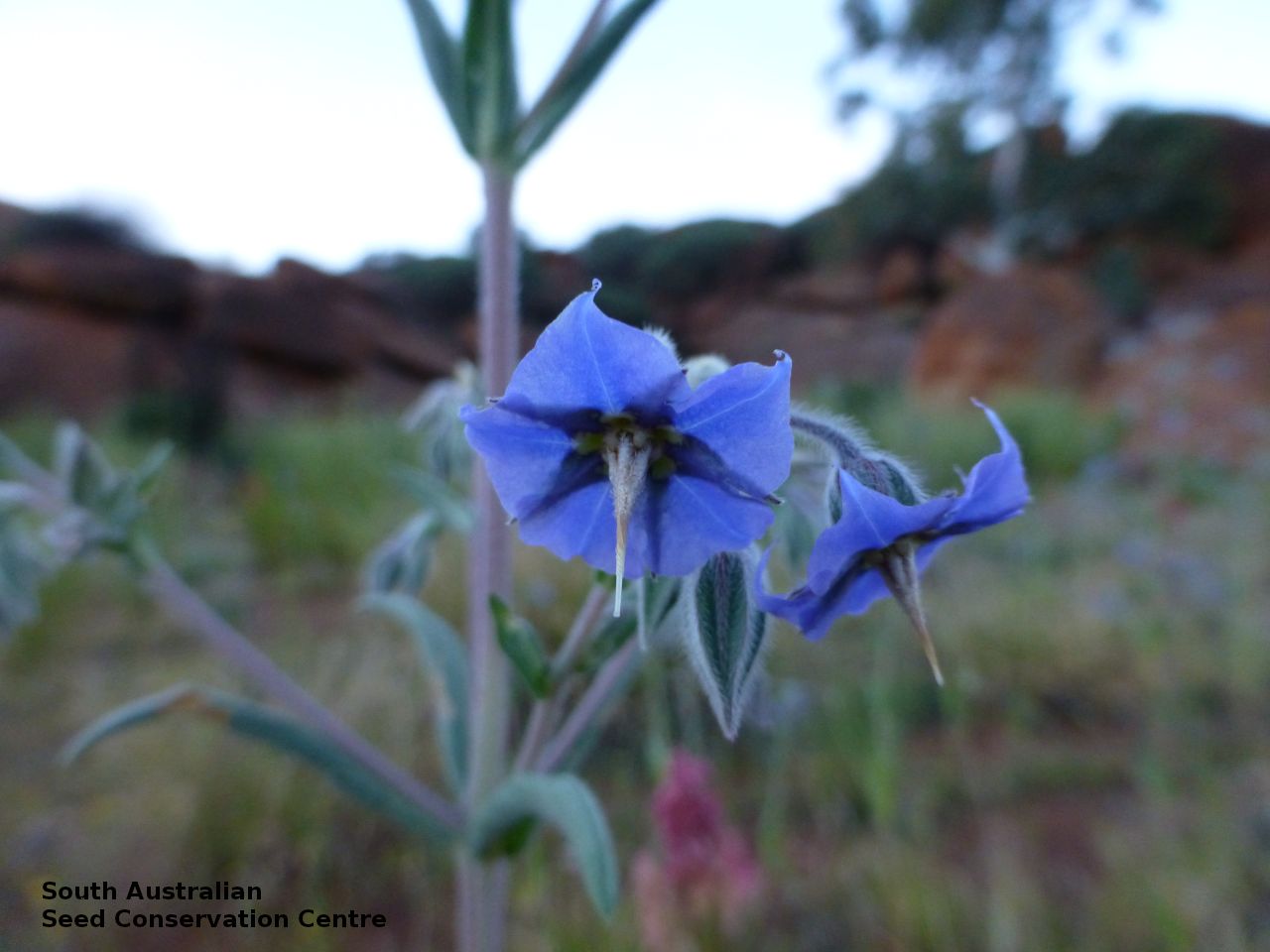
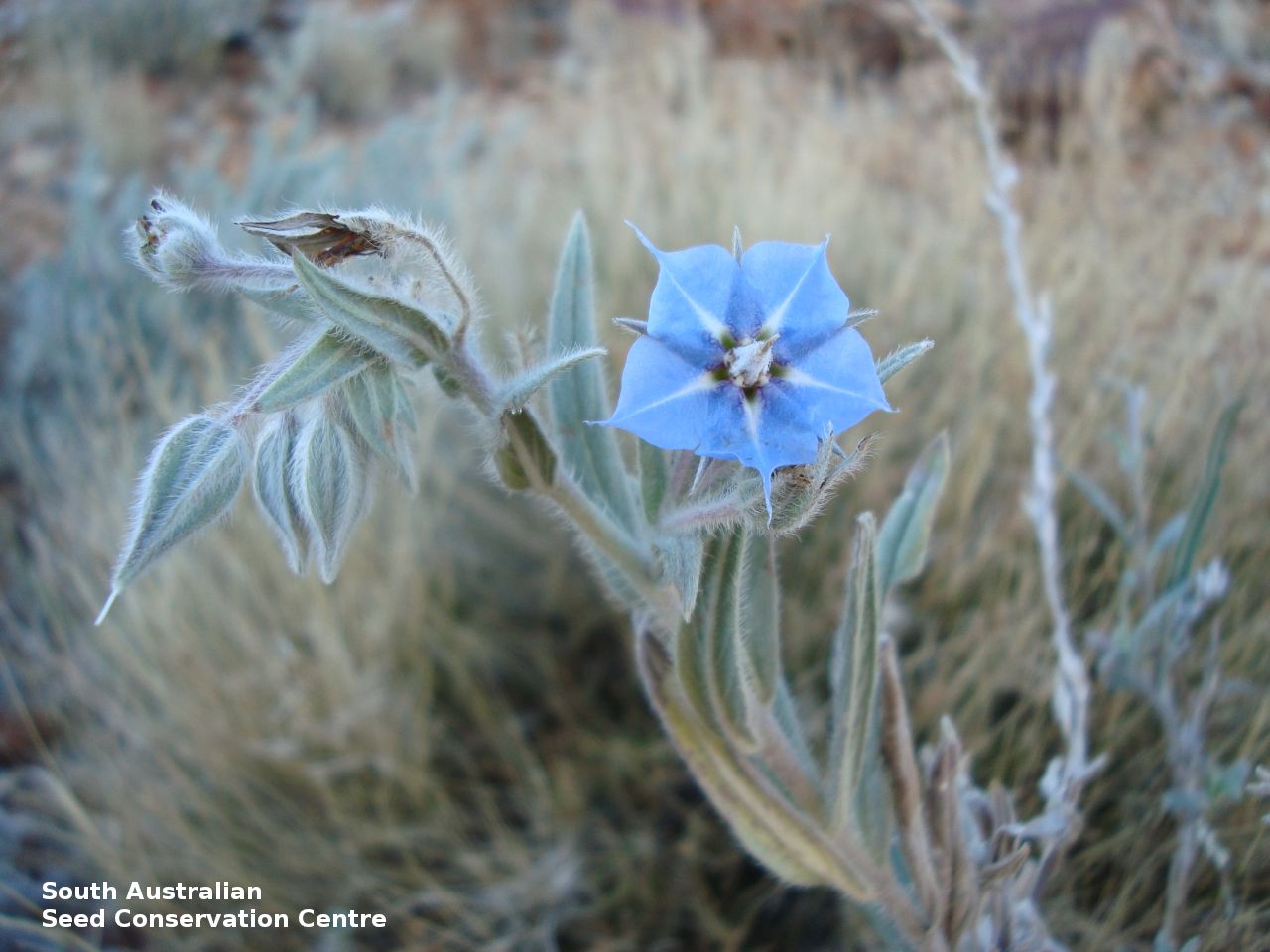
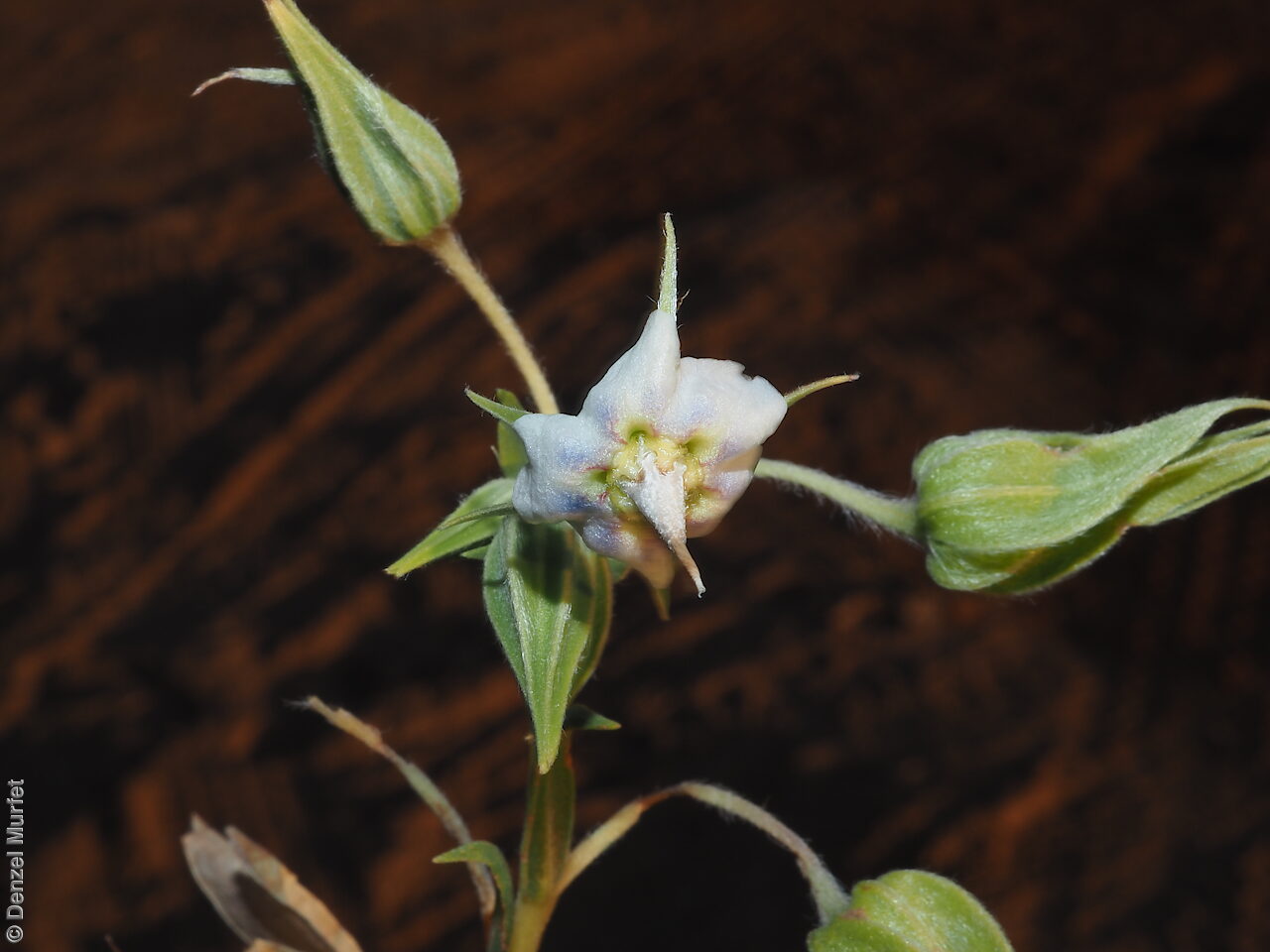
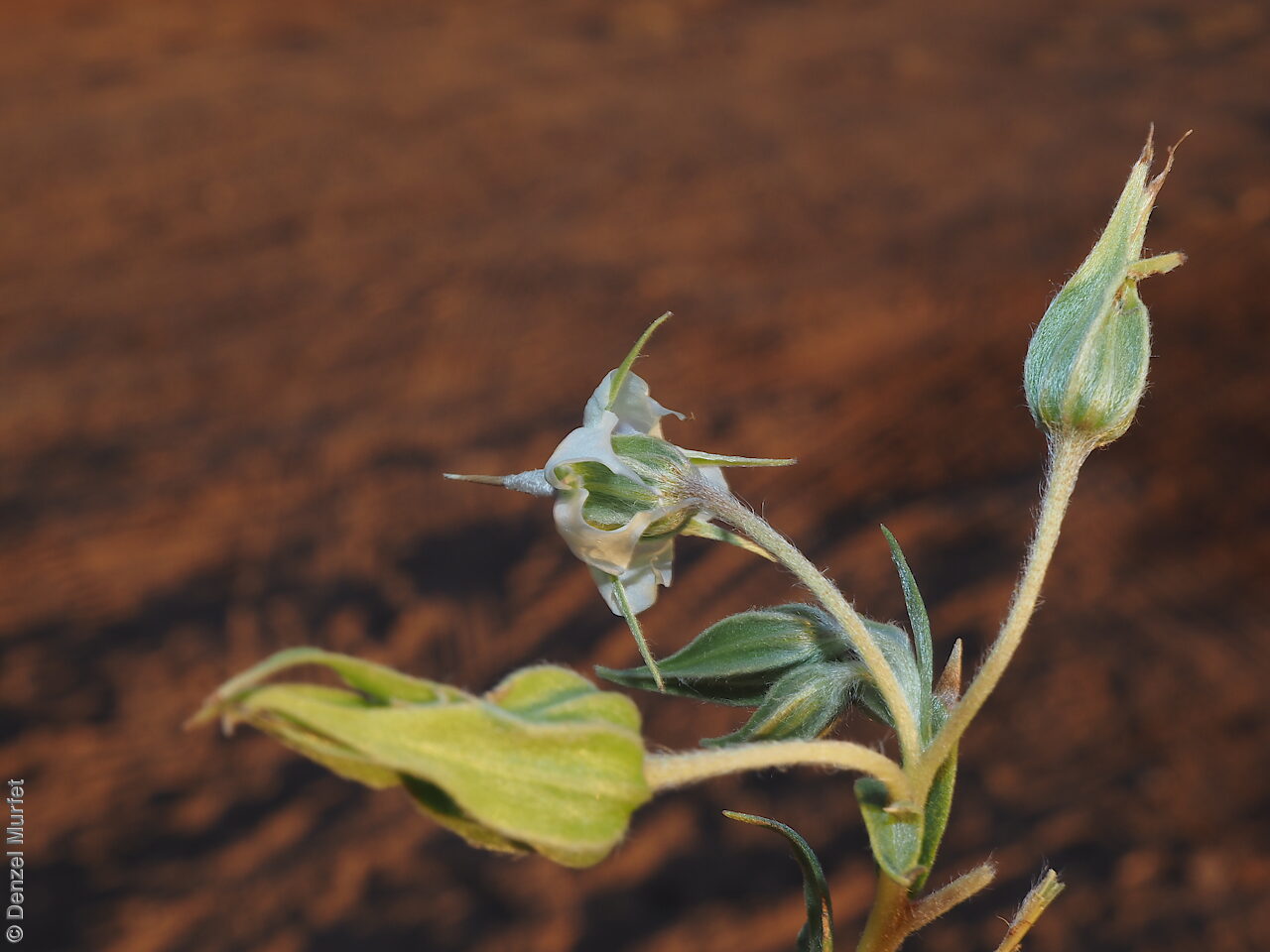
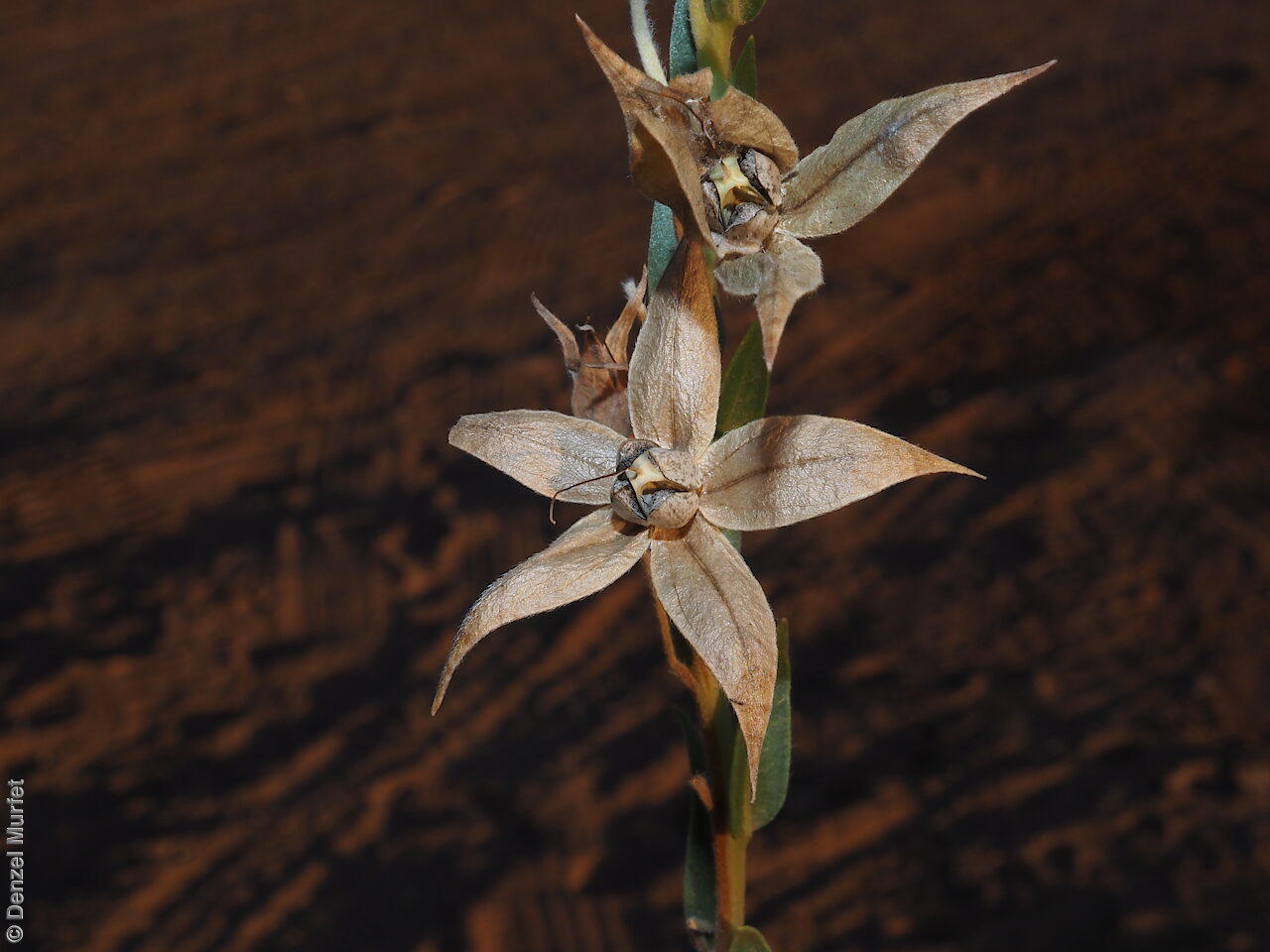
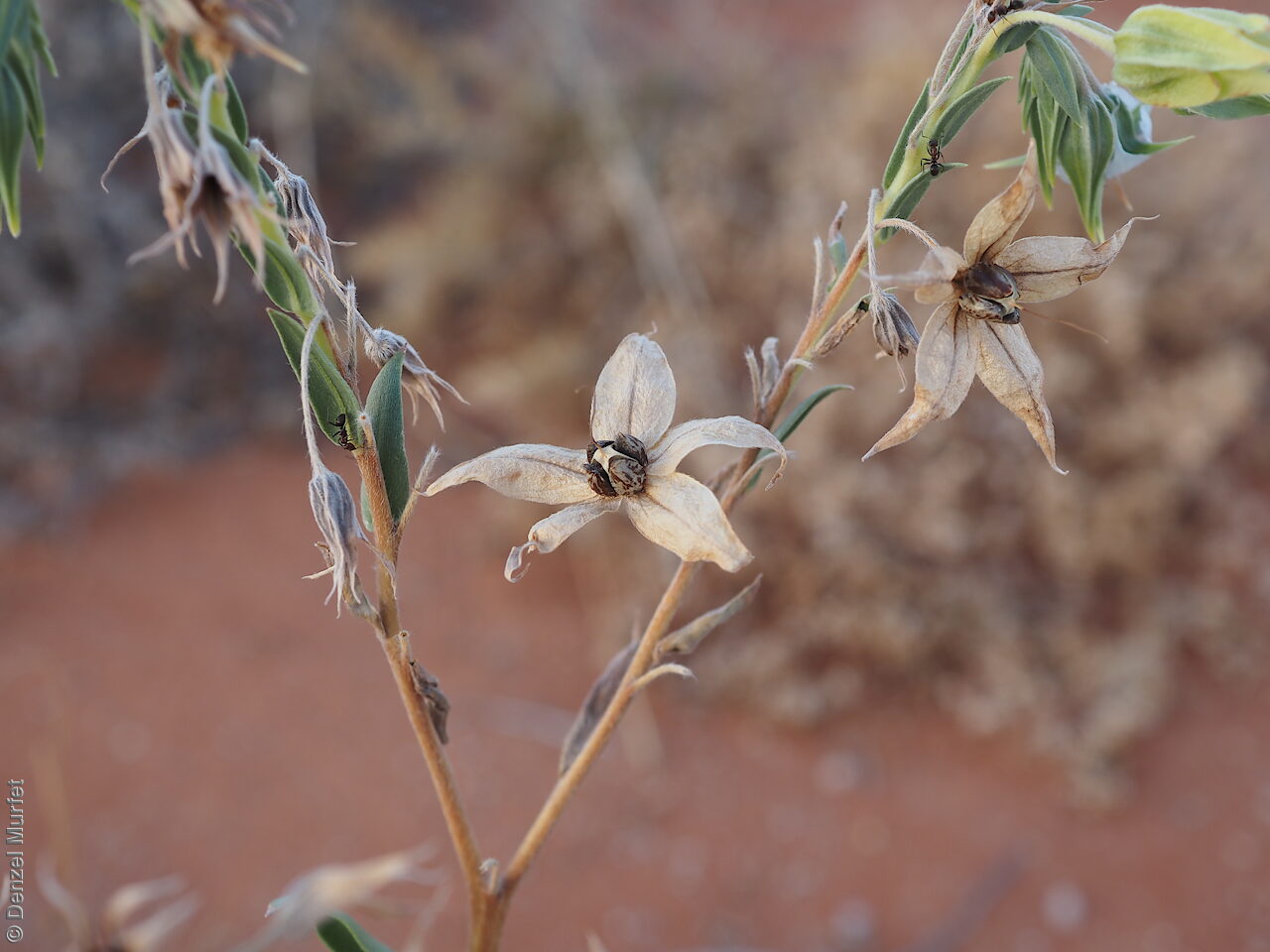
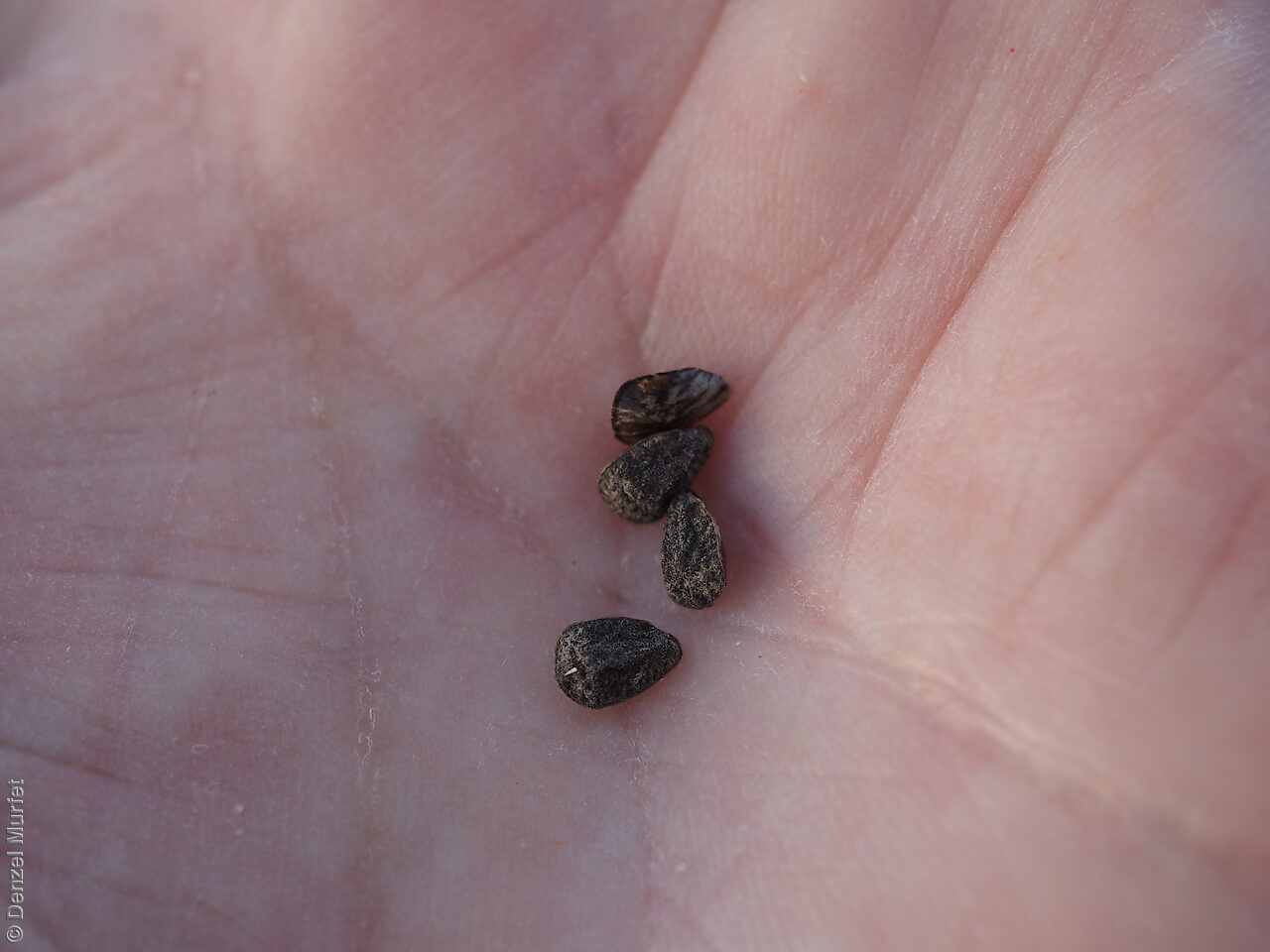
