

















Botanical art
Prior names
Bergia tripetala
Bergia ammannioides var. trimera
Bergia ammannioides var. triandra
Common names
Three-parts Water-fire
Three-part Water-fire
Small Water-fire
Etymology
Bergia named after Dr Petter Jonas Bergius (1730-90), Swedish physician and botanist. Trimera from the Greek 'treis' meaning three and 'merus' meaning part; referring to the predominantly 3-merous flowers, a distinguishing feature from the closely related Bergia ammannioides.
Distribution and status
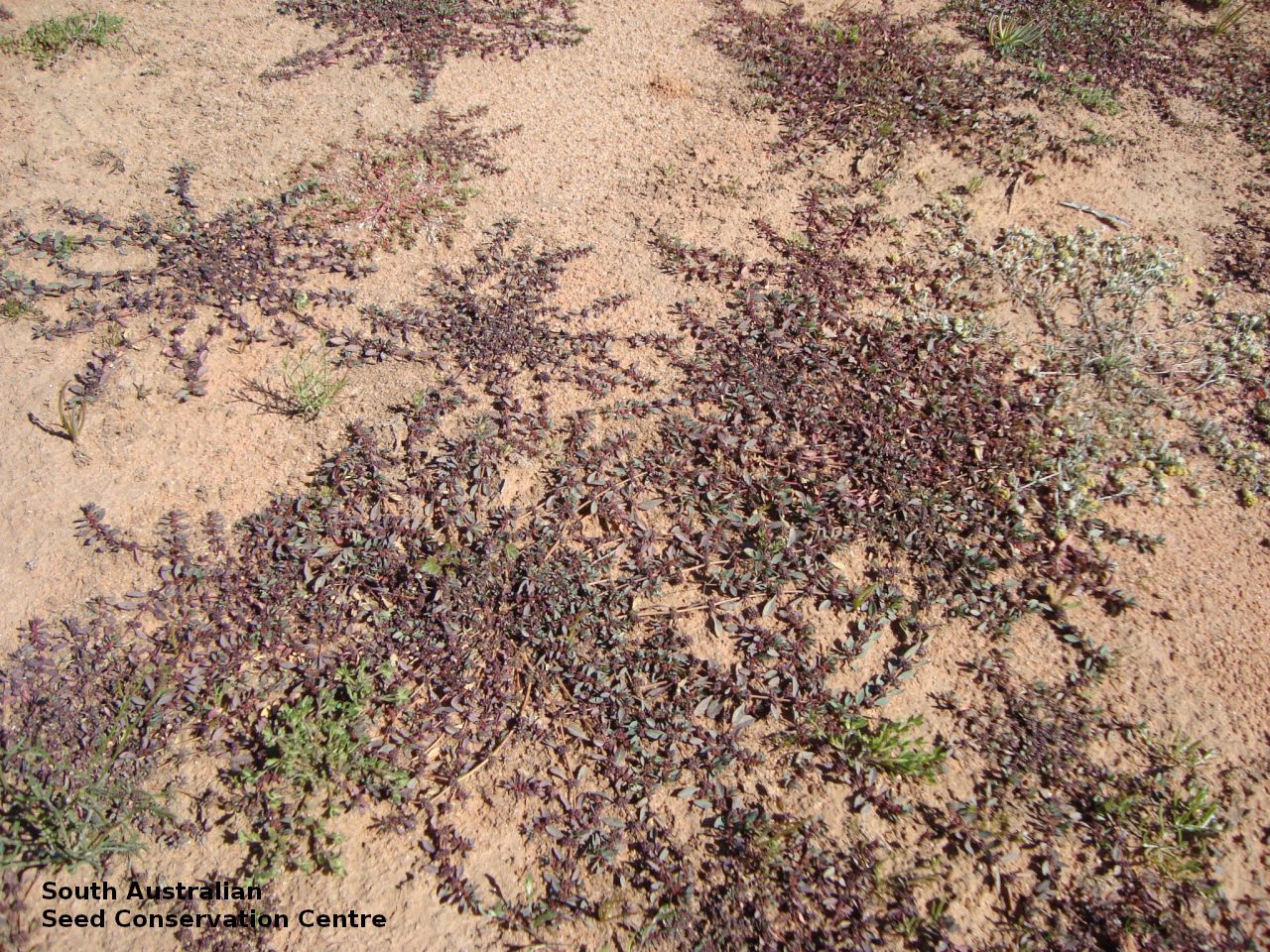
Found in the Eastern, Gairdner-Torrens, Lake Eyre Basin and North-western regions of South Australia, in sand, loam or clay soils, often saline. Also found in all other mainland states. Native. Common in South Australia. Common in other states.
