



















Botanical art
Prior names
Lepidium praetervisum
Lepidium ruderale var. robusta
Lepidium hyssopifolium f. intercedens
Lepidium hyssopifolium var. desvauxii
Lepidium desvauxii var. typicum
Lepidium halmaturinum
Etymology
Lepidium from the Greek 'lepis' meaning a scale; referring to the appearance of the fruits. Desvauxii named after Nicaise Auguste Descvaux (1784-1856), a French botanist and director of the botanic garden in Angers, France.
Distribution and status
Found on Kangaroo Island in South Australia with an isolated collection from Flinders Island, growing in coastal habitats. Also found in Western Australia, Victoria and Tasmania. Native. Rare in South Australia. Rare in Western Australia and Victoria. Common in Tasmania.
Herbarium regions: Eyre Peninsula, Kangaroo Island
NRM regions: Eyre Peninsula, Kangaroo Island
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
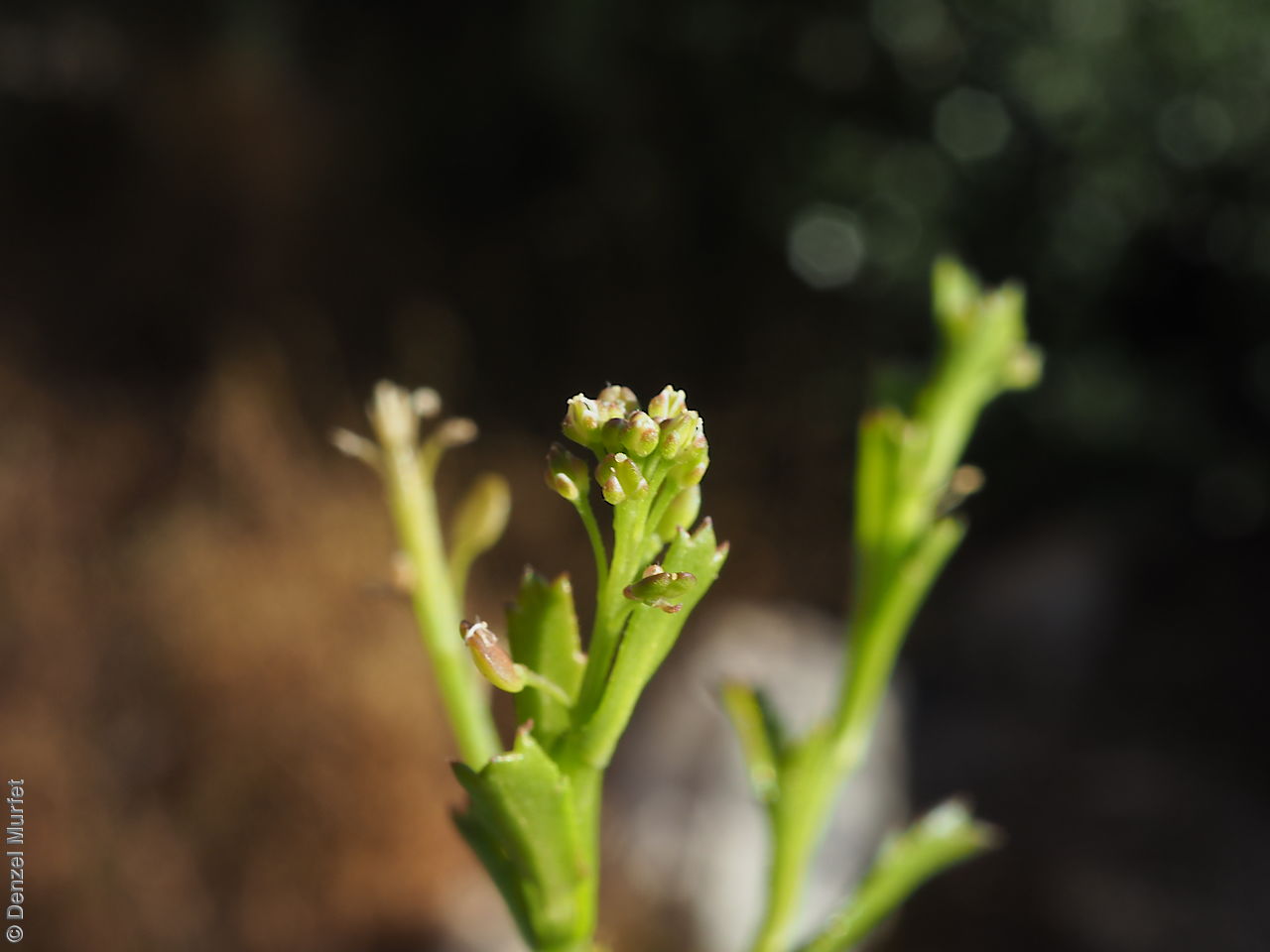
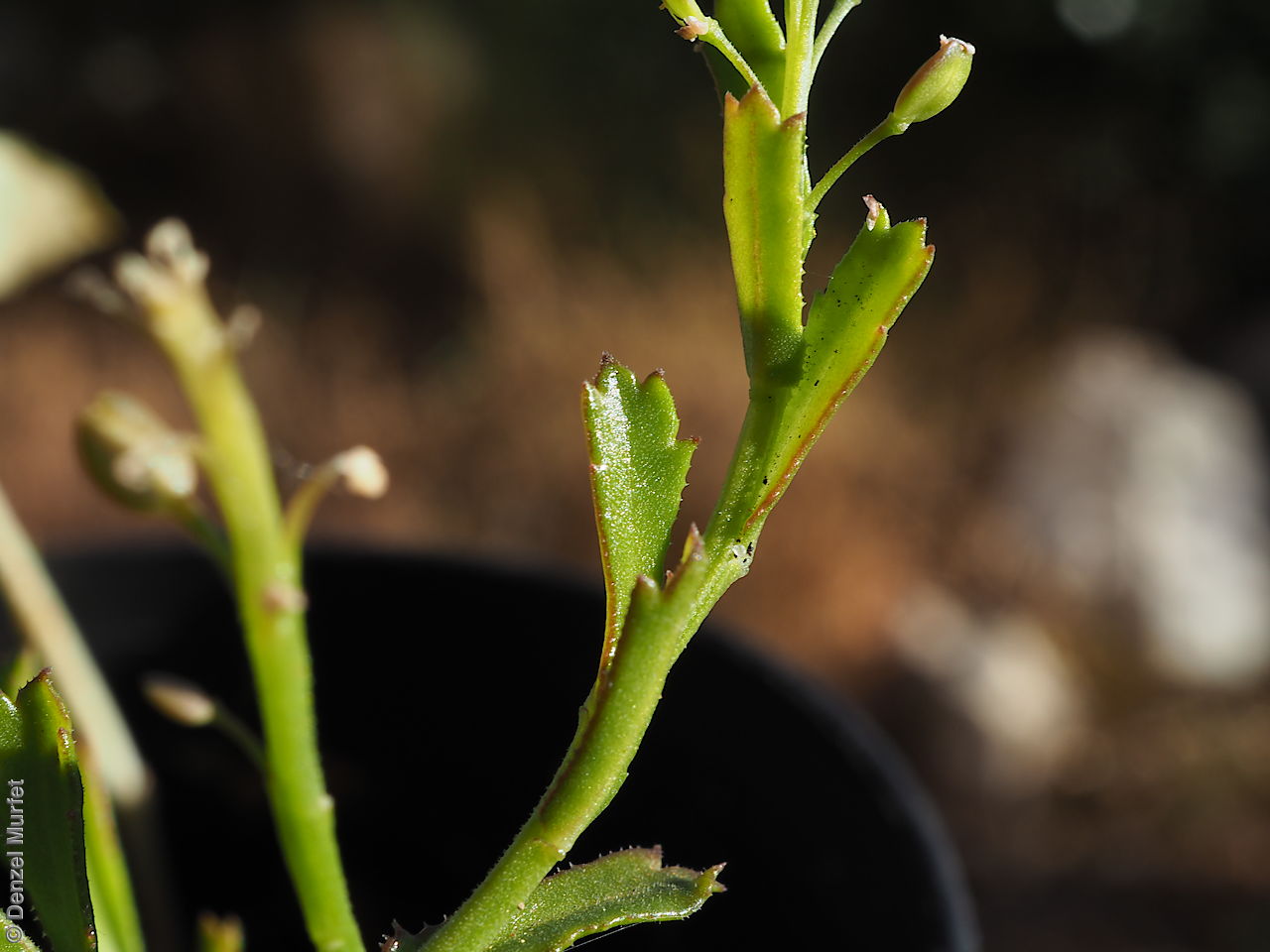
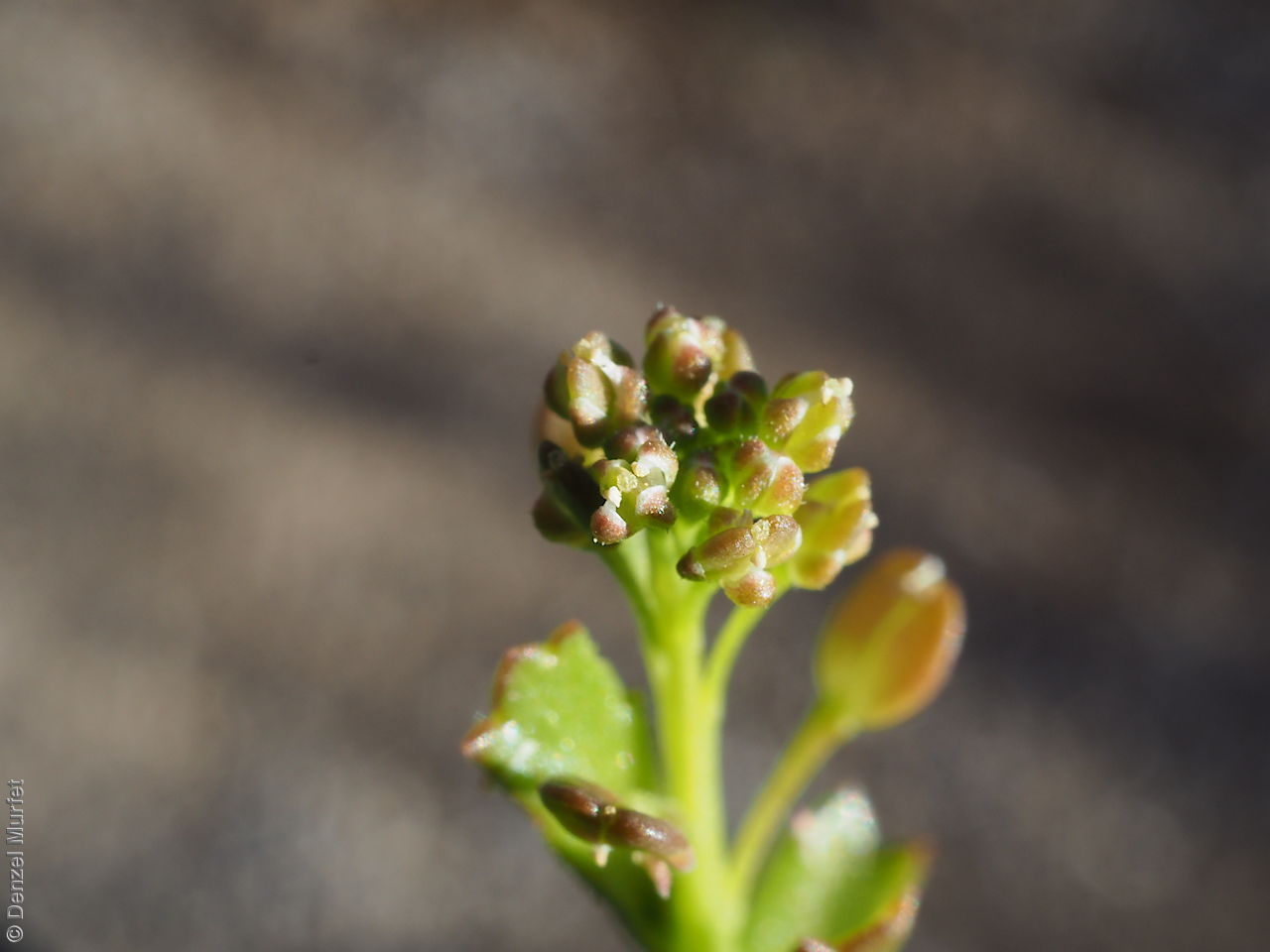
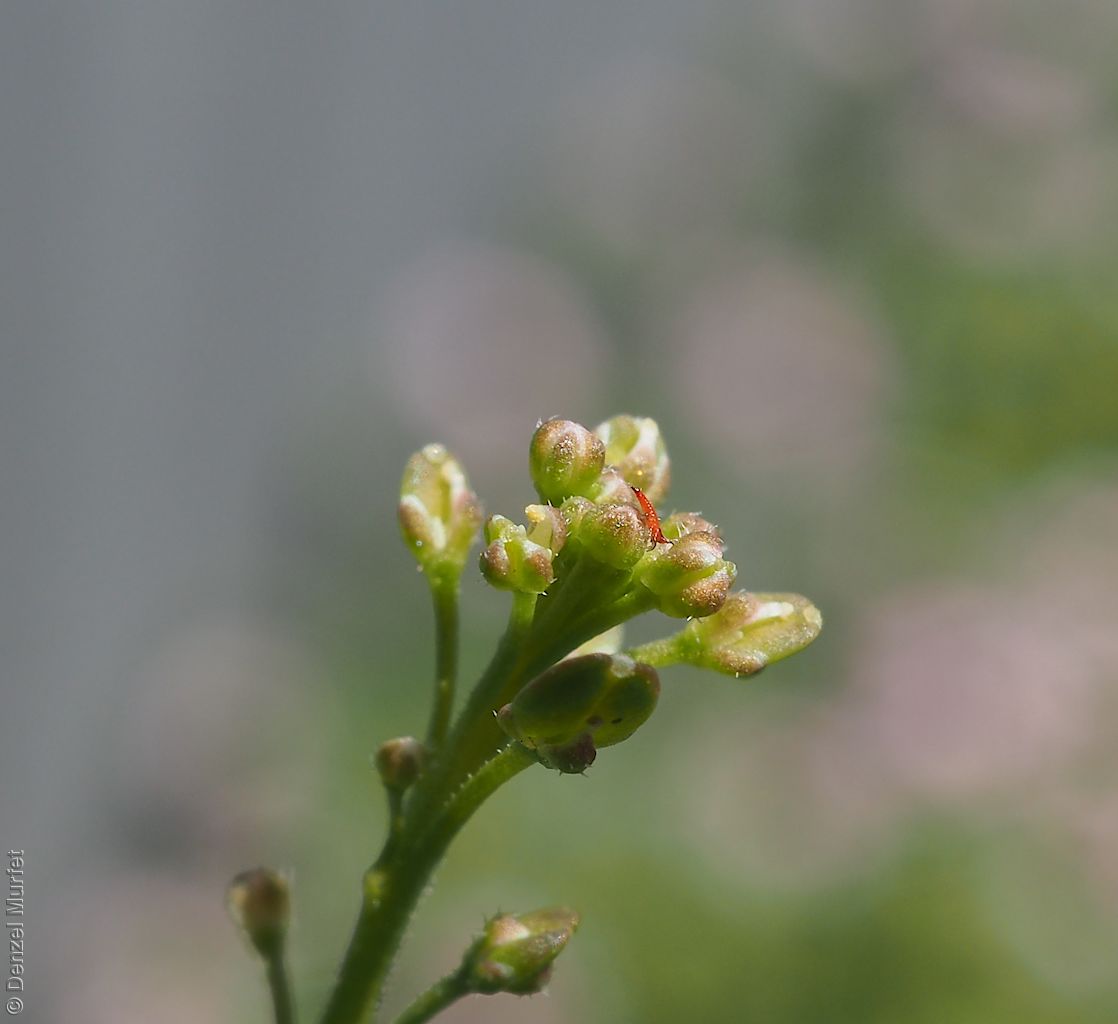