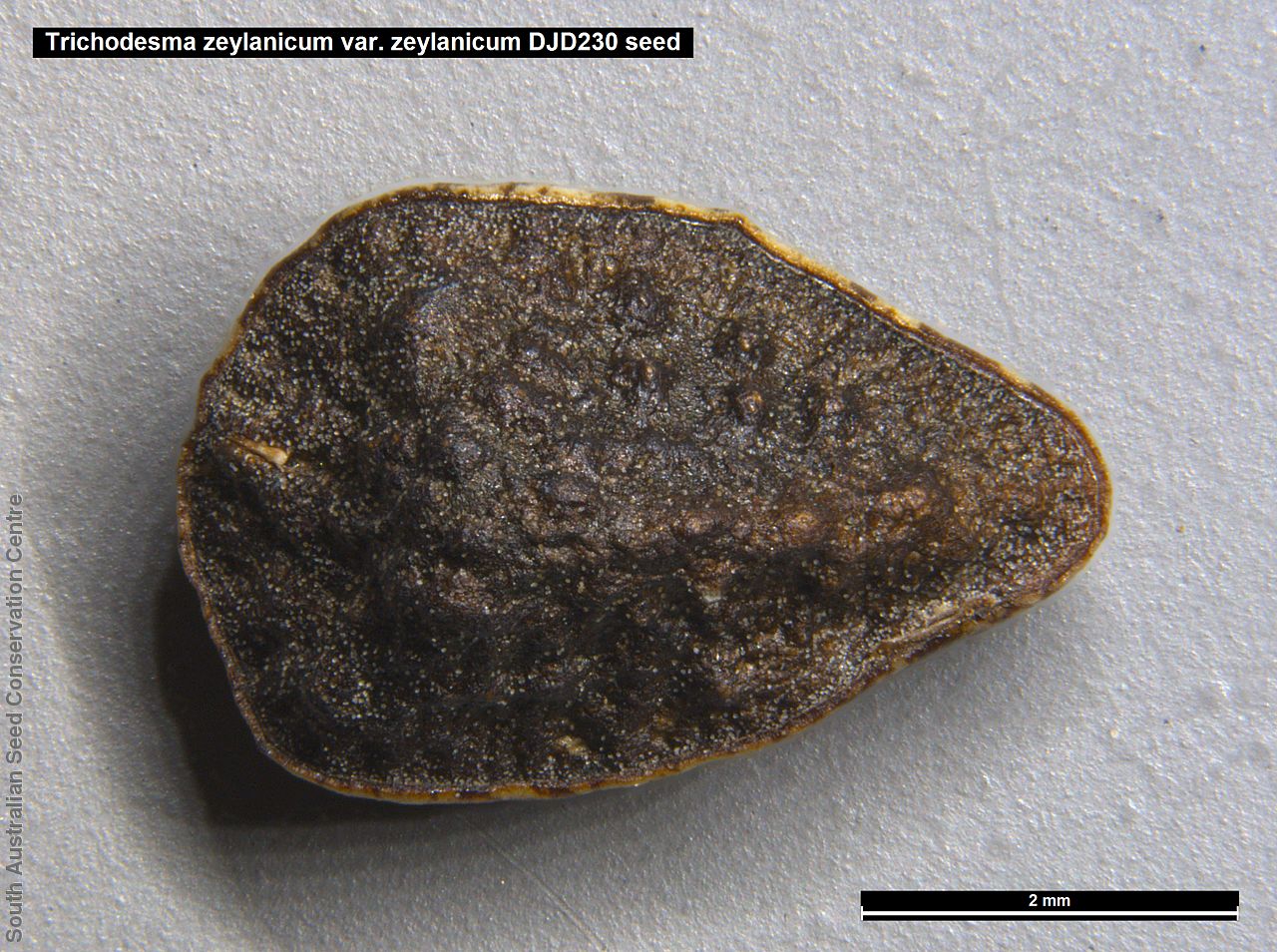
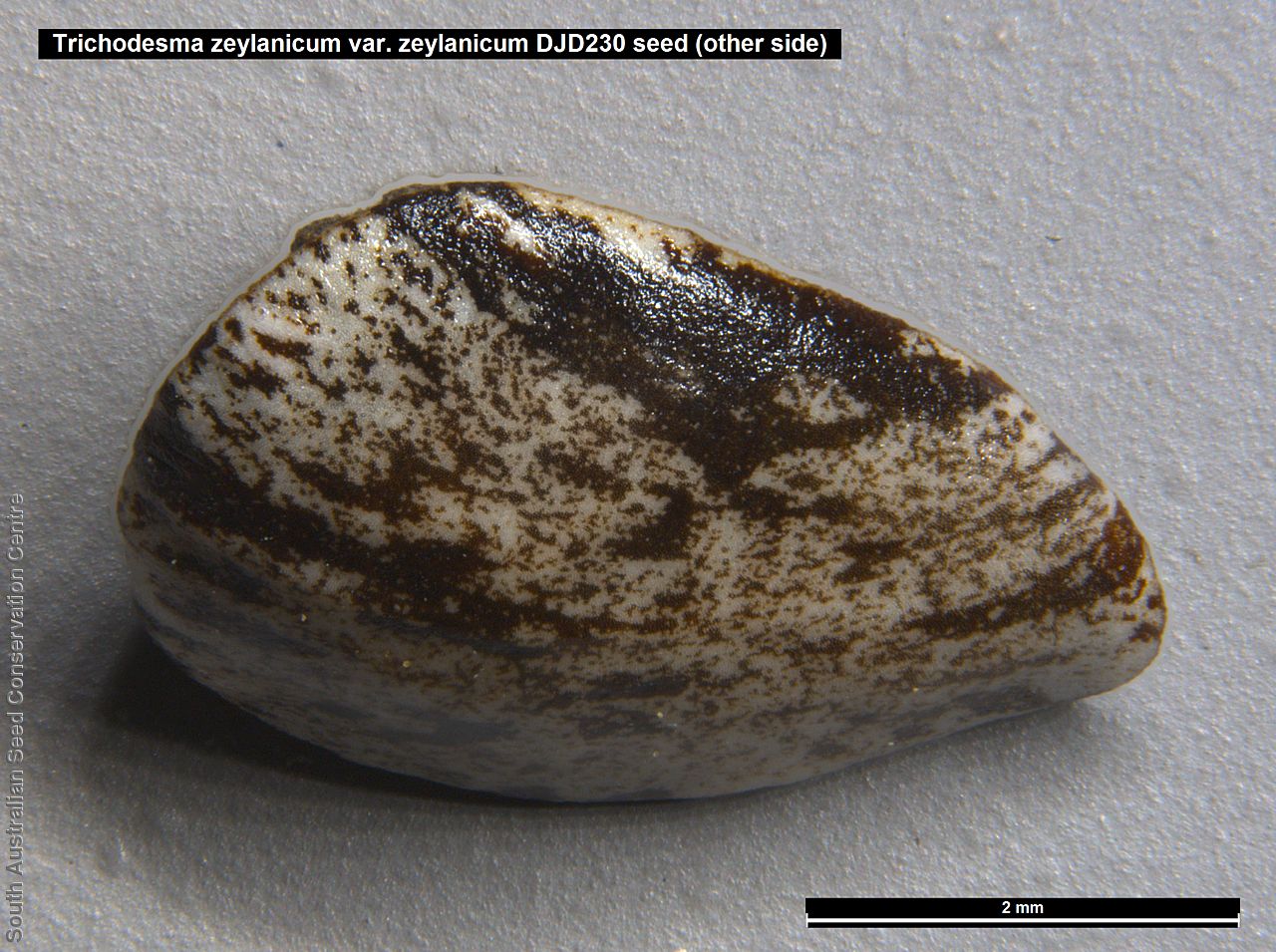
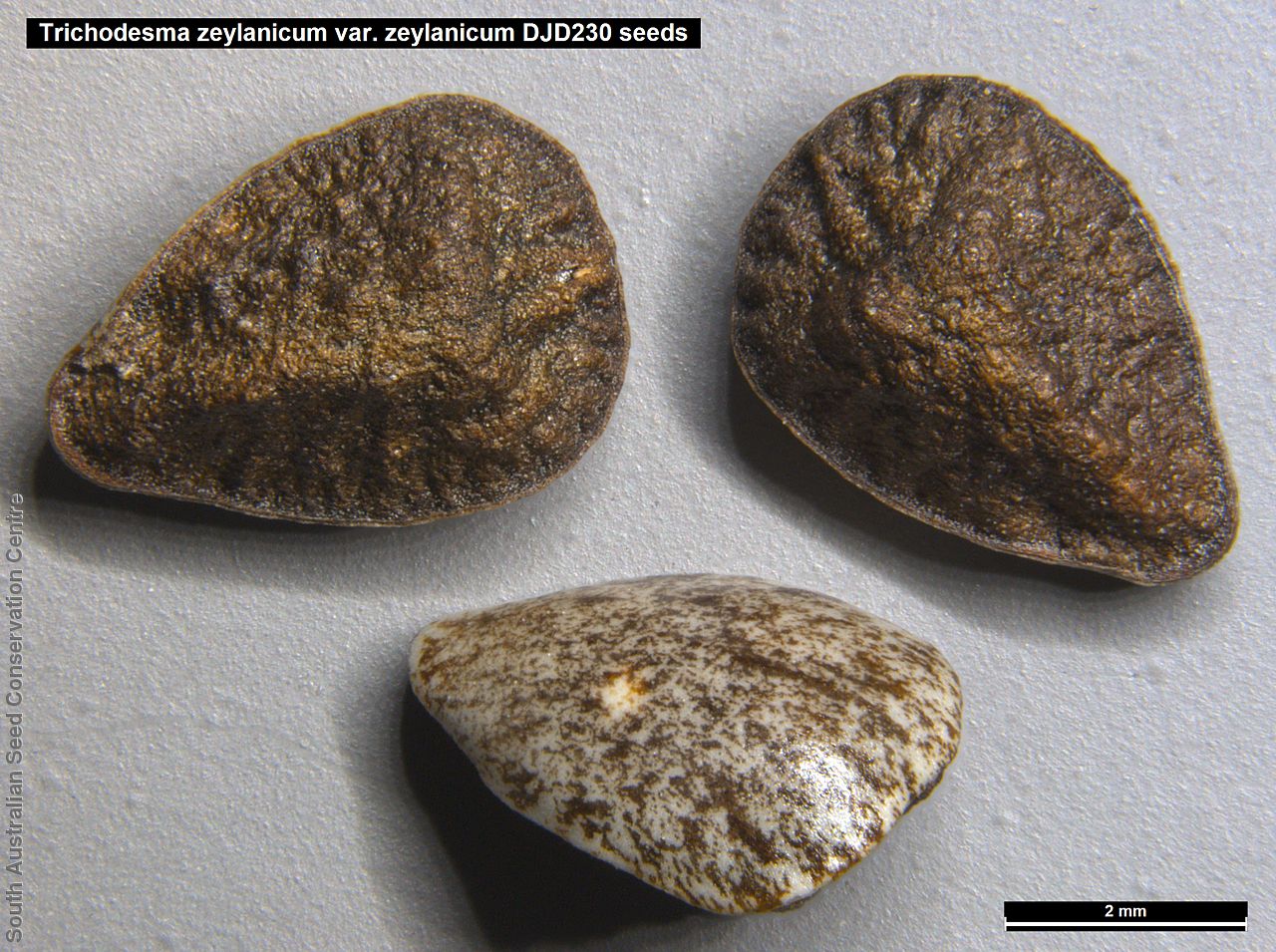
Annual herbs to perennials shrubs to 1.2 m high, woody at least at the base, with a robust tap root, sparsely to densely branched, more or less densely covered with hairs. Leaves opposite, and