
















Botanical art
Etymology
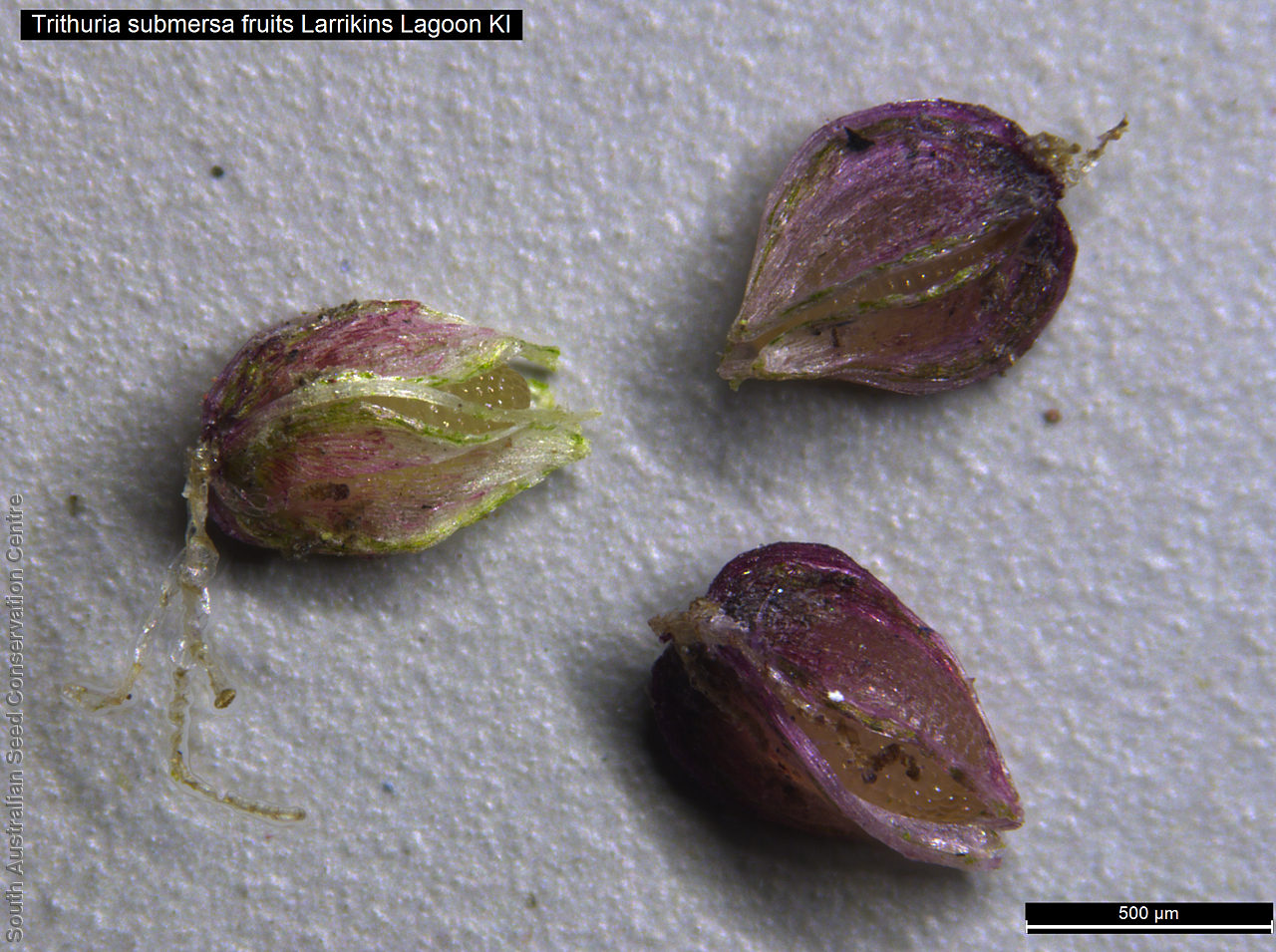
Trithuria from the Greek 'treis' meaning three and 'thyris' meaning window; referring to the dehiscence of the fruit of this species. Submersa meaning underwater; referring to the species aquatic habitat.