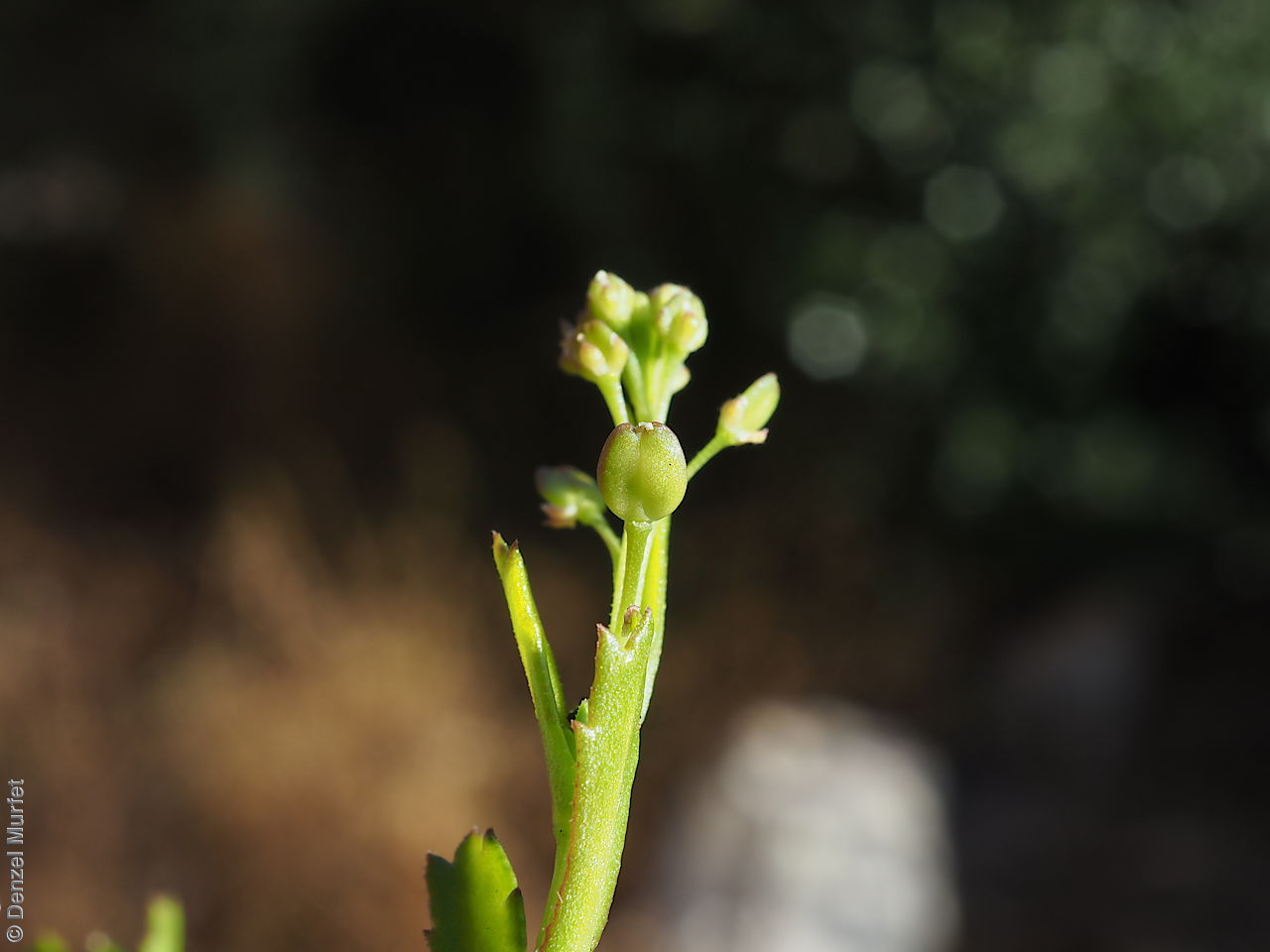
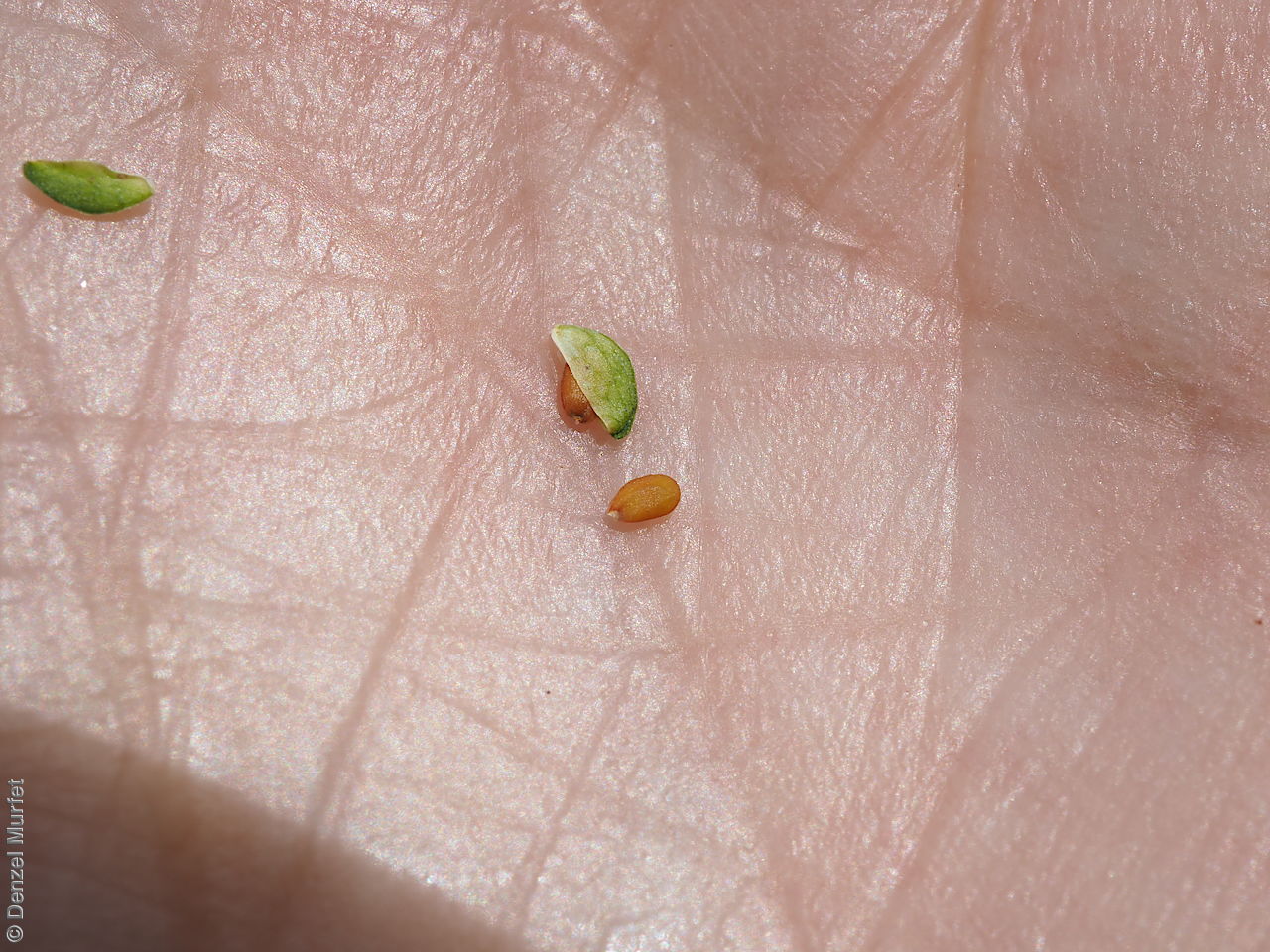
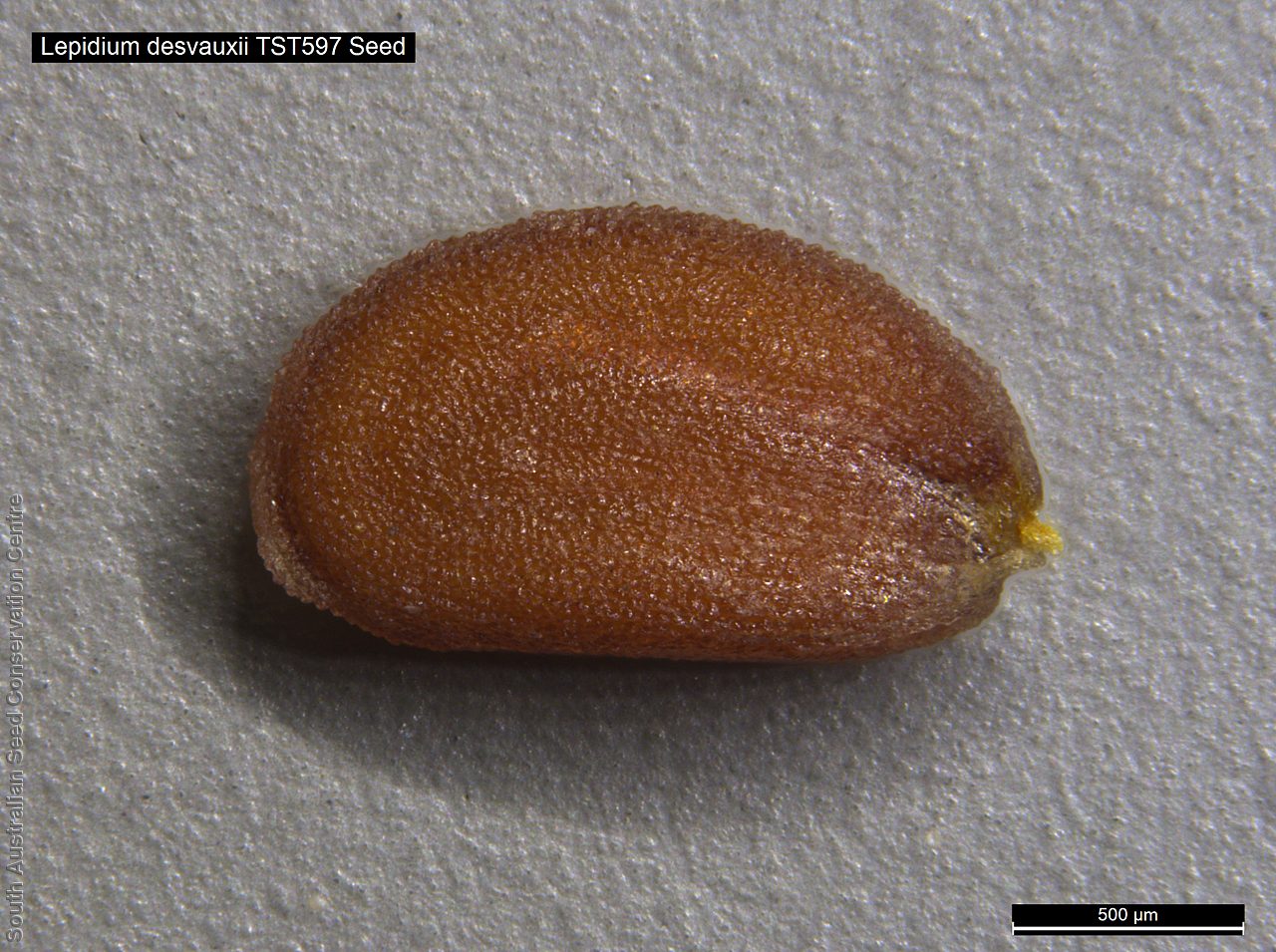
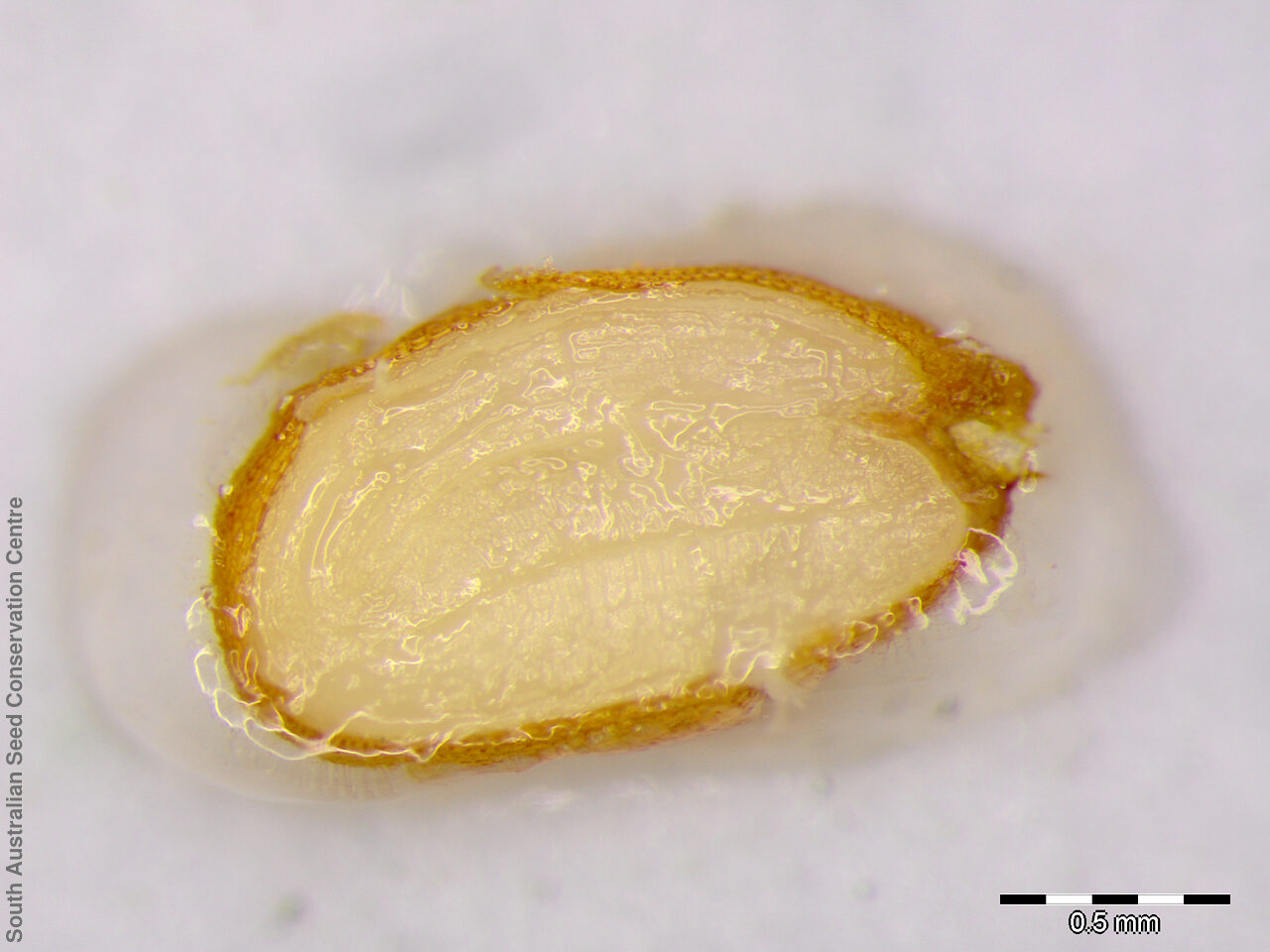
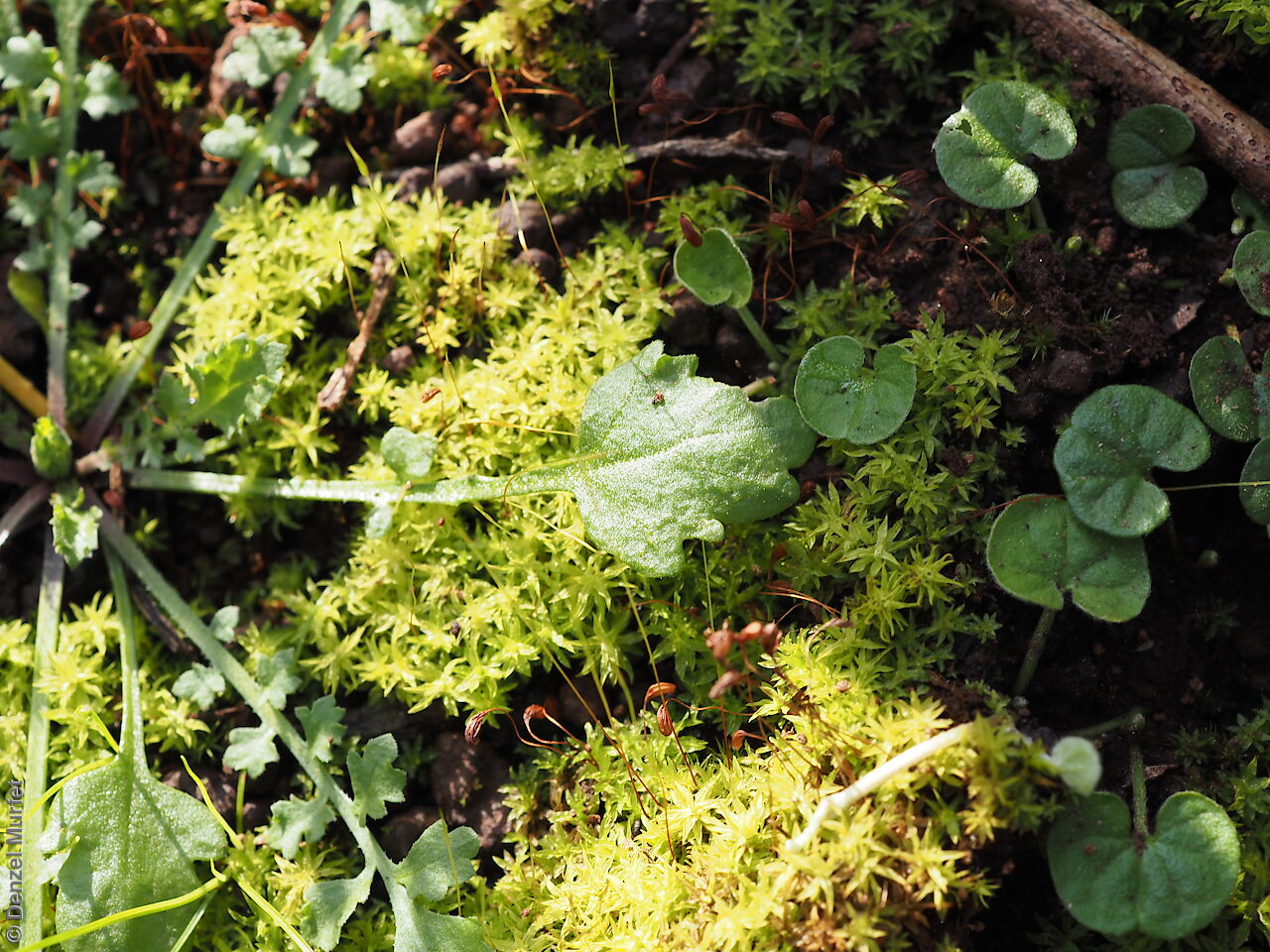
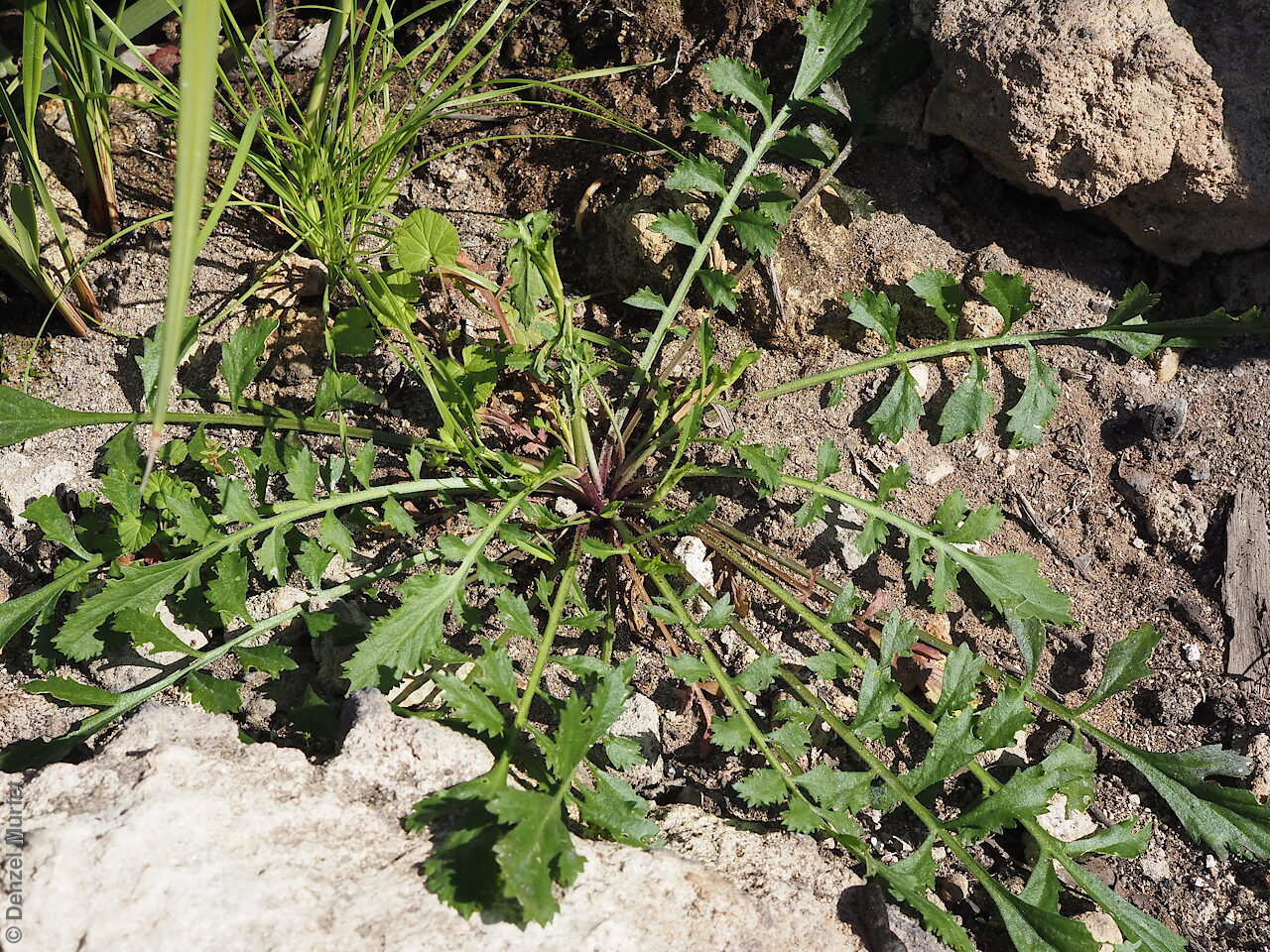
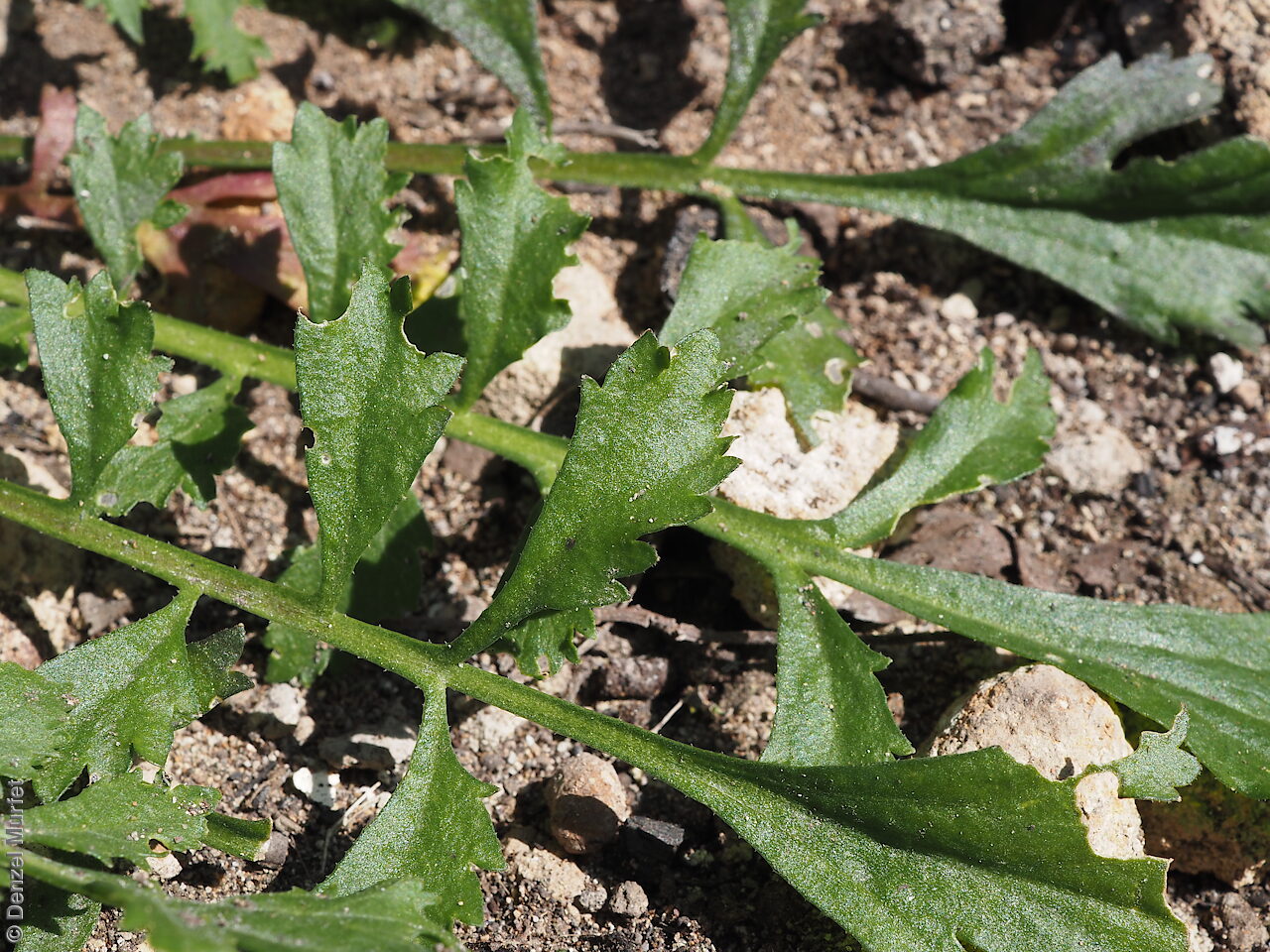
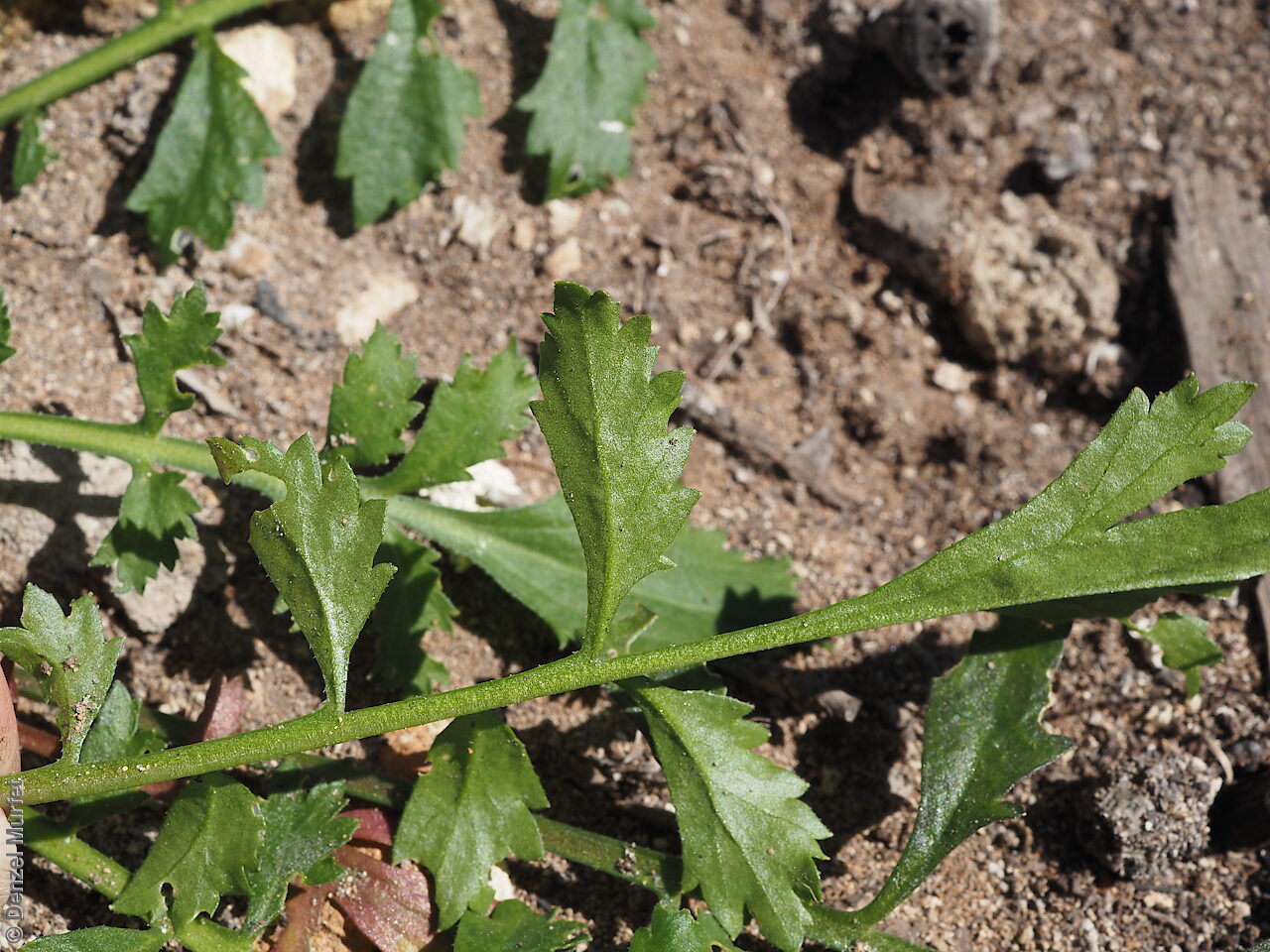