Herbarium regions: North Western, Lake Eyre, Gairdner-Torrens, Eastern, Eyre Peninsula, Murray
NRM regions: Alinytjara Wilurara, Eyre Peninsula, South Australian Arid Lands, South Australian Murray-Darling Basin
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
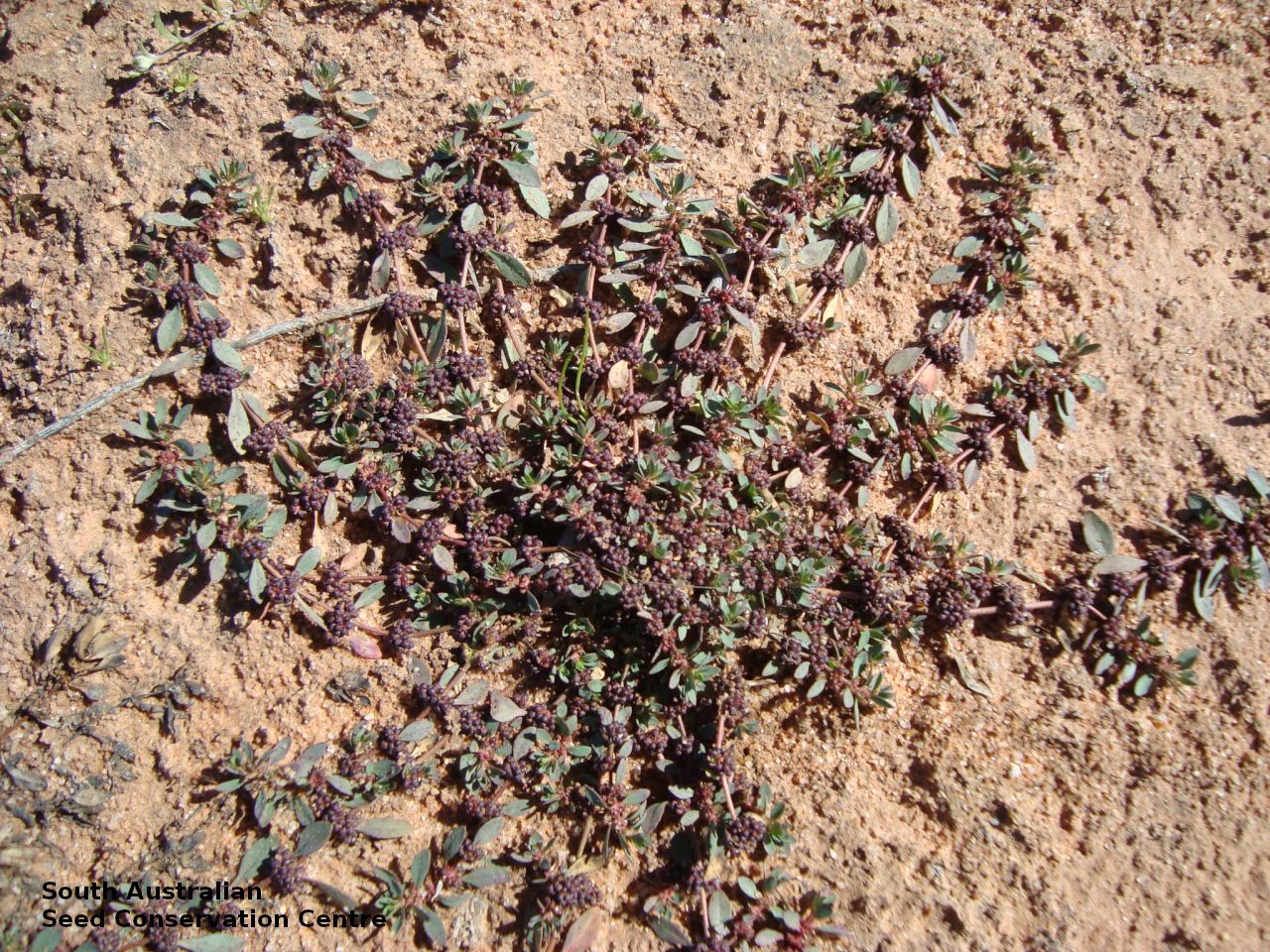
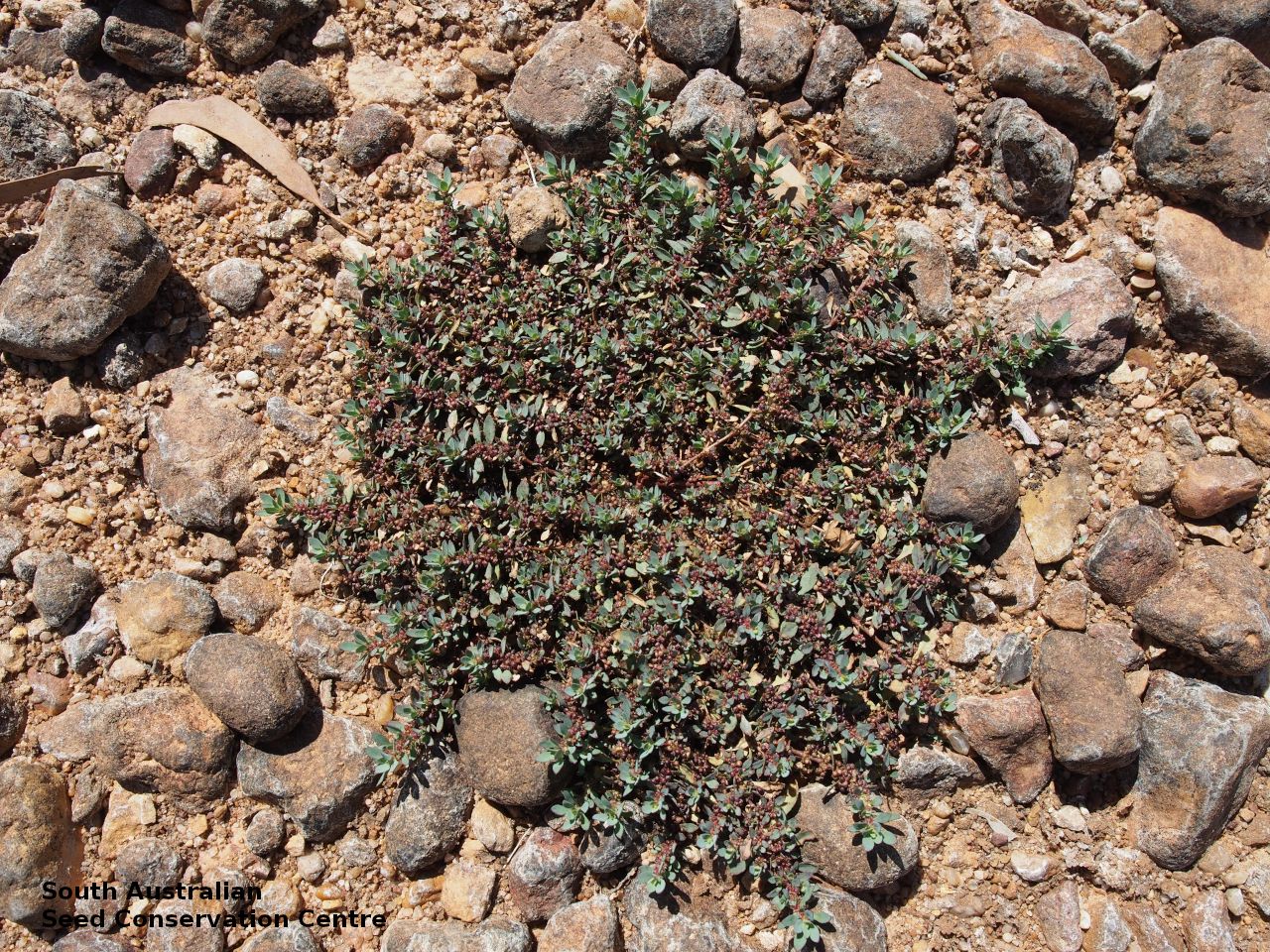
