



















Botanical art
Prior names
Acacia falcinella
Acacia petiolaris
Etymology
Acacia from the Greek 'akakia' and derived from 'ake' or 'akis' meaning a sharp point or thorn and 'akazo' meaning to sharpen. Dioscorides, the Greek physician and botanist used the word in the 1st century AD for the Egyptian thorn tree, Acacia arabica. Pycnantha from the Greek 'pycna' meaning thick, dense, compact and 'anthos' meaning flowers.
Distribution and status
Found in the wetter part of South Australia, south of the Flinders Ranges. Also found in New South Wales and Victoria. Introduced to Tasmania and Western Australia. Native. Common in South Australia. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: Flinders Ranges, Eastern, Eyre Peninsula, Northern Lofty, Murray, Yorke Peninsula, Southern Lofty, Kangaroo Island, South Eastern, Green Adelaide
NRM regions: Adelaide and Mount Lofty Ranges, Eyre Peninsula, Kangaroo Island, Northern and Yorke, South Australian Murray-Darling Basin, South East
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
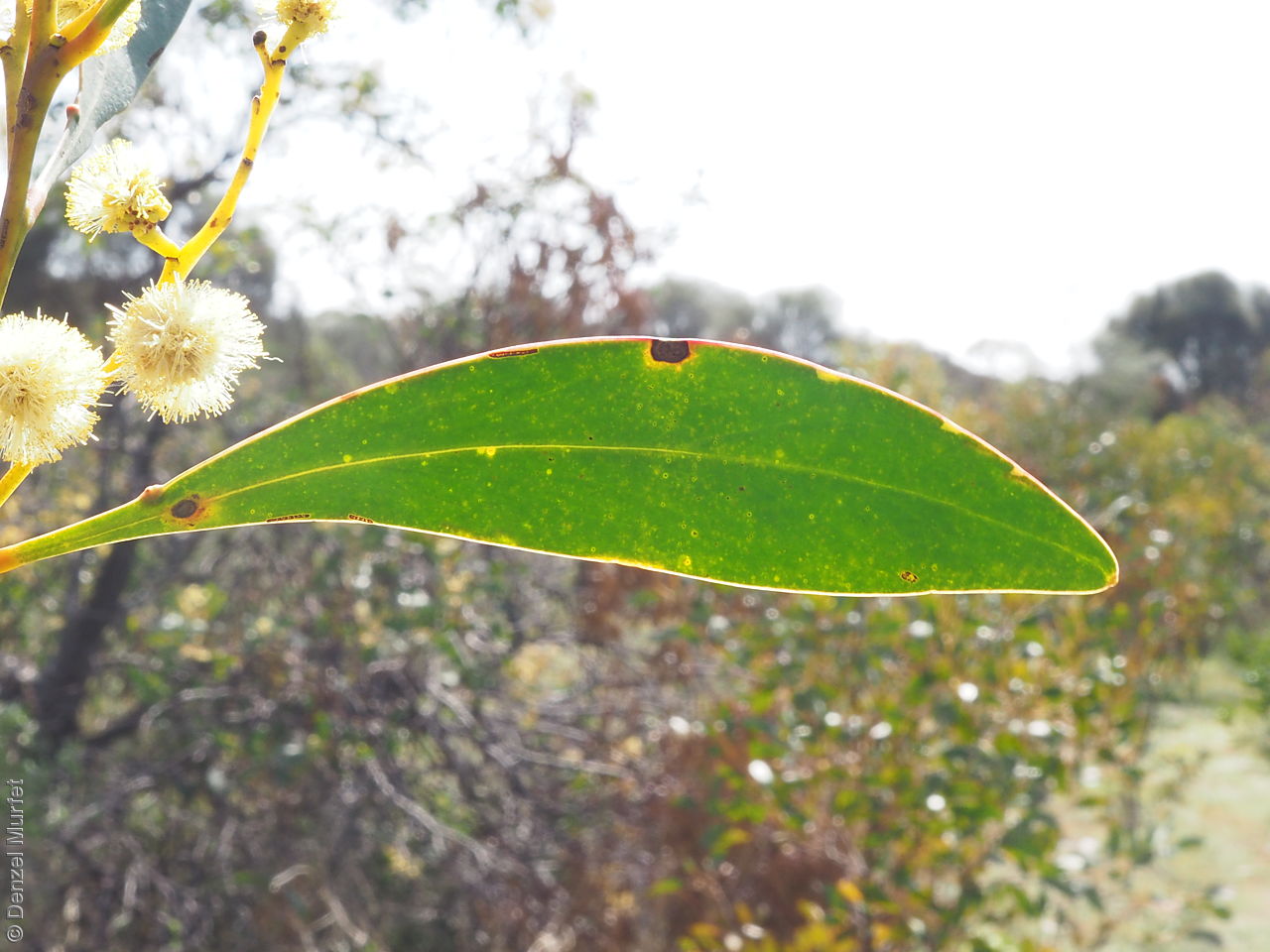
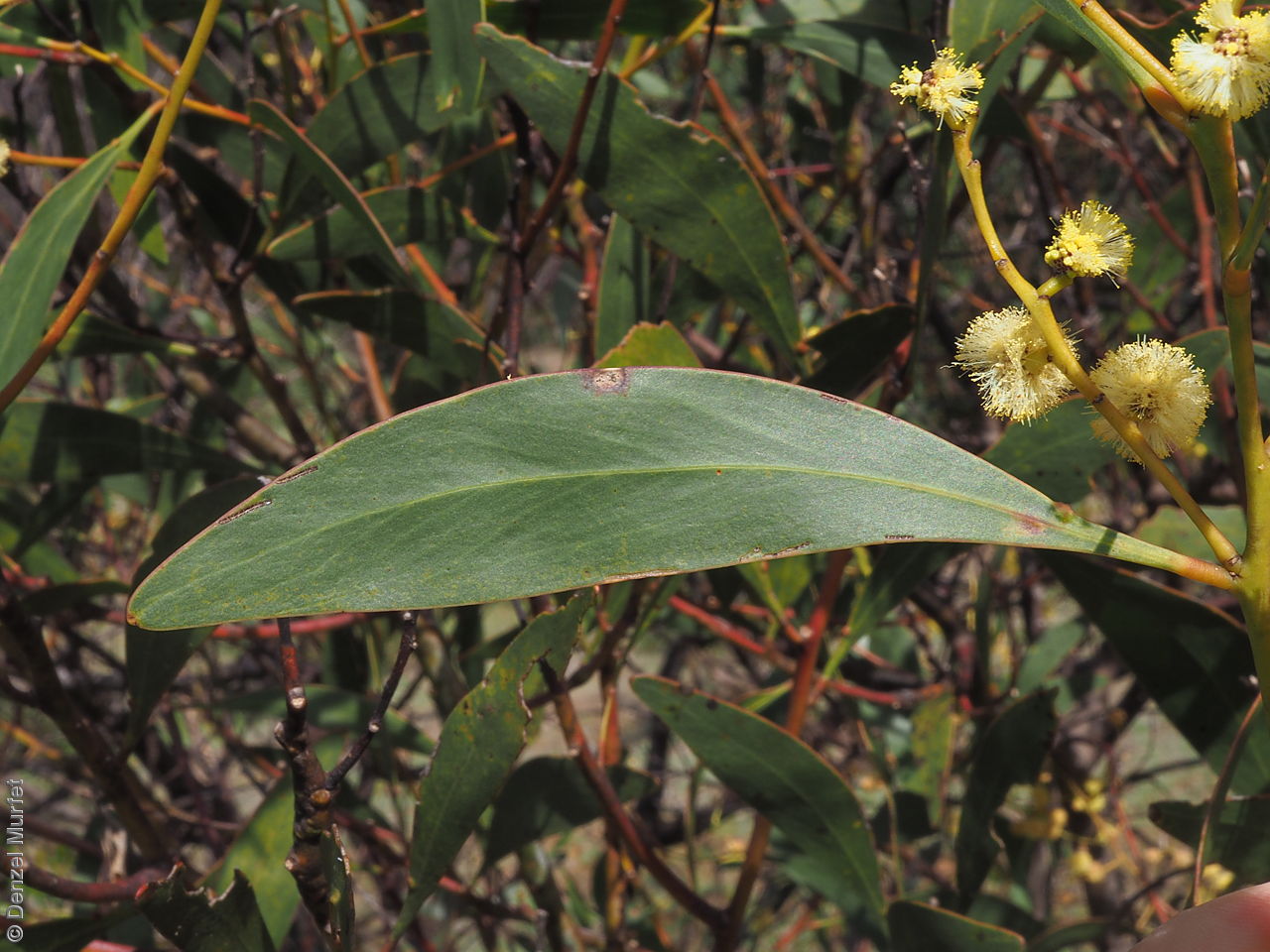
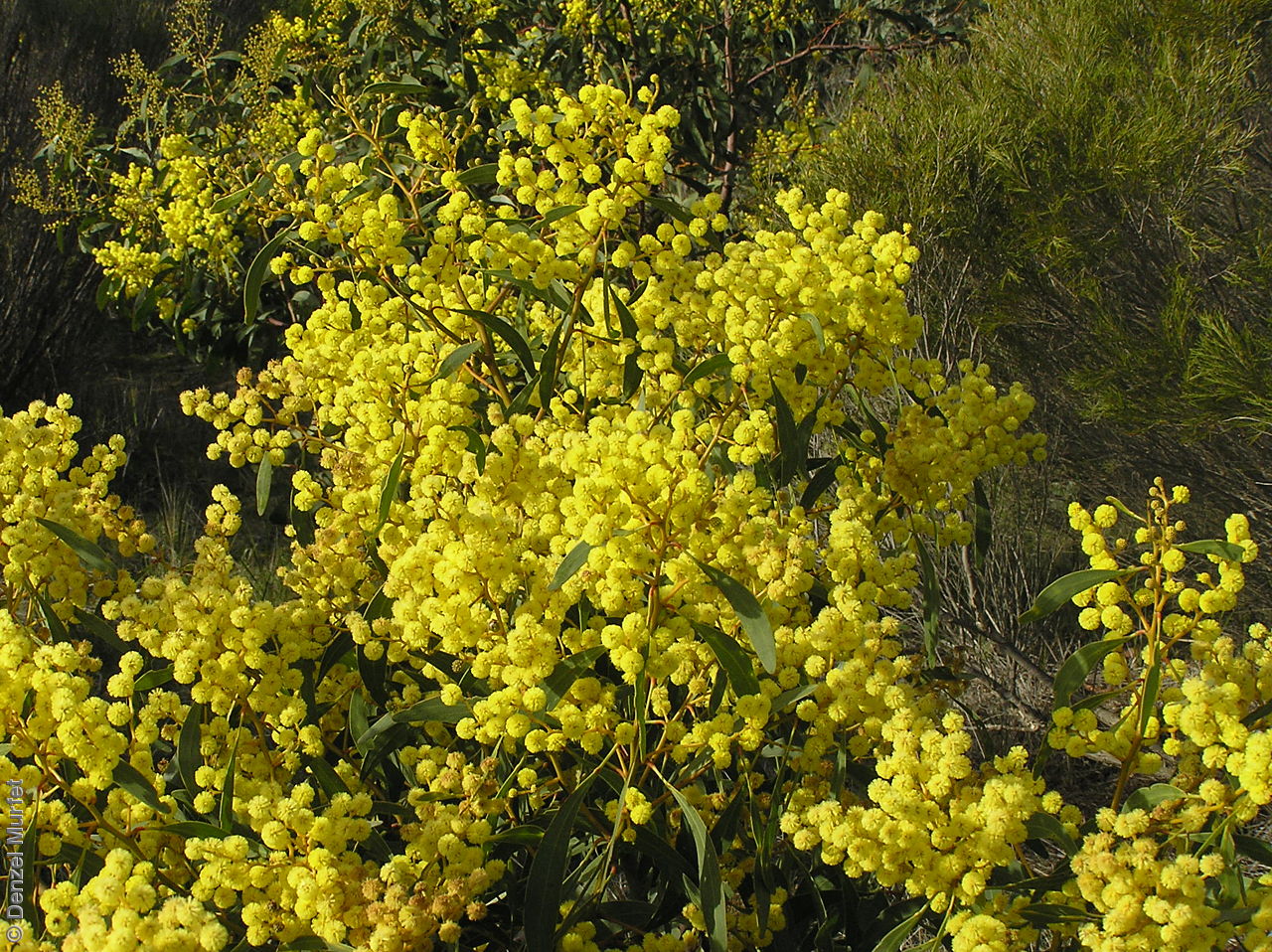
Plant description
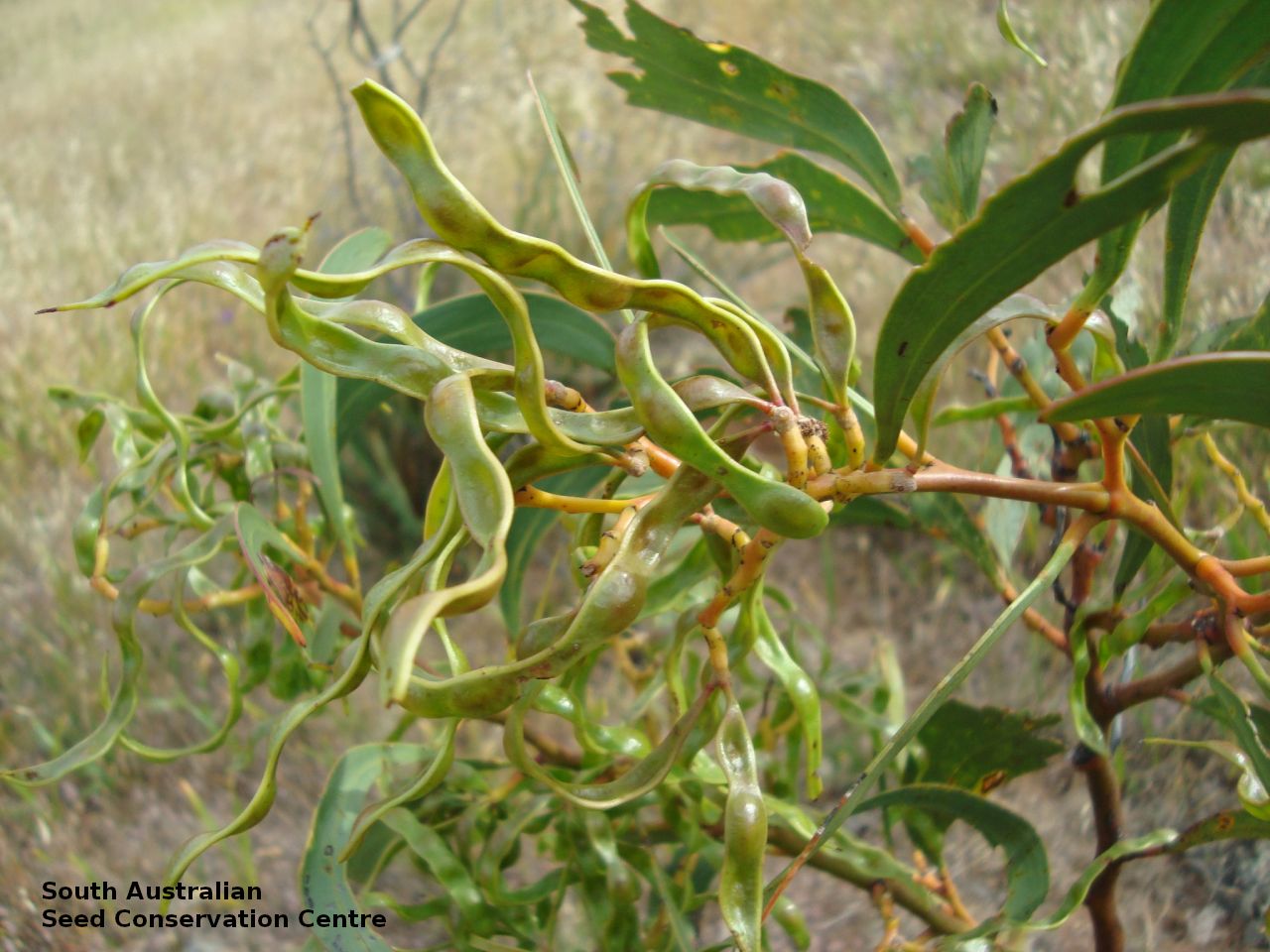
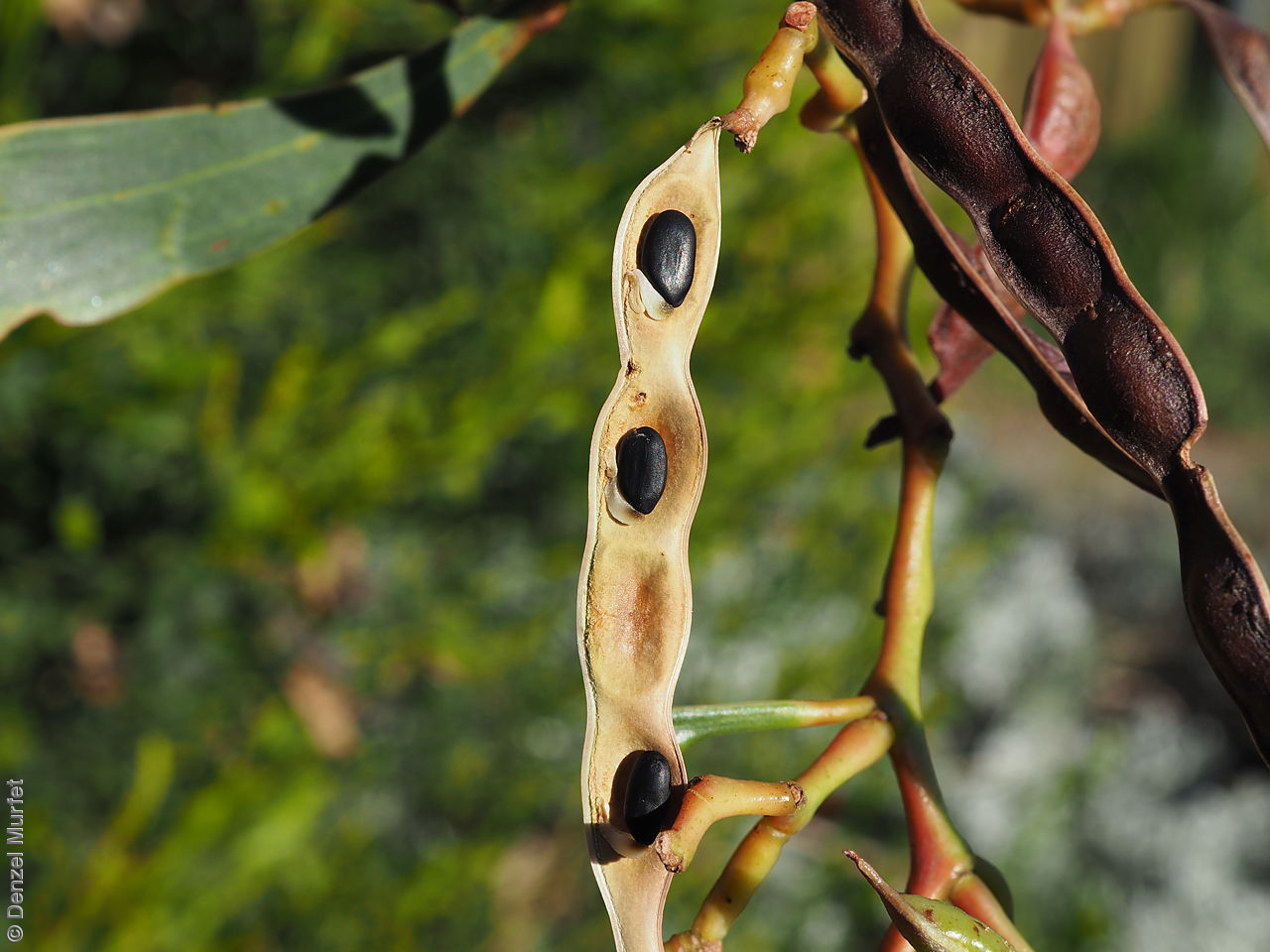
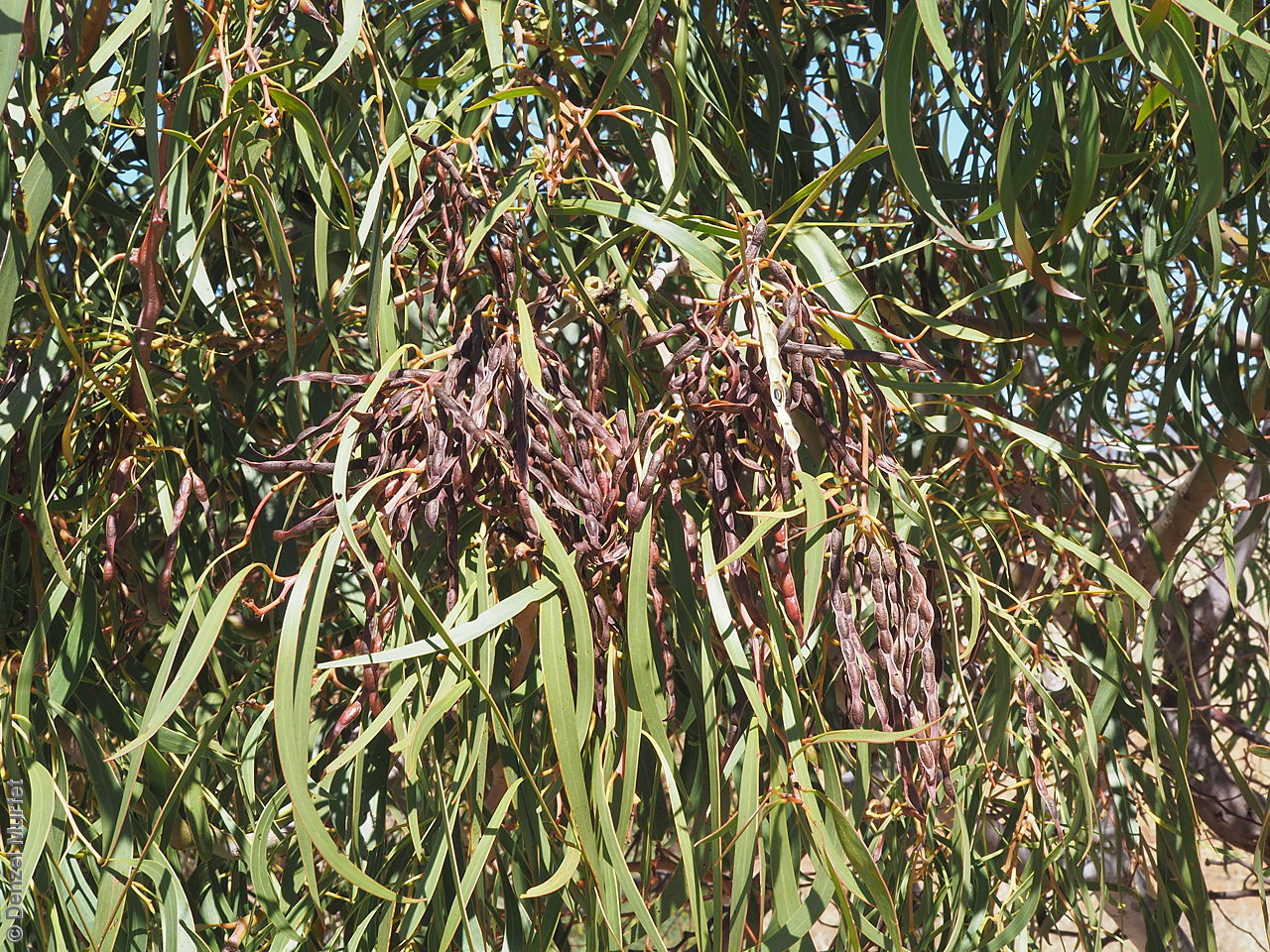
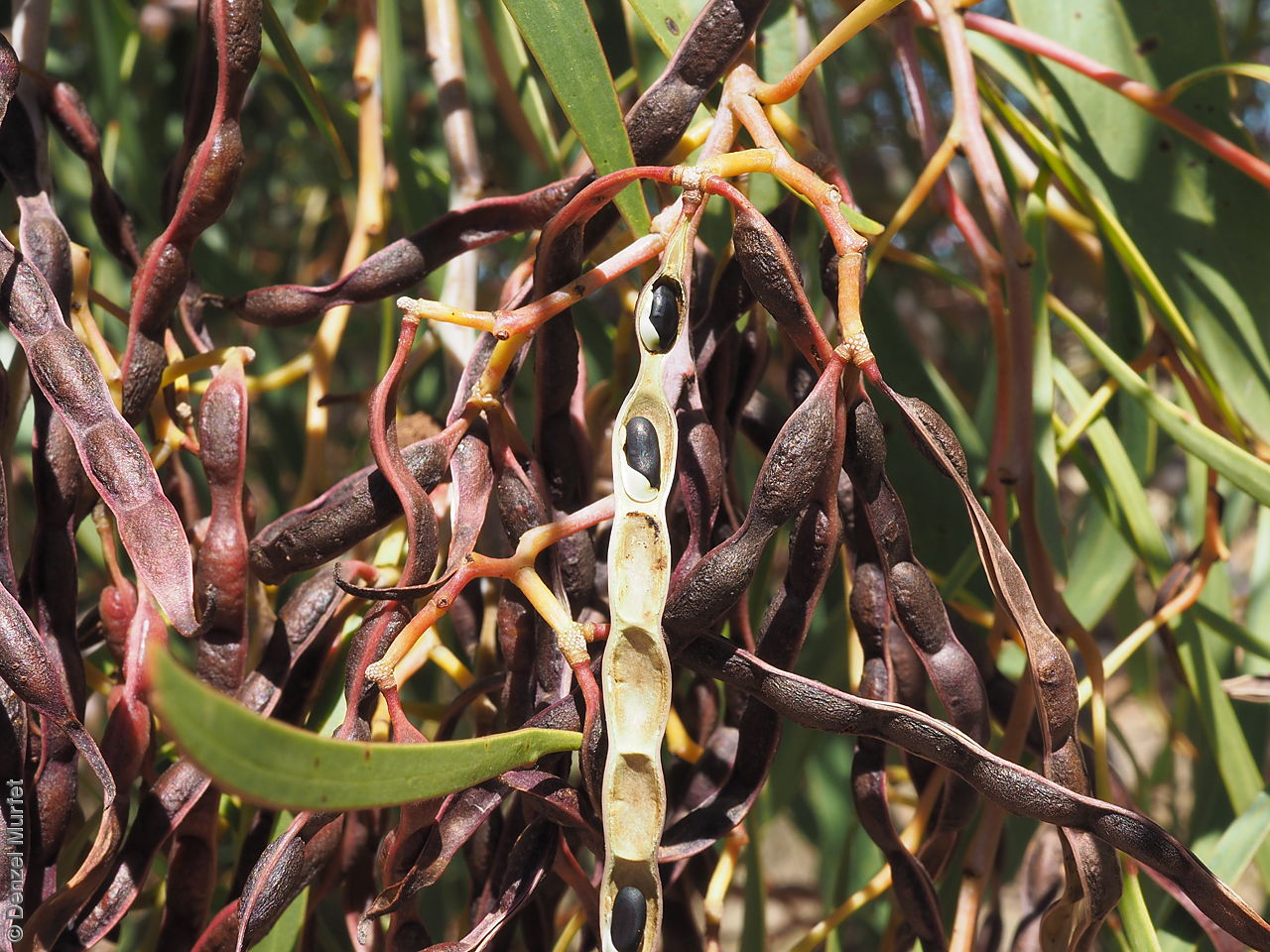