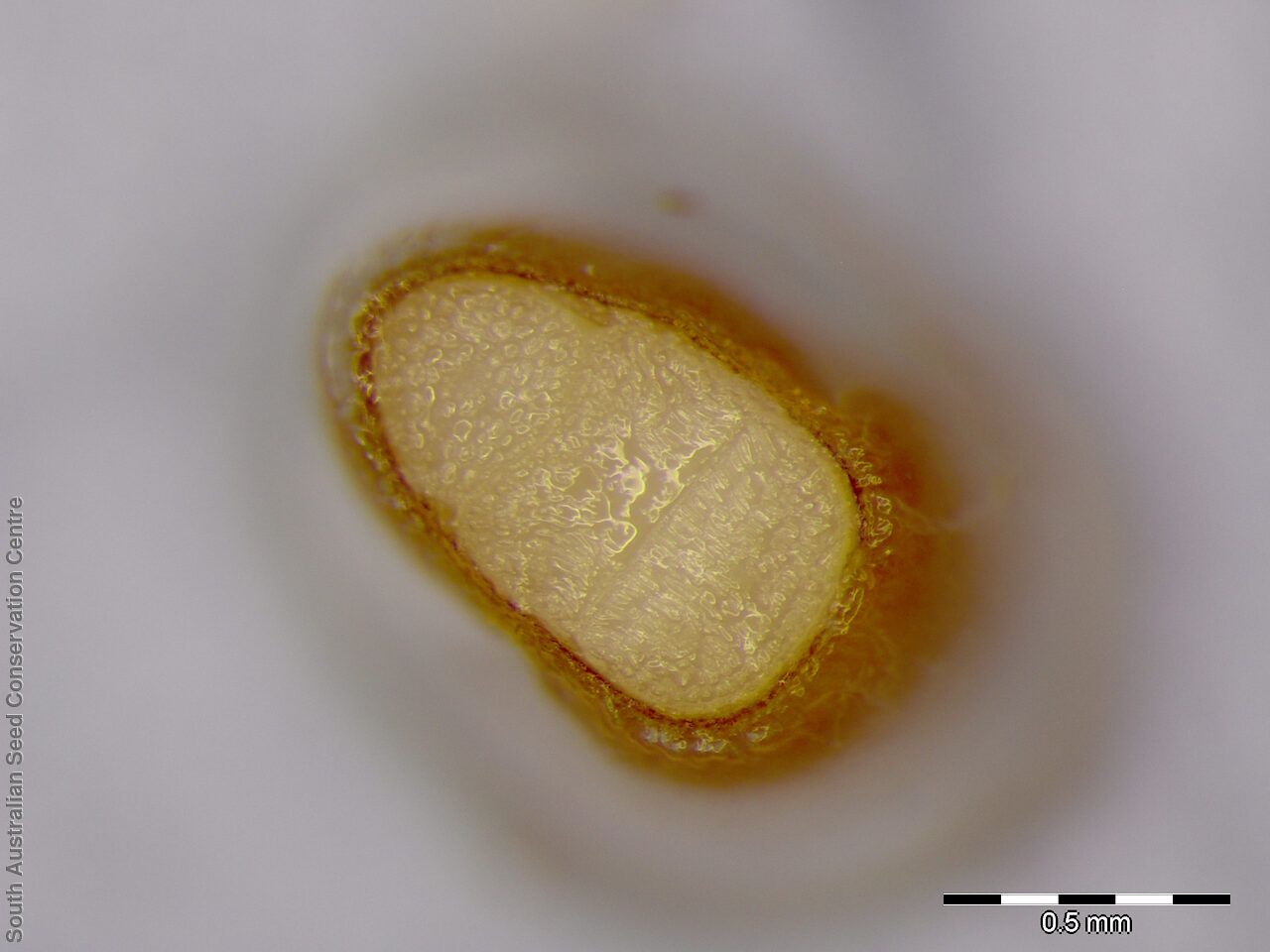
Perennial herb to 40 cm high with erect to spreading hairy stems. Basal leaves pinnate, the lobes toothed, terminal lobe the largest, with often large, coarse hairs, stem leaves spathulate to narrowly wedge-shaped, toothed near apex, base tapering, marginal hairs arising from warty projection, often bilobed. Inflorescence an elongating spike with tiny white flower. Flowers possibly throughout the year. Fruits are brown ovoid capsule to 3 mm long and 3 mm wide, glabrous, wings narrow, forming small apical notch. Seeds are brown reinform seed to 1.9 mm long and 0.9 mm wide, with fine tuberculated surface. Seed embryo type is bent.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between January and December. Collect maturing pods those turning pale brown with hard seeds inside. Be gentle with the pods as they split open easily. Place the pods in a tray and cover with paper to prevent seeds from popping out and leave to dry for a week. Then rub the dried pods gently by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. From one collection, the seed viability was high, at 95%.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 3,100 (1.38 g) 3,100 (1.38 g) | 25+ | 11-Nov-2005 | TST597 Kangaroo Island | 20-Jul-2009 | 95% | +5°C, -18°C |
| BGA | 200 (0.263 g) | 15 | 31-Aug-2021 | DJD4036 Kangaroo Island | 7-Jul-2022 | 90% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.