Distribution and status
Winter annual growing in mud of stream margins, seasonal swamps and pools on Kangaroo Island and the Southeast in South Australia with isolated collections from Eyre Peninsula and Mount Lofty Ranges. Also found in Western Australia, New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania. Native. Uncommon in South Australia. Common in the other states.
Herbarium regions: Eyre Peninsula, Southern Lofty, Kangaroo Island, South Eastern
NRM regions: Adelaide and Mount Lofty Ranges, Eyre Peninsula, Kangaroo Island, South East
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
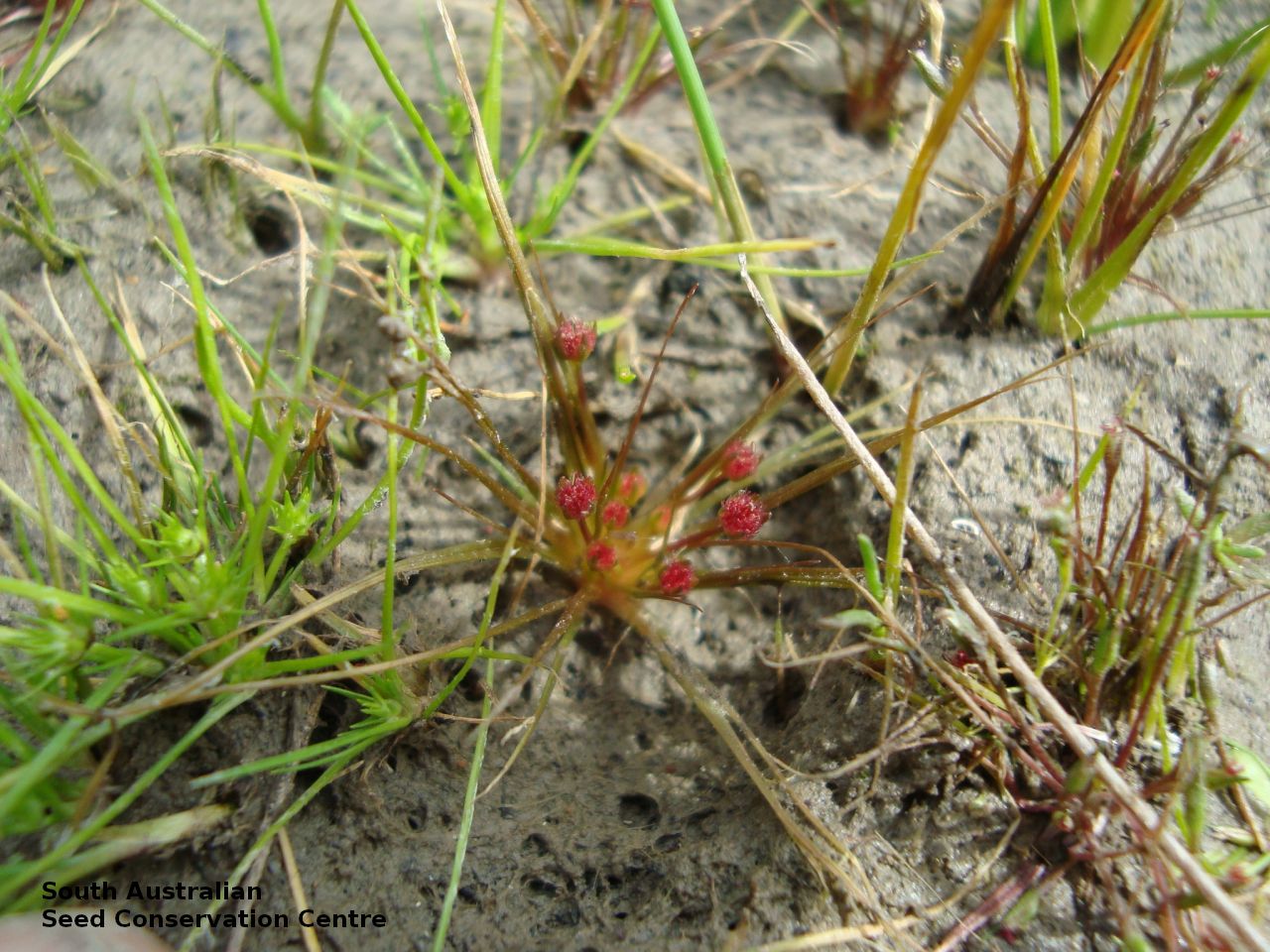