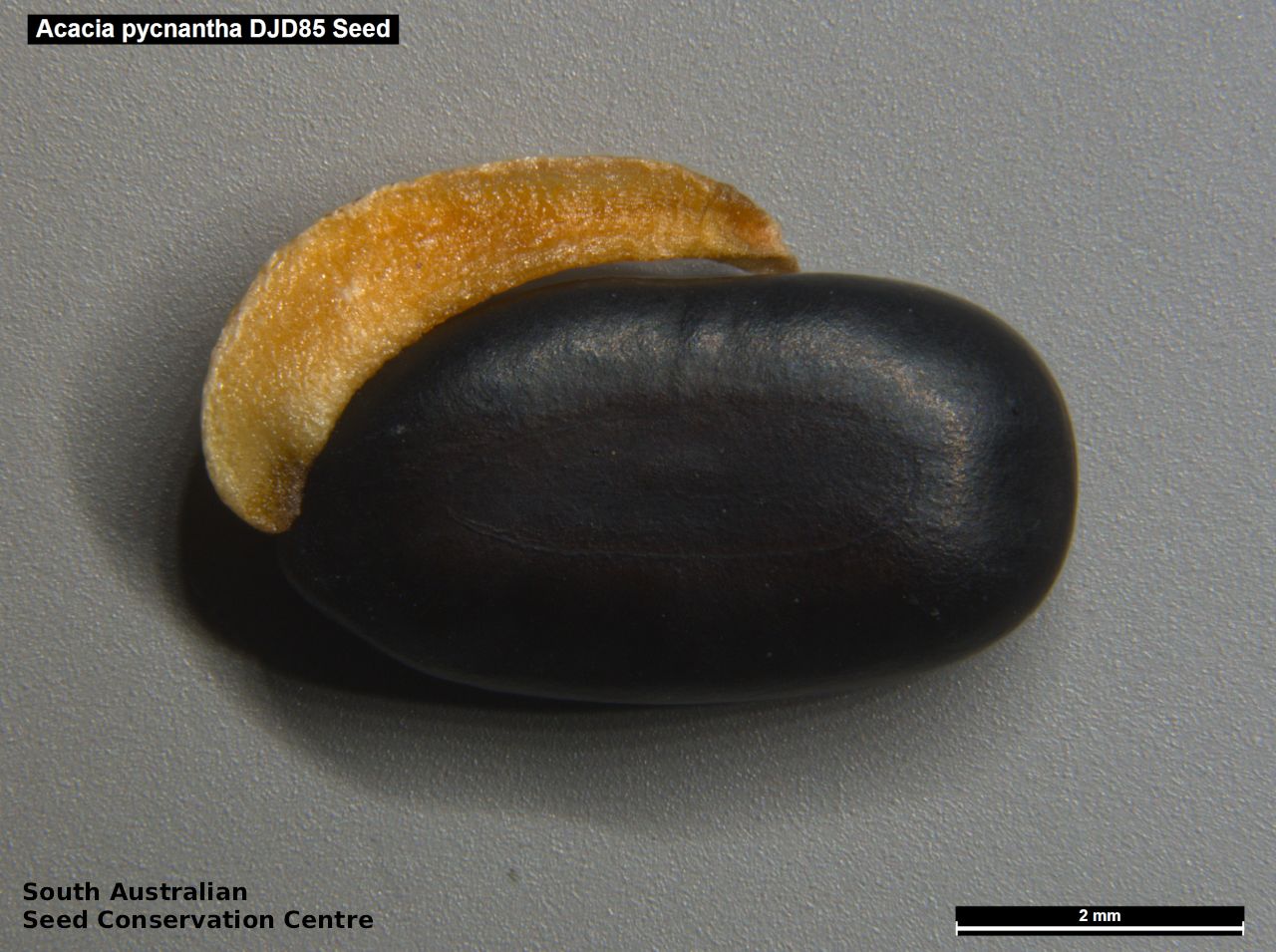
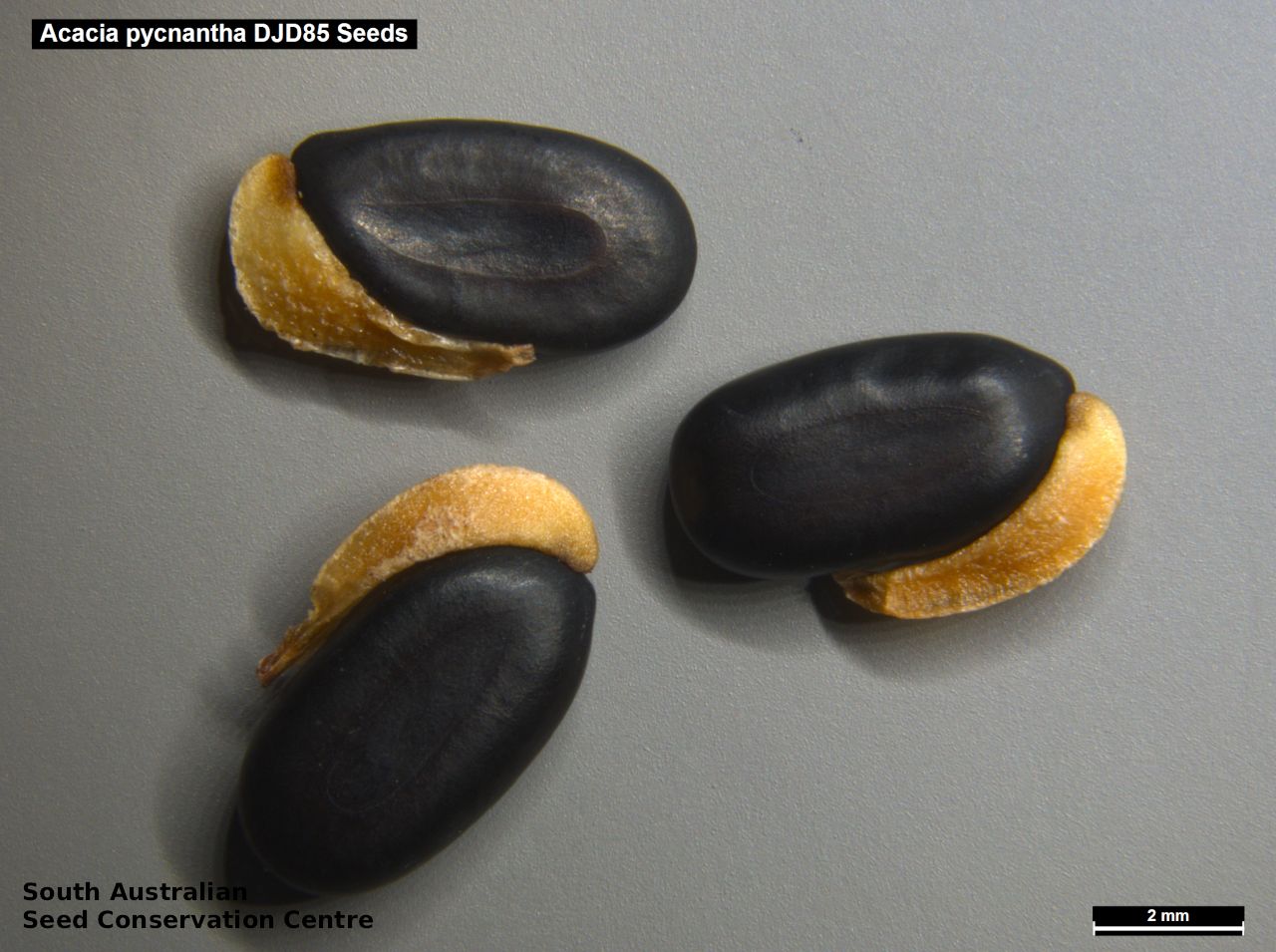
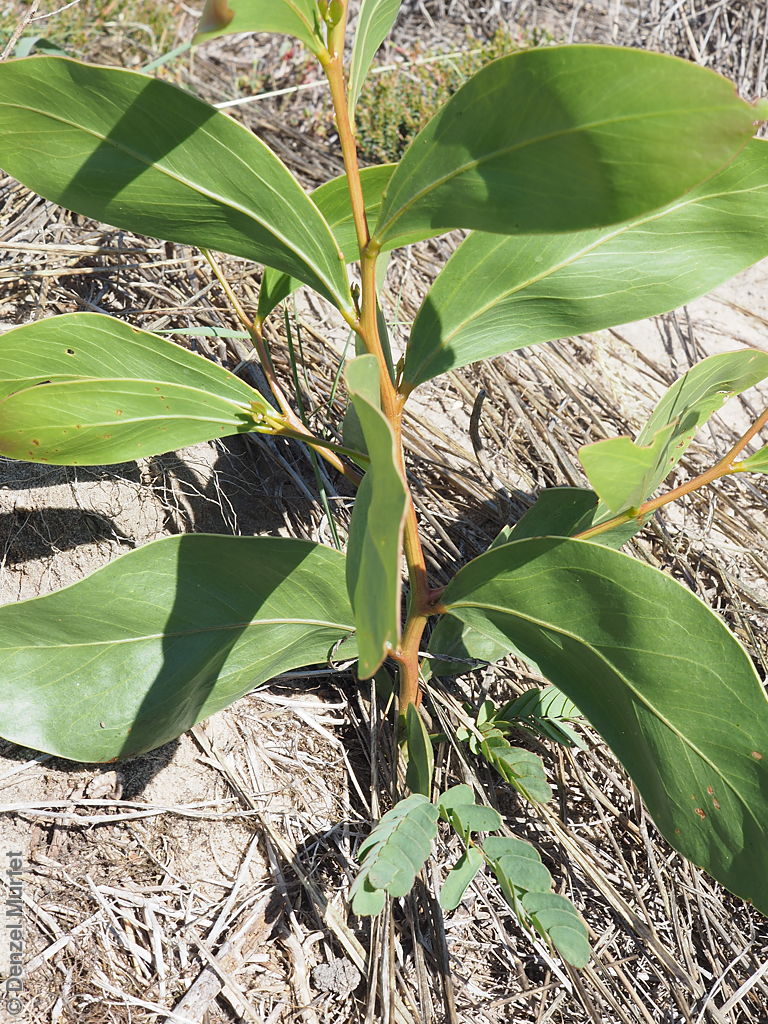
An erect small tree to 8 m high, usually with a rough dark brown to black bark, (or a smooth whitish-grey bark in the northern population). Leaves are large, lance-shaped and bright green. Flowers are contained within yellow-balls, appearing