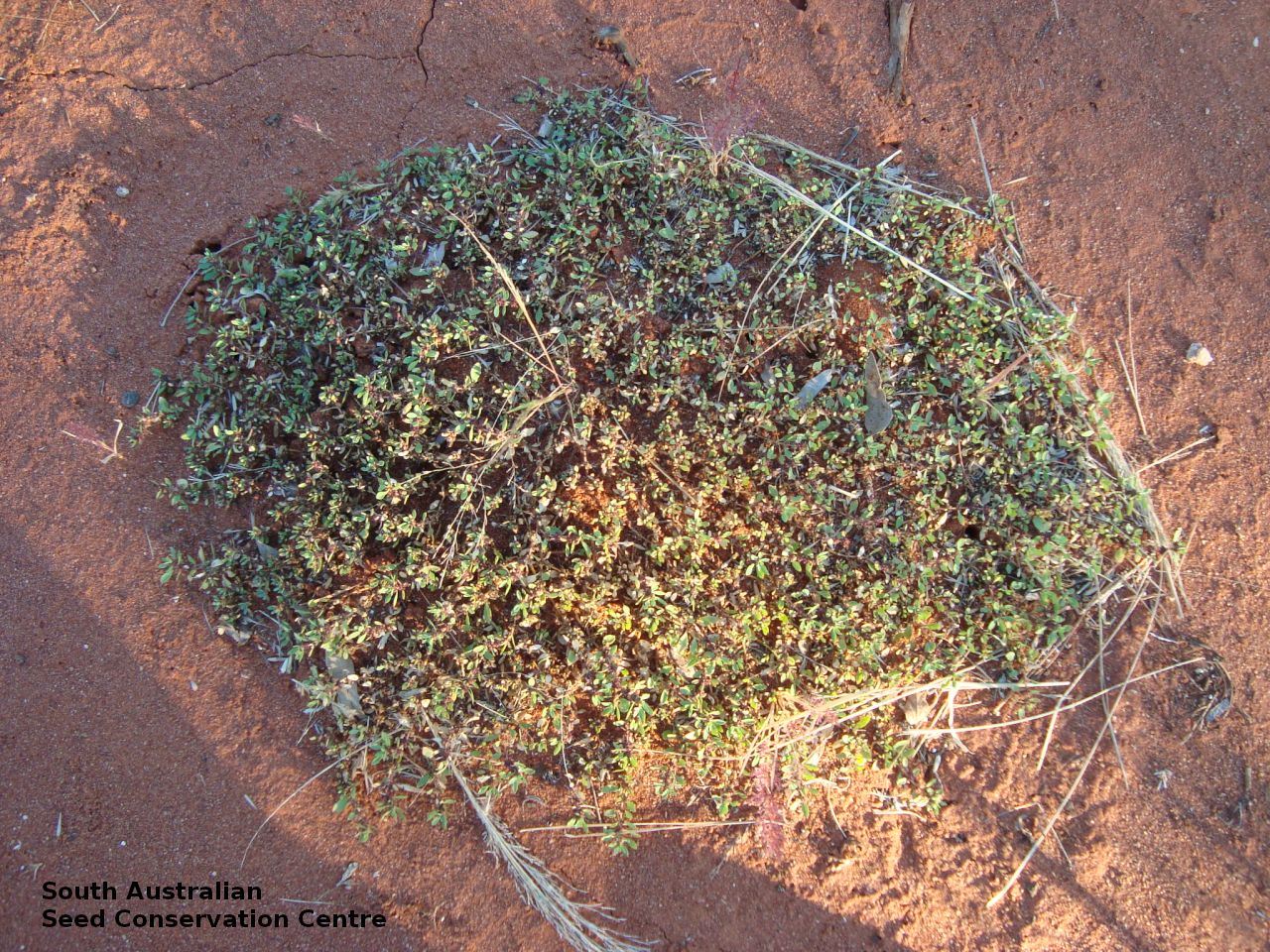
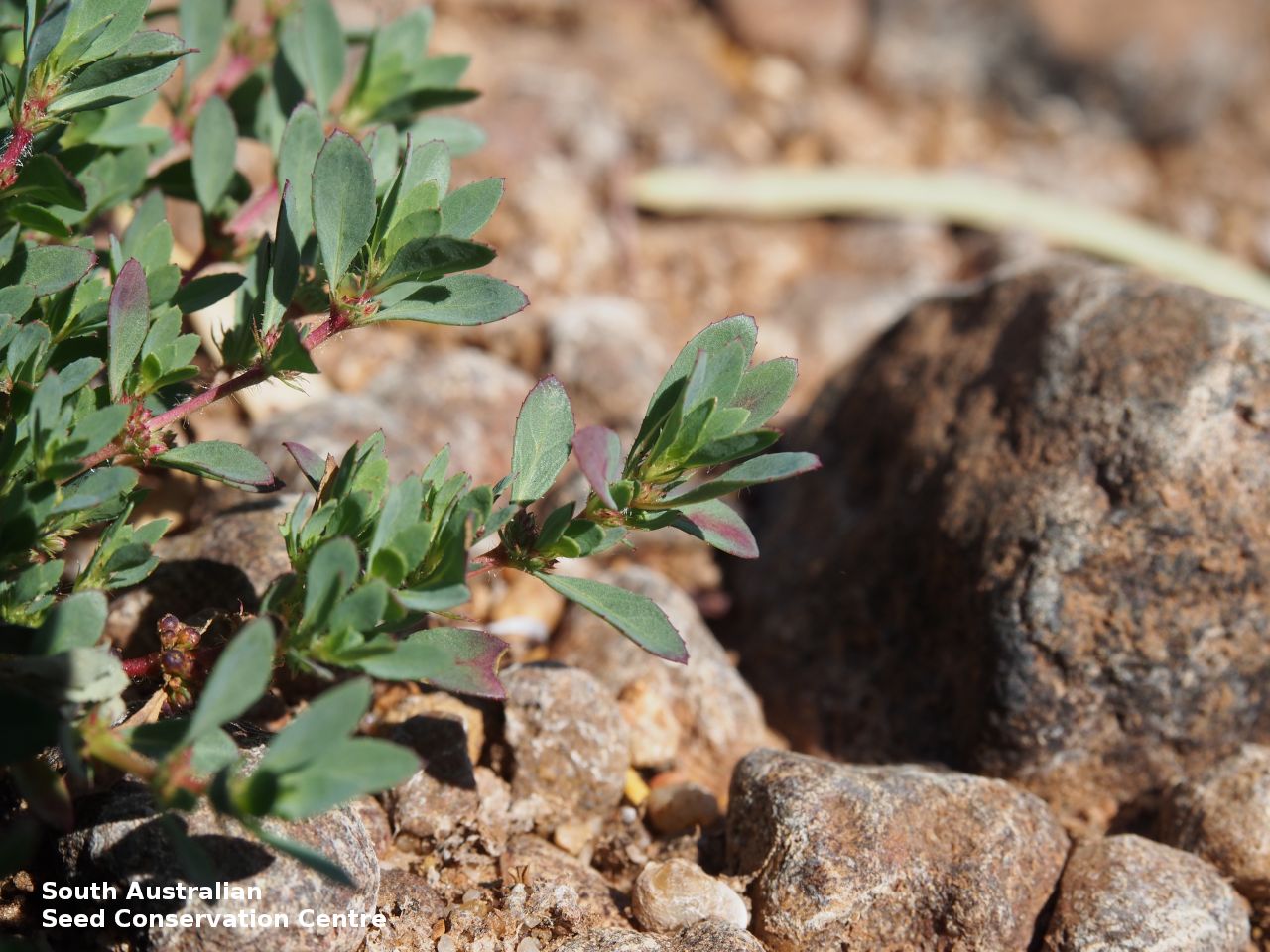
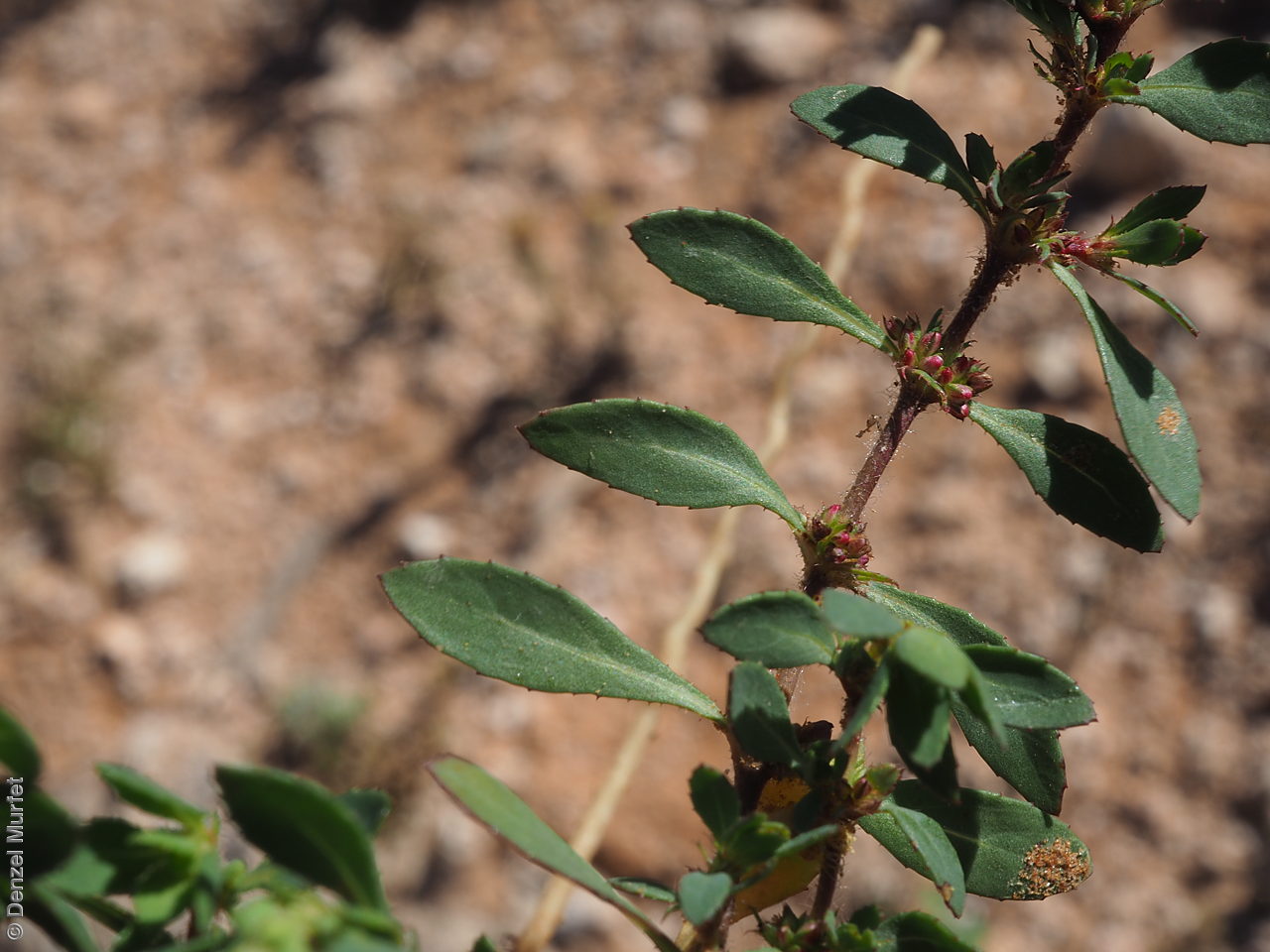
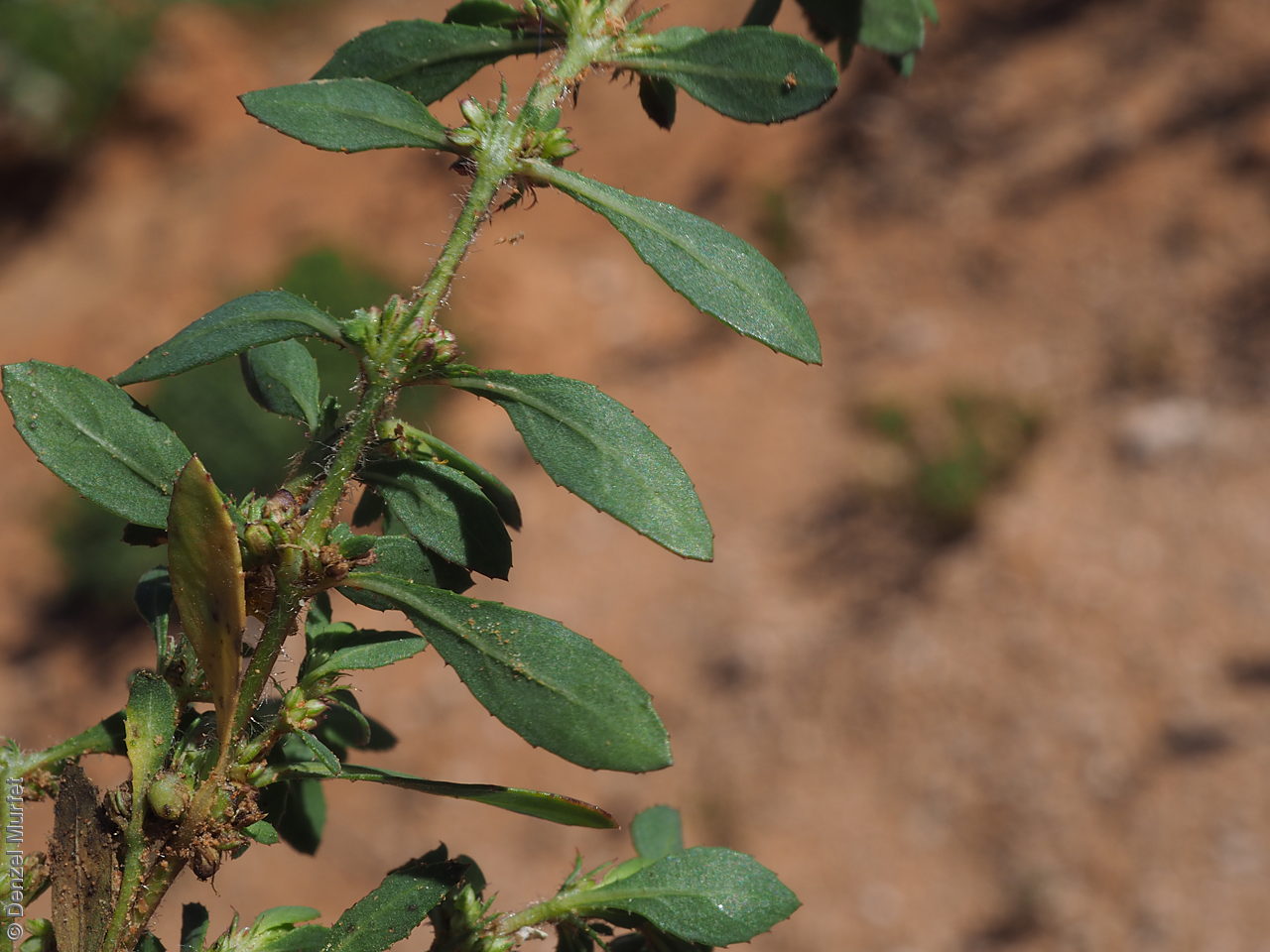
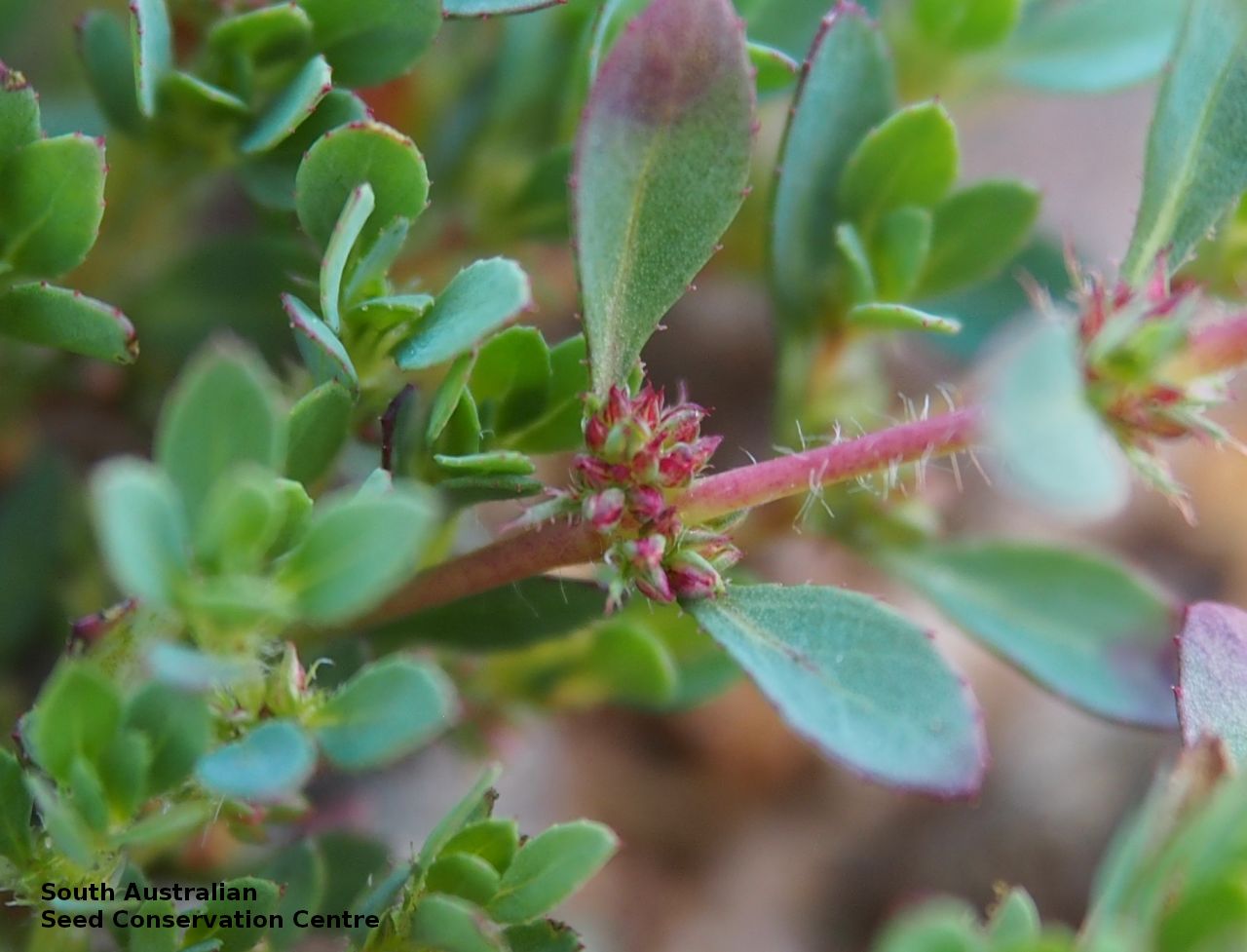
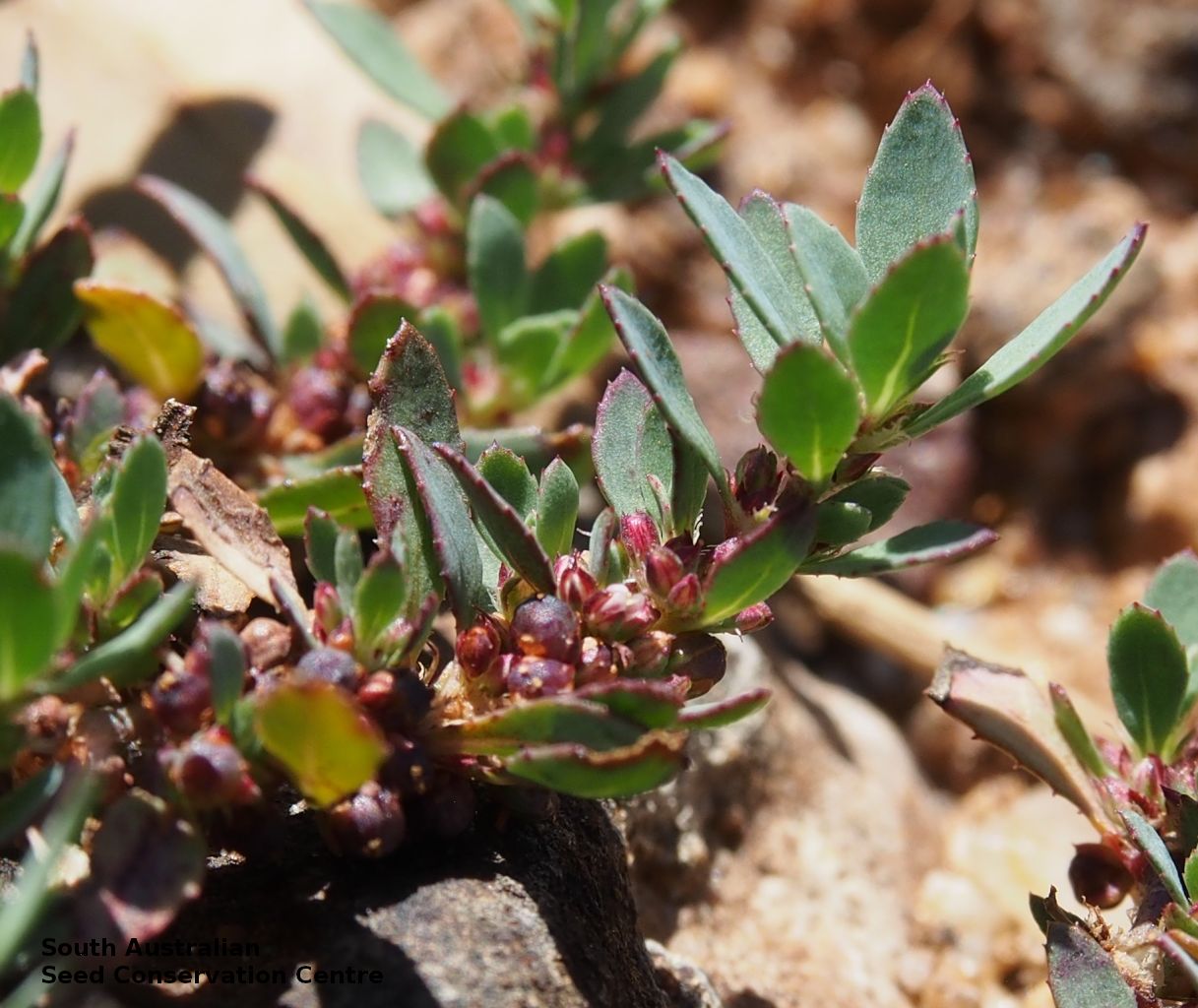
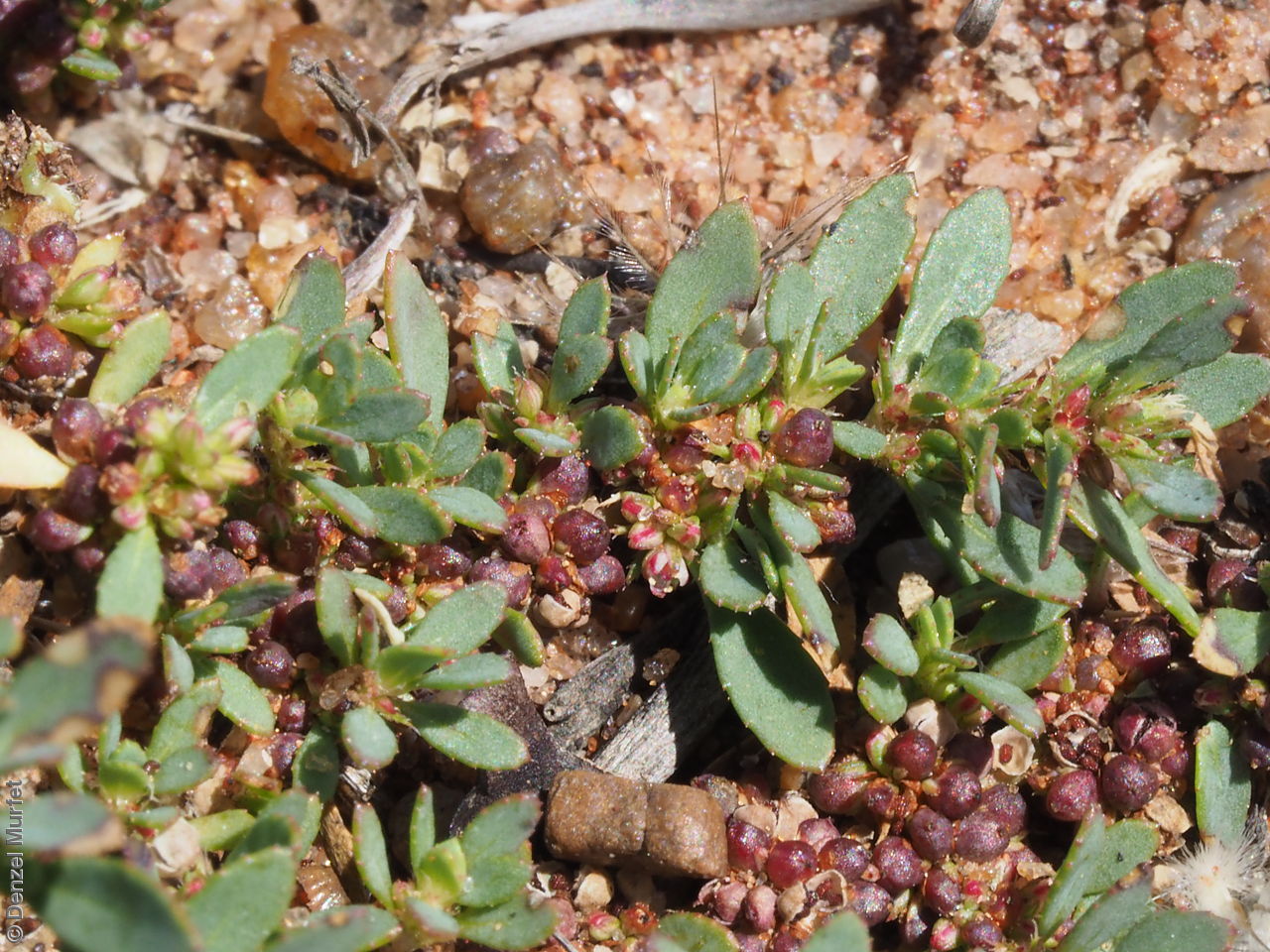
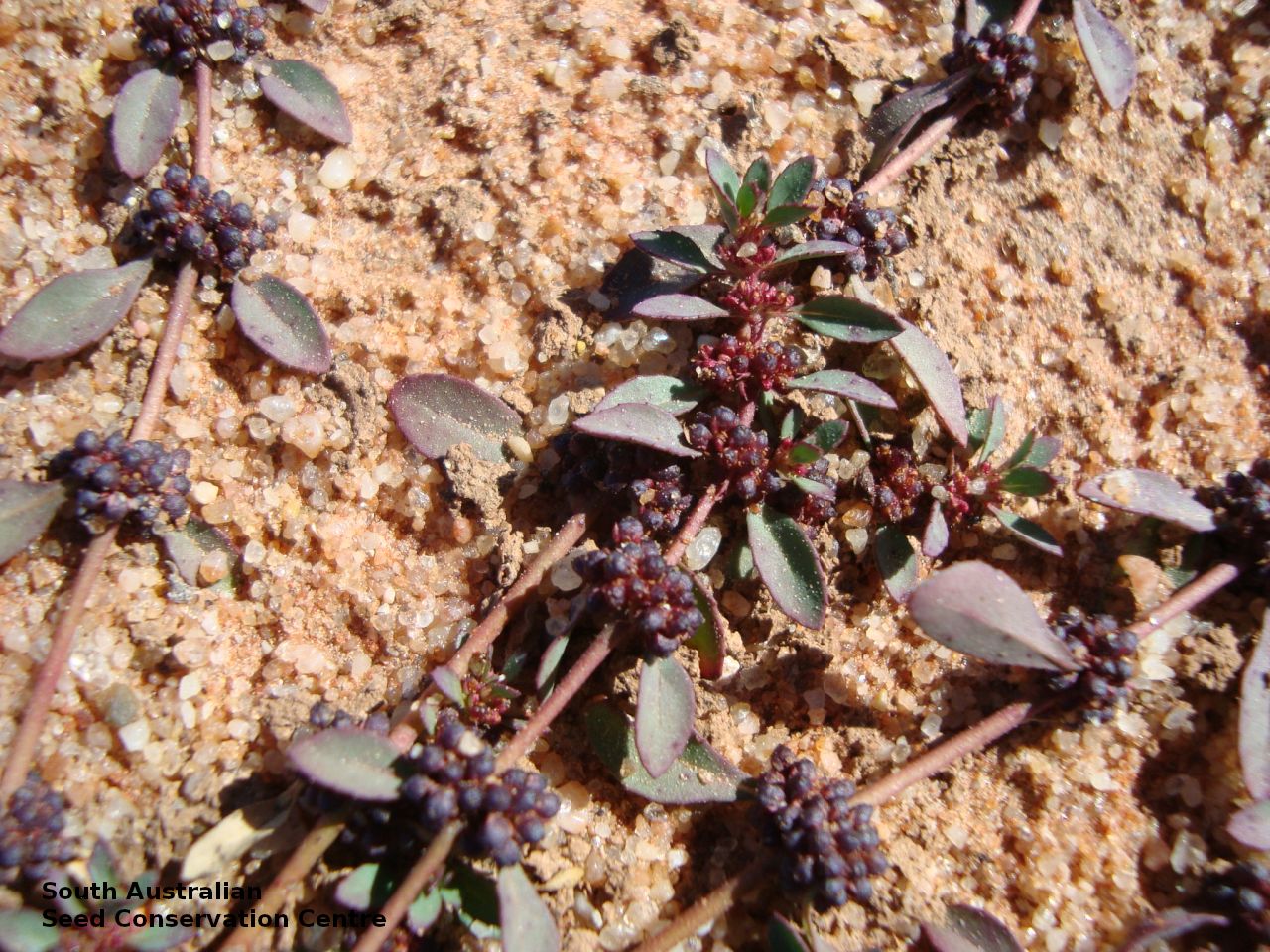
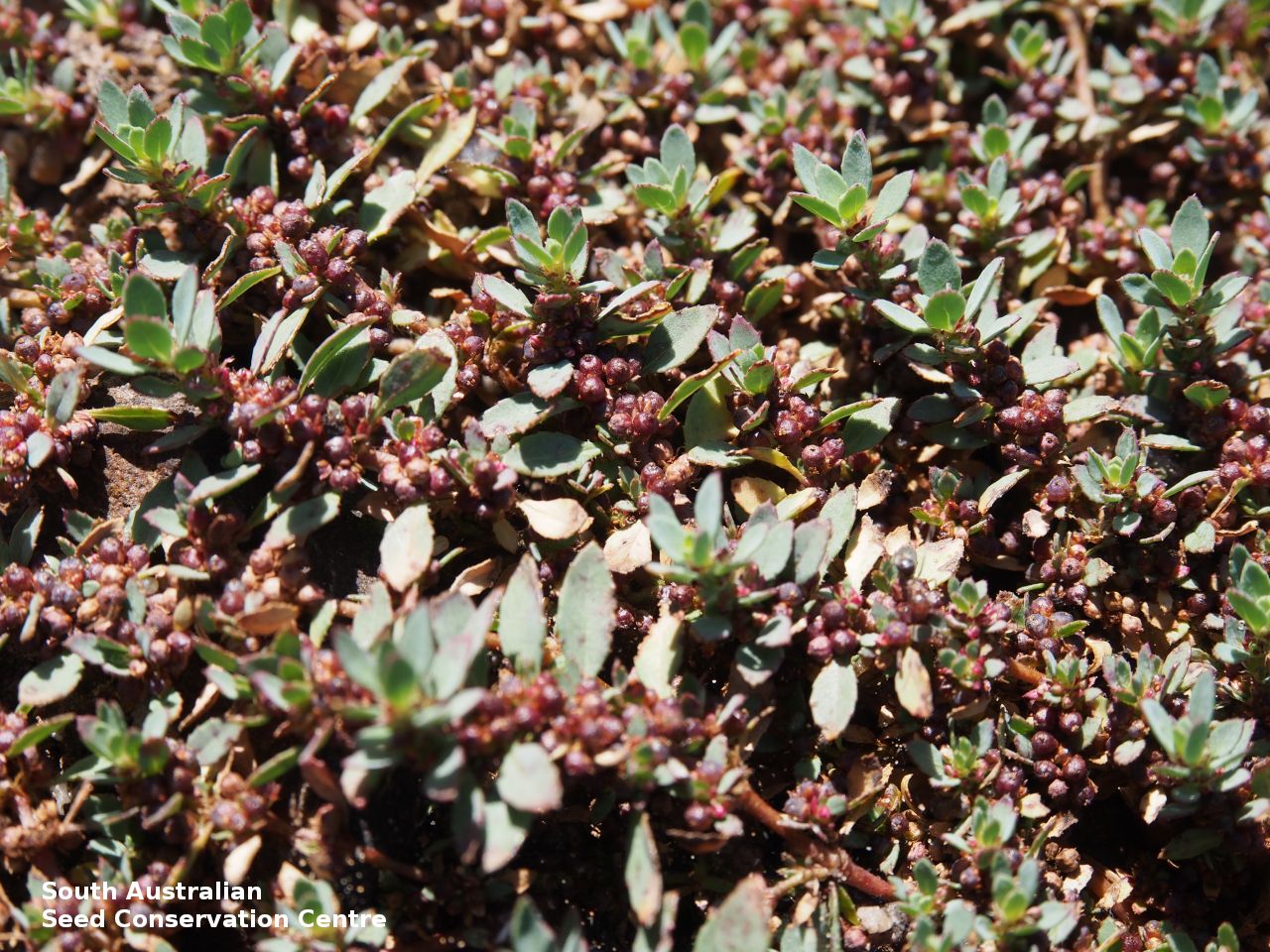
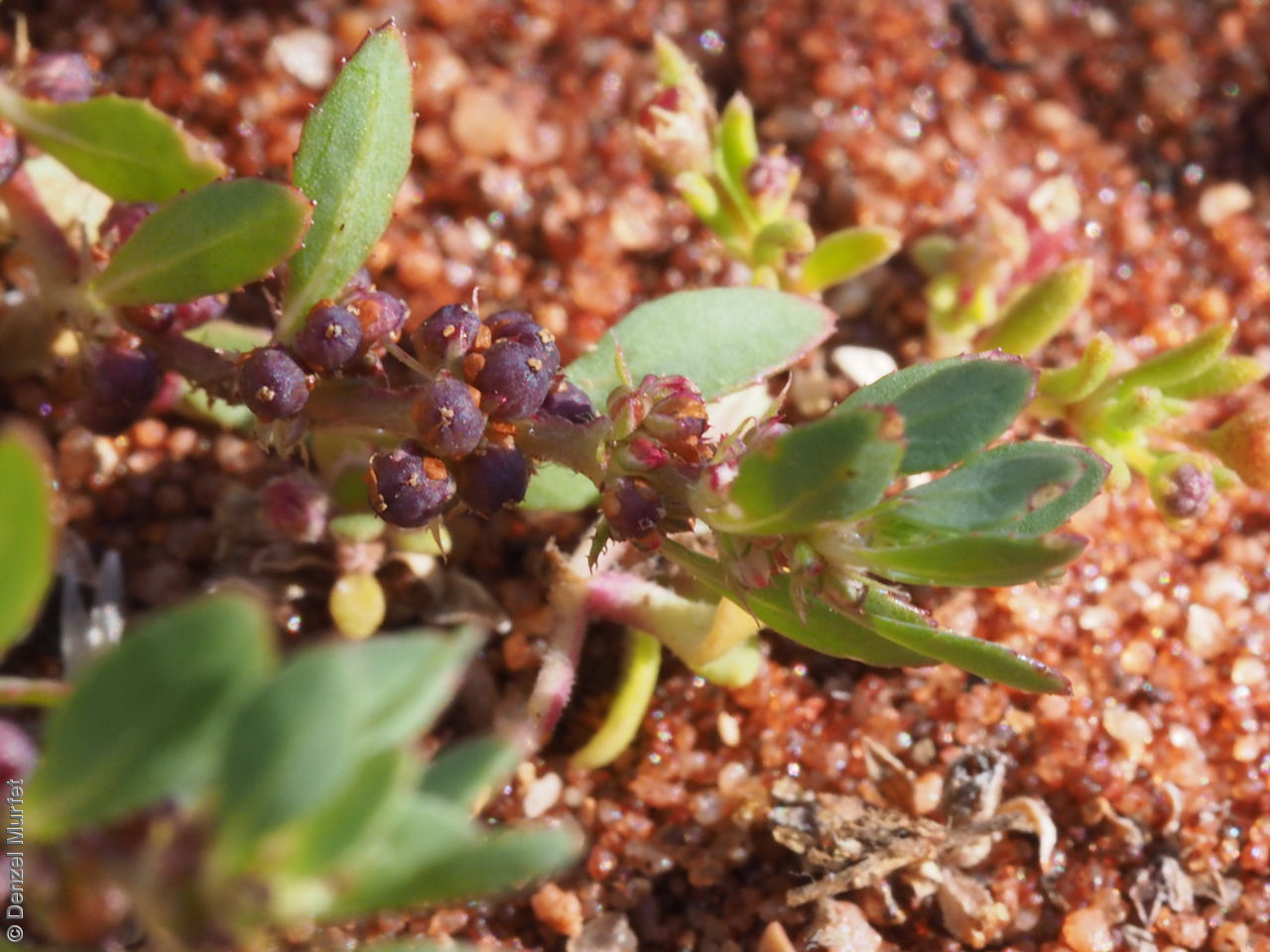
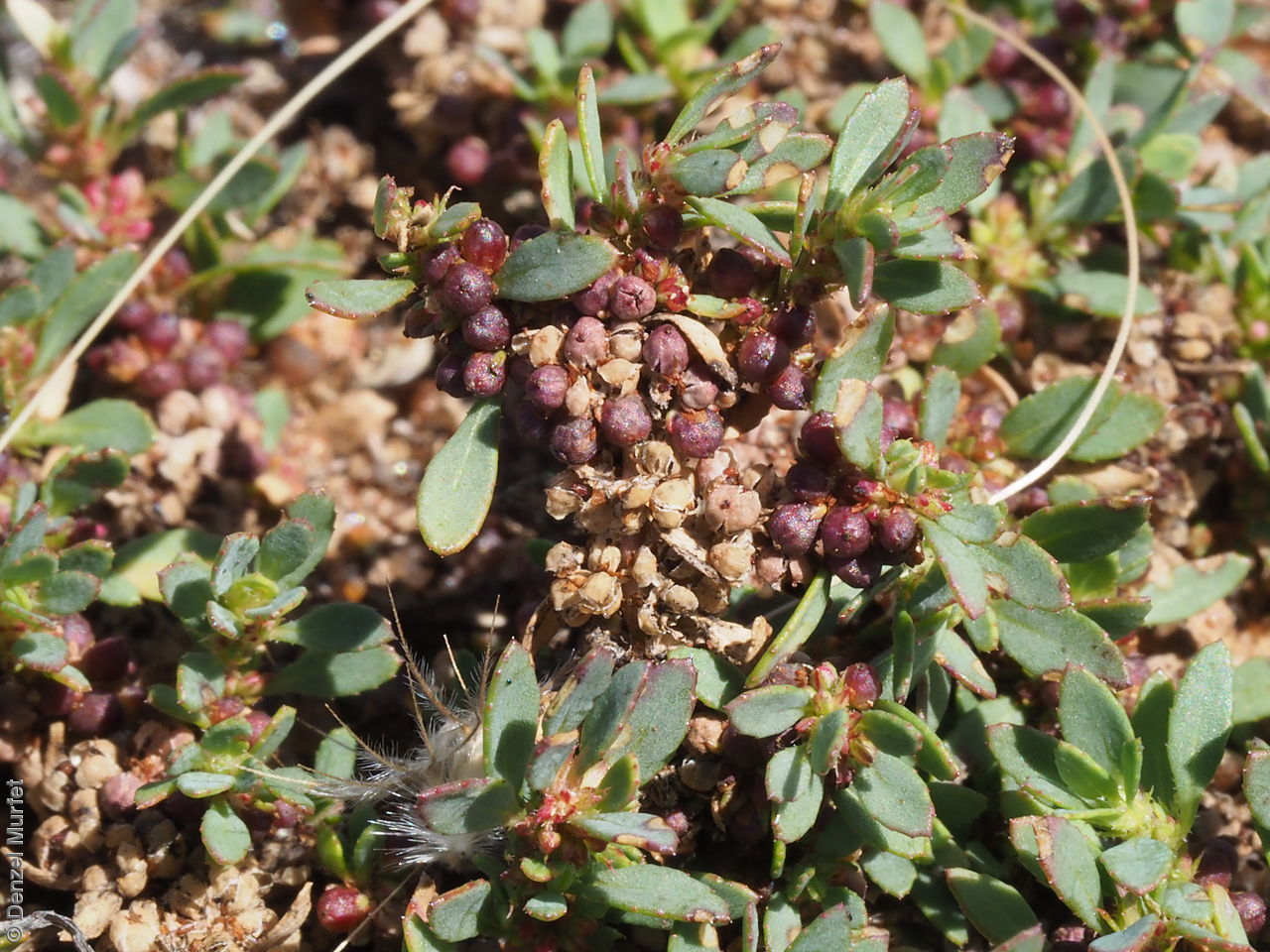
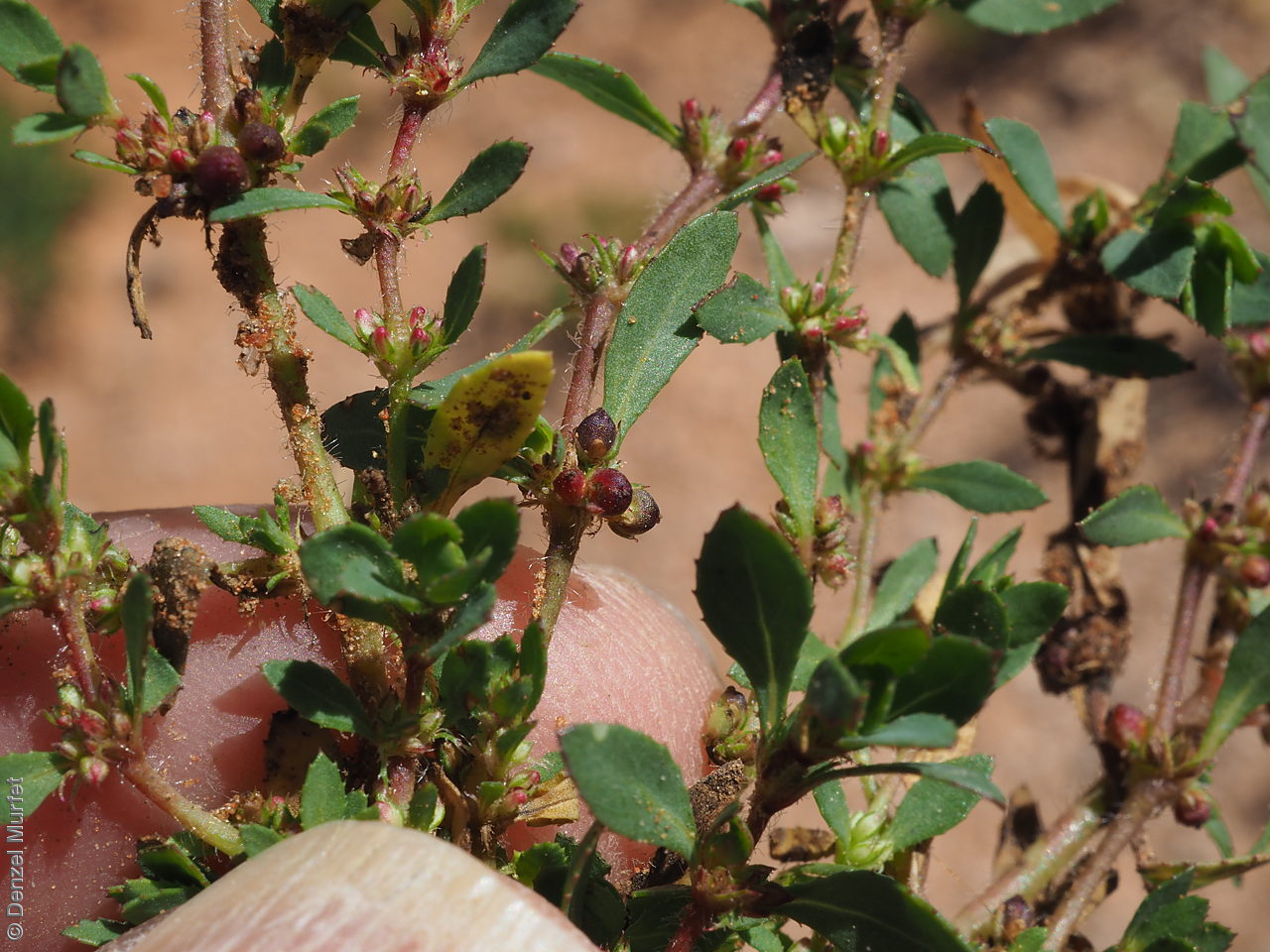
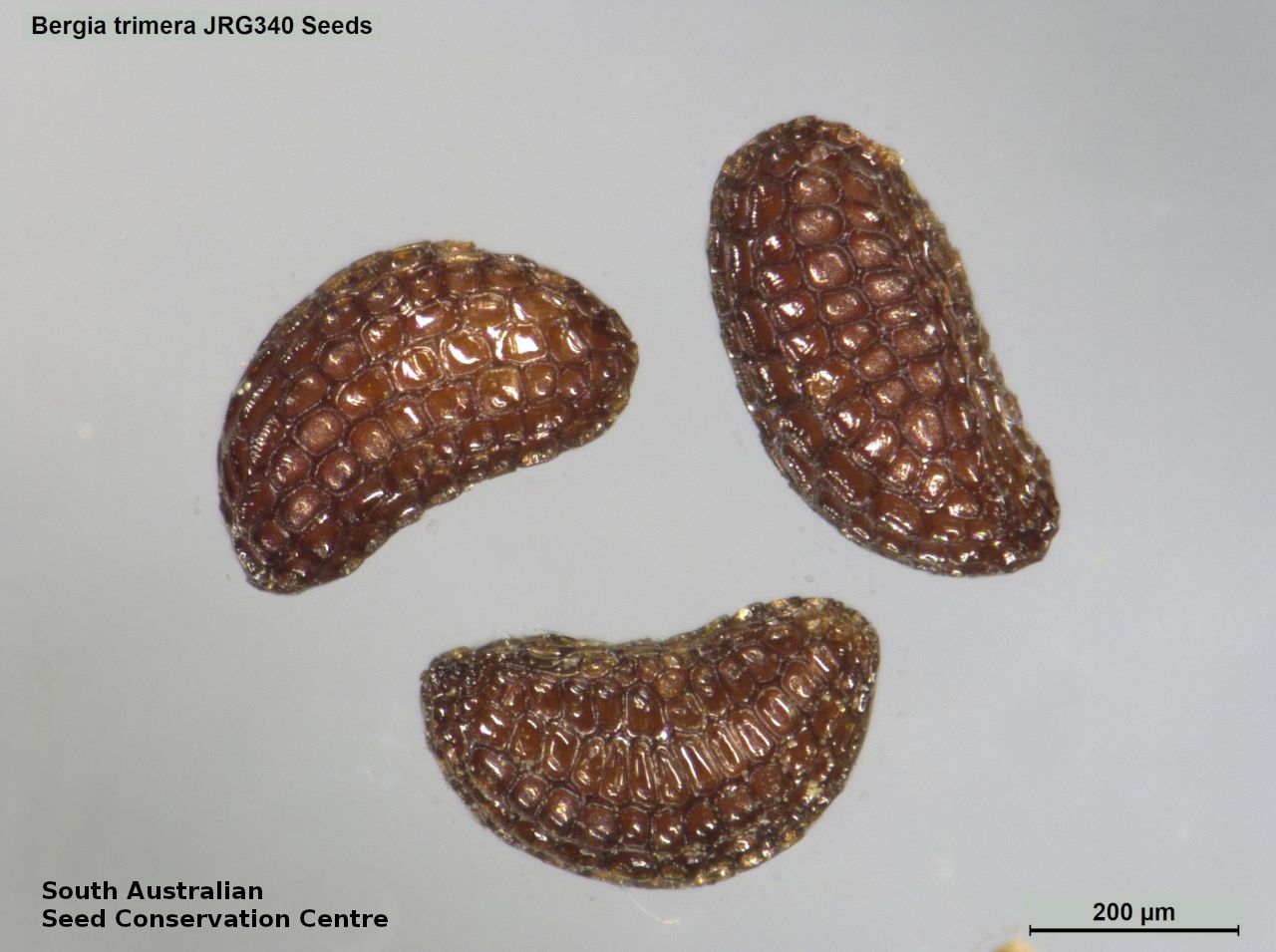
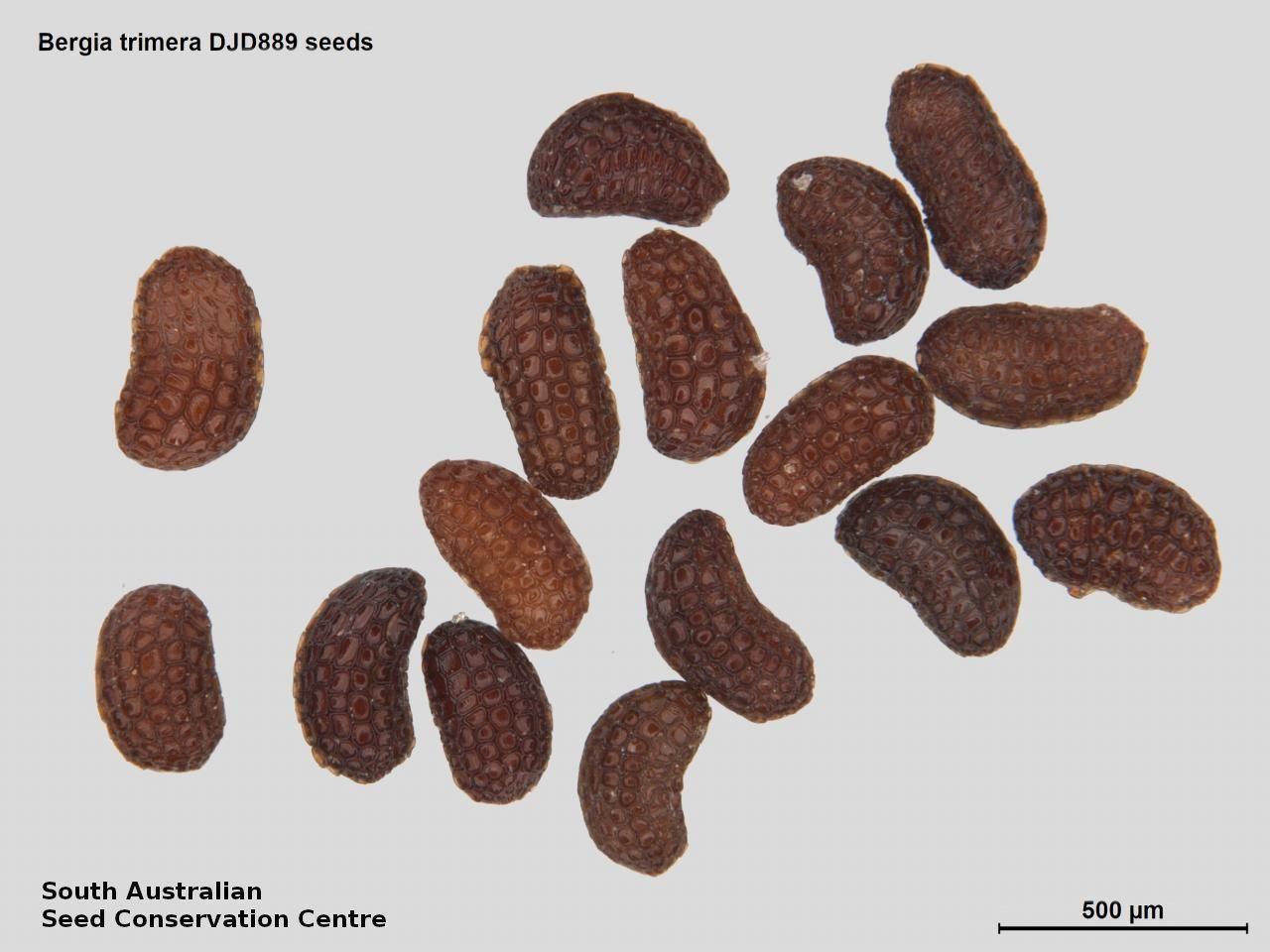
Prostrate or erect annual herb to 15 cm. Leaves narrow-obovate to narrow-elliptic, to 30 mm long and 8 mm wide, acute, glabrous, margin serrate. Flowers pink with 3-4 petals in dense clusters. Flowering throughout the year. Fruits are purple red globular capsule to 1.2 mm diameter. Seeds are red brown ovoid to reniform seed to 0.5mm long, with a net-like surface. Seed embryo type is linear.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between January and December. Collect whole plant with maturing capsules, those turning purple red and contain brown seeds. Place the plant in a tray and leave to dry for one to two weeks. Then rub the plant especially the capsules gently by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a fine sieve to separate the unwanted material. Be very careful as the seeds are very small. The seeds are shiny brown. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. From two collections, the seed viability were high, ranging from 95% and 100%.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 249,700 (8.99 g) 249,700 (8.99 g) | 50+ | 29-Sep-2007 | DJD889 Lake Eyre | 19-Sep-2008 | 100% | -18°C |
| BGA | 200,000 (8.55 g) | 20+ | 12-Aug-2010 | DJD1840 Lake Eyre | 1-Jan-2012 | 95% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.