subpetiolate-cuneate below becoming alternate, sessile and cordate to rarely auriculate on or below the inflorescence, lanceolate to narrowly elliptic or oblong, rarely ovate, to 12 cm long and 2 cm wide, with long hairs often restricted to the veins on the under surface. Inflorescence terminal, with one to several clusters with leaf-like bracts, flowers dark-blue to rarely white. Sepals scarcely connate basally, with lobes linear-lanceolate to ovate, to 1.8 cm long and increasing after flowering, usually pointed. Corolla rotate with tube continued into spreading part, dark-blue to rarely white, to 18 mm long, lobes broadly ovate, abruptly tapering into an often coiled point, stamens attached just below the throat of the corolla, with anthers sessile, narrowly triangular, each with 2 rows of dorsal hairs spreading laterally and continued into a vertically coiled appendage and usually interlocking with those of the anthers to form a cone around the style. Flowering between May and October. Fruits are brown capsules along the spike, splitting open at maturity. Seeds are mottled brown ovoid seed to 5 mm long and 4 mm wide, smooth. Seed embryo type is spatulate fully developed.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between October and December. Collect mature capsule, those that are drying off, turning brown and contain dark, hard seeds inside. Can collect individual capsule or break off whole spike. Place the capsules in a tray and leave to dry for one to two weeks. Then rub the fruits gently by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. From one collection, the seed viability was high, at 95%.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 4,200 (43.58 g) 4,200 (43.58 g) | 20+ | 24-Nov-2005 | DJD230 Gairdner-Torrens | 28-Jul-2006 | 95% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.