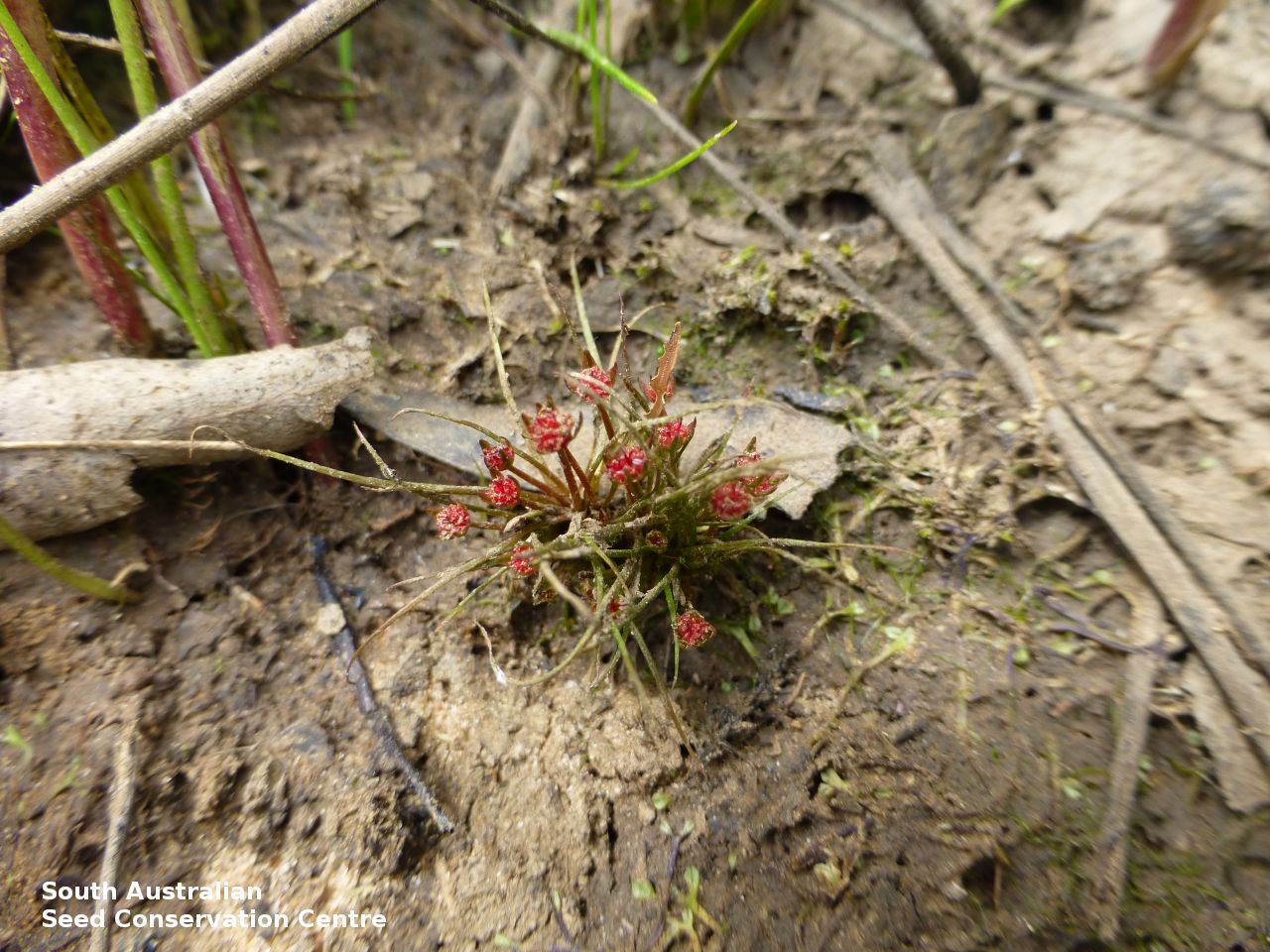
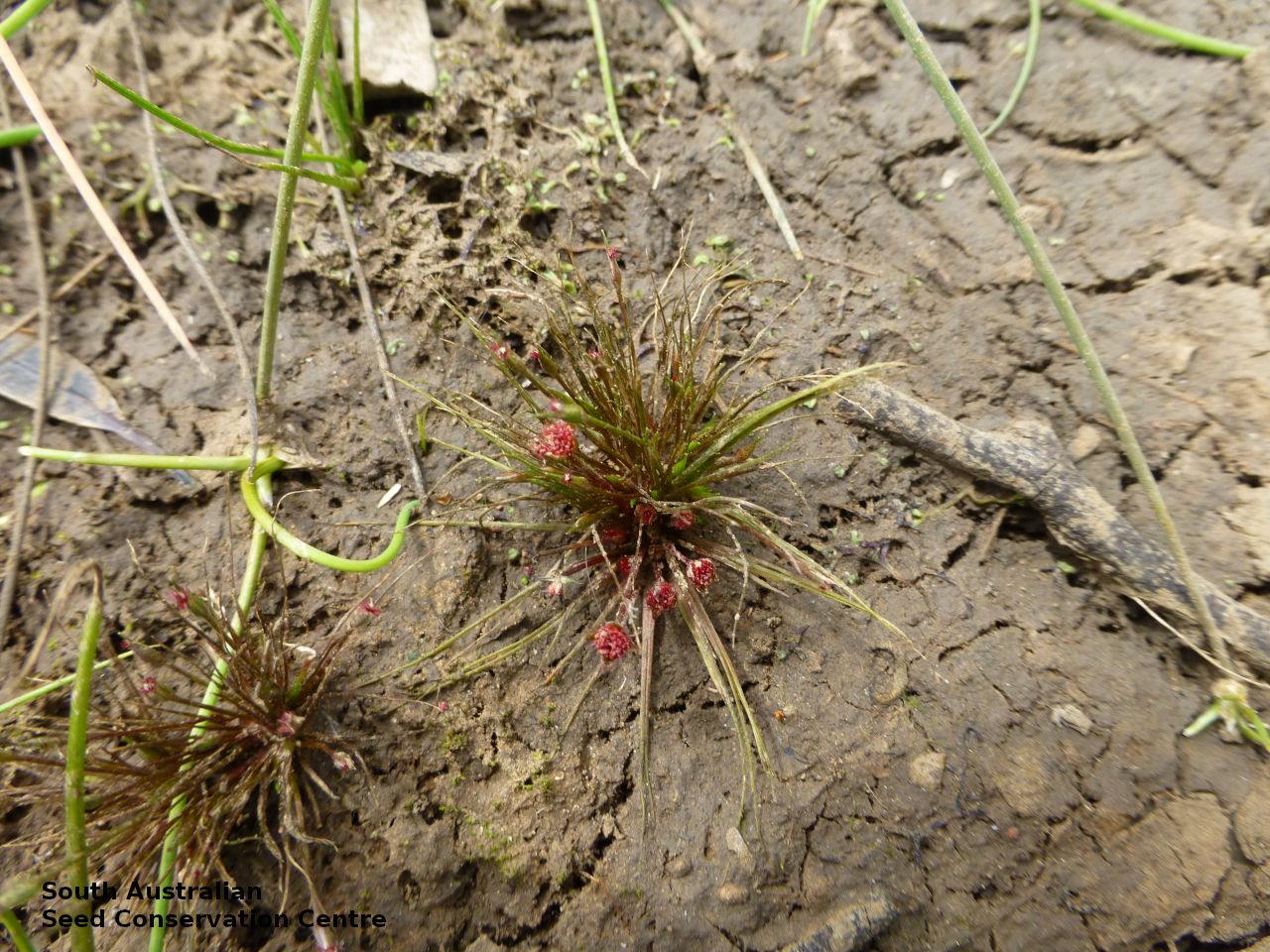
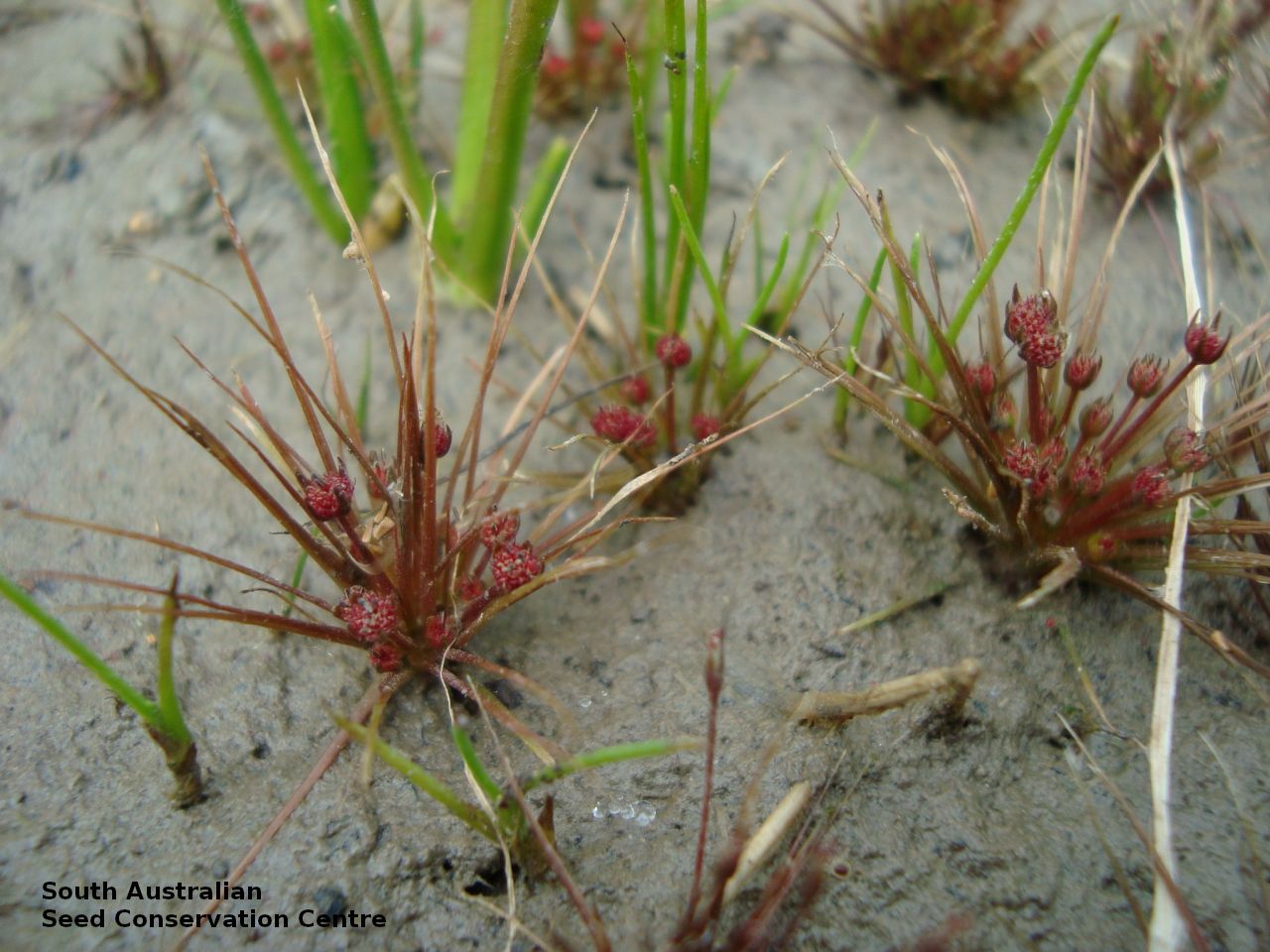
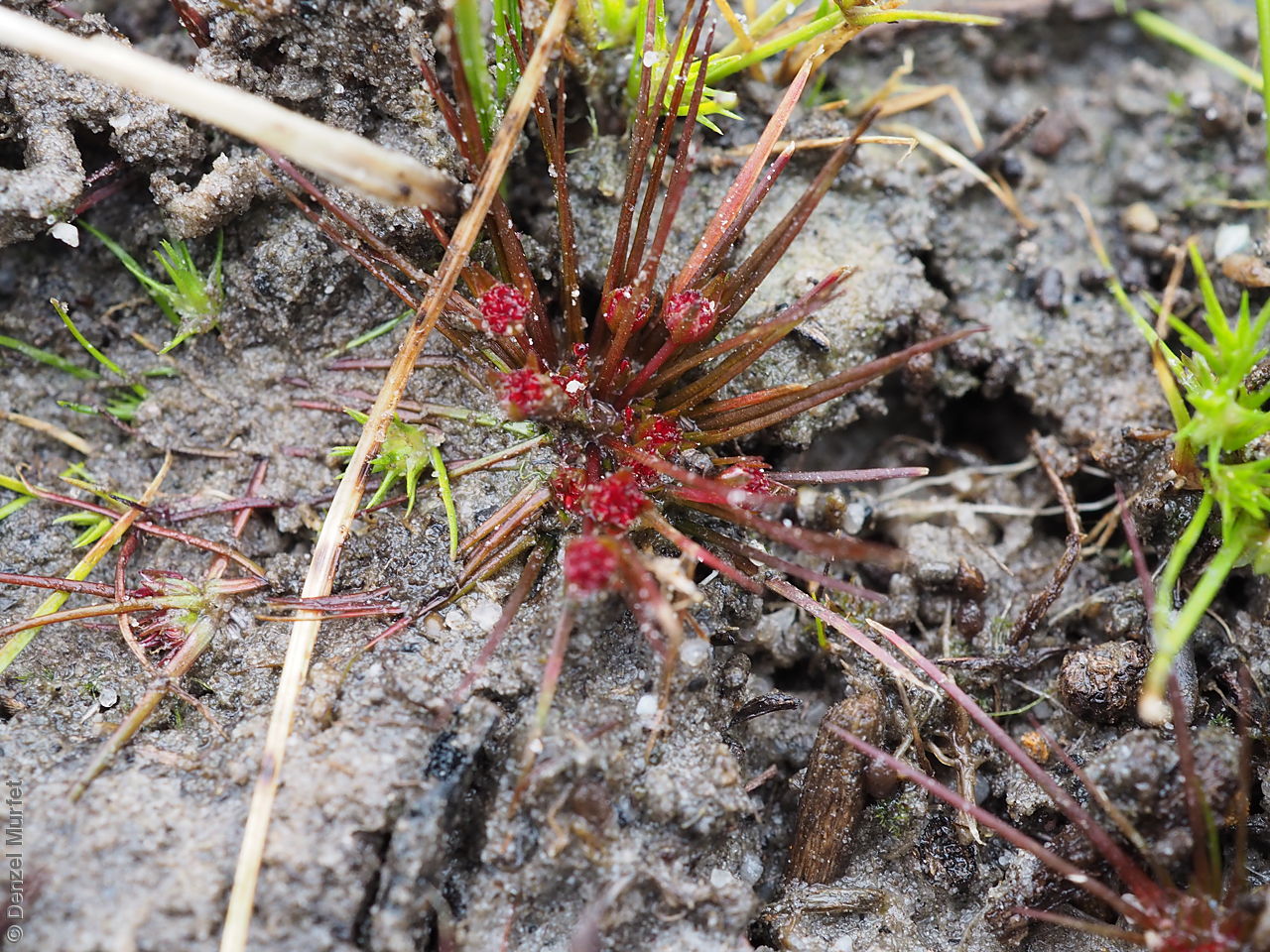
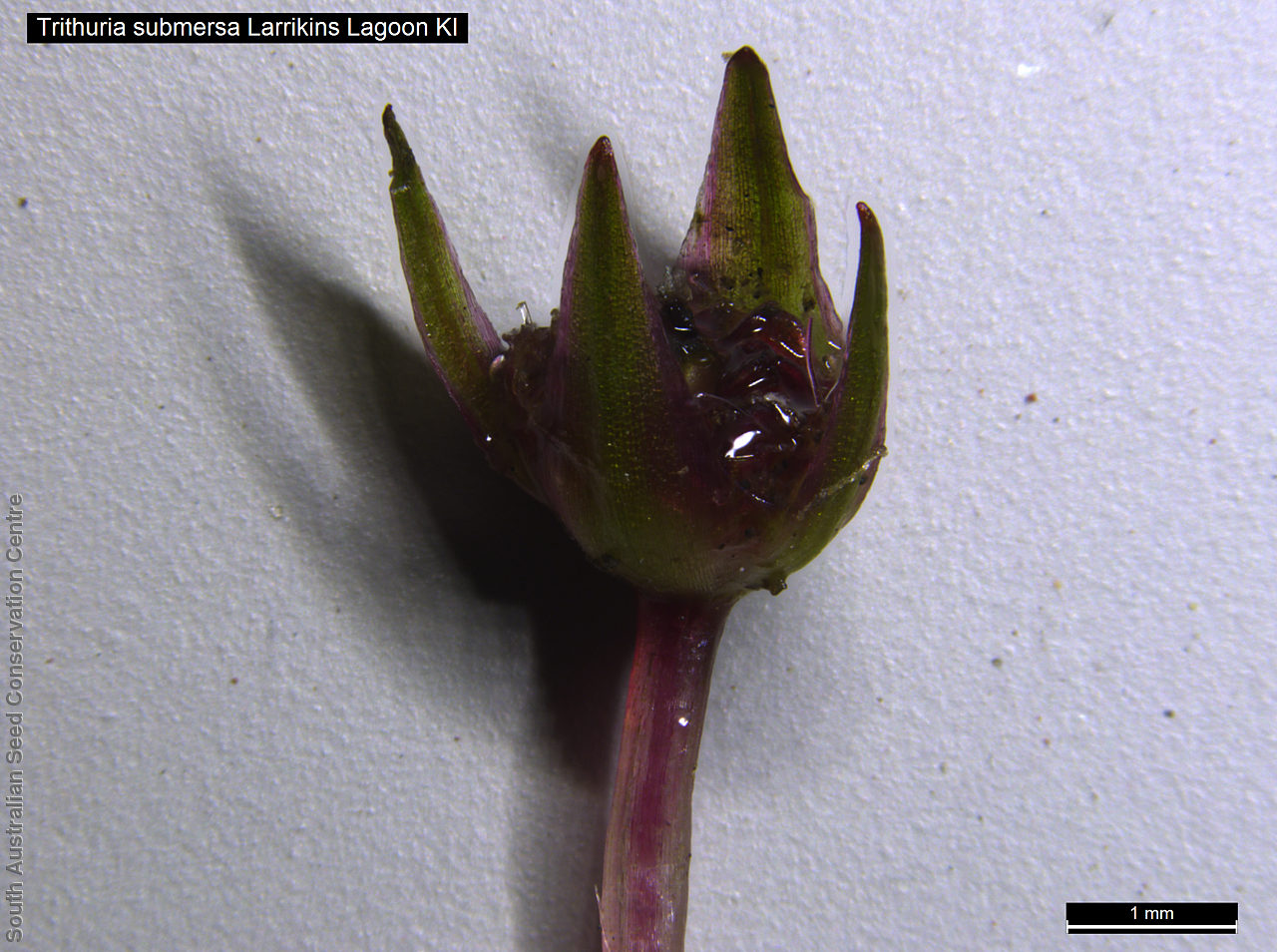
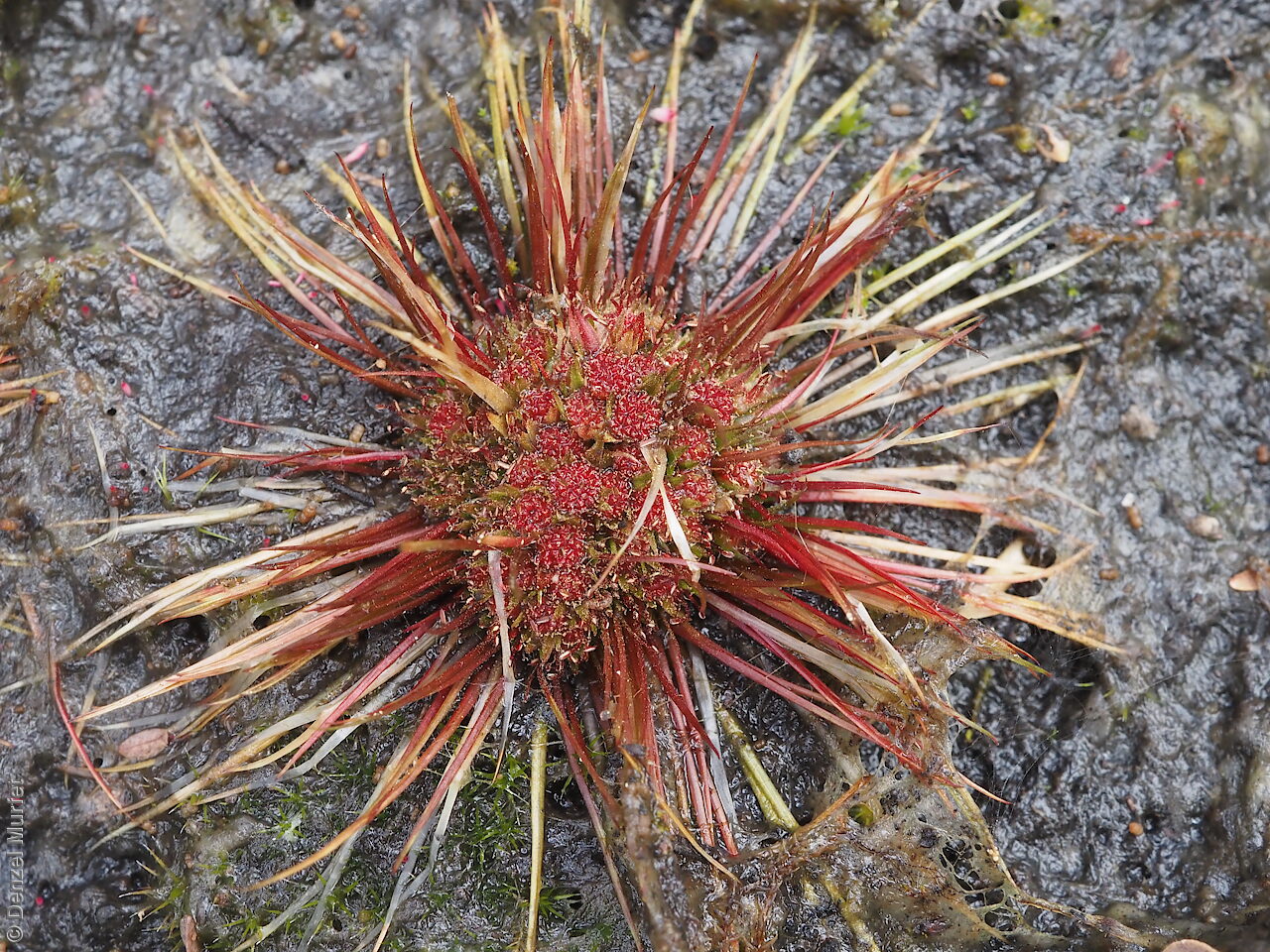