in winter and spring. Fruits are long, straight, brown pod to 12 cm long and 7 mm wide. Seeds are black semi-flat, ovoid to 6 mm long and 3 mm wide. Seed embryo type is investing.
Seed collection and propagation
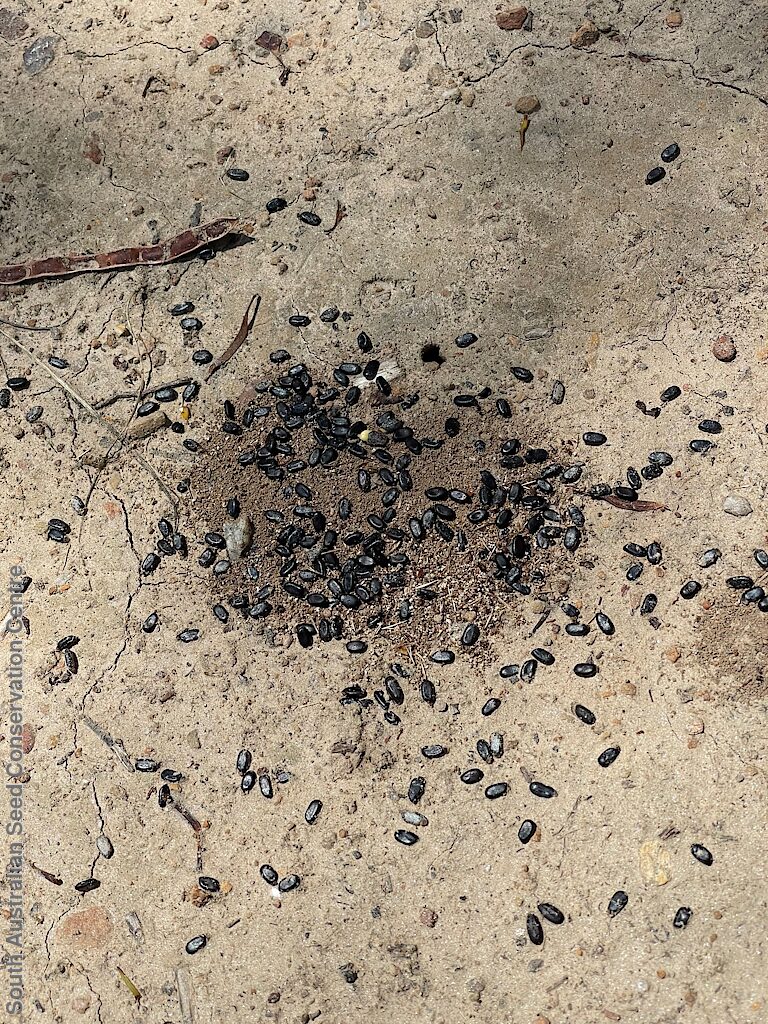
Collect seeds between November and January. Collect pods that are turning brown, with hard, dark seeds inside. For immediate propagation, the seeds can be collected prior to the seed coat hardening. Place the pods in a tray and leave to dry for 1-2 weeks or until the pods begin to split. Then rub the dried pods to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate any unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Seed viability is usually high. This species has physical dormancy that needs to be overcome for the seed to germinate (e.g. nicking or softening the seed coat).
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 6,800 (135 g) 6,800 (135 g) | 50 | 13-Dec-2004 | DJD85 Southern Lofty | 31-Mar-2006 | 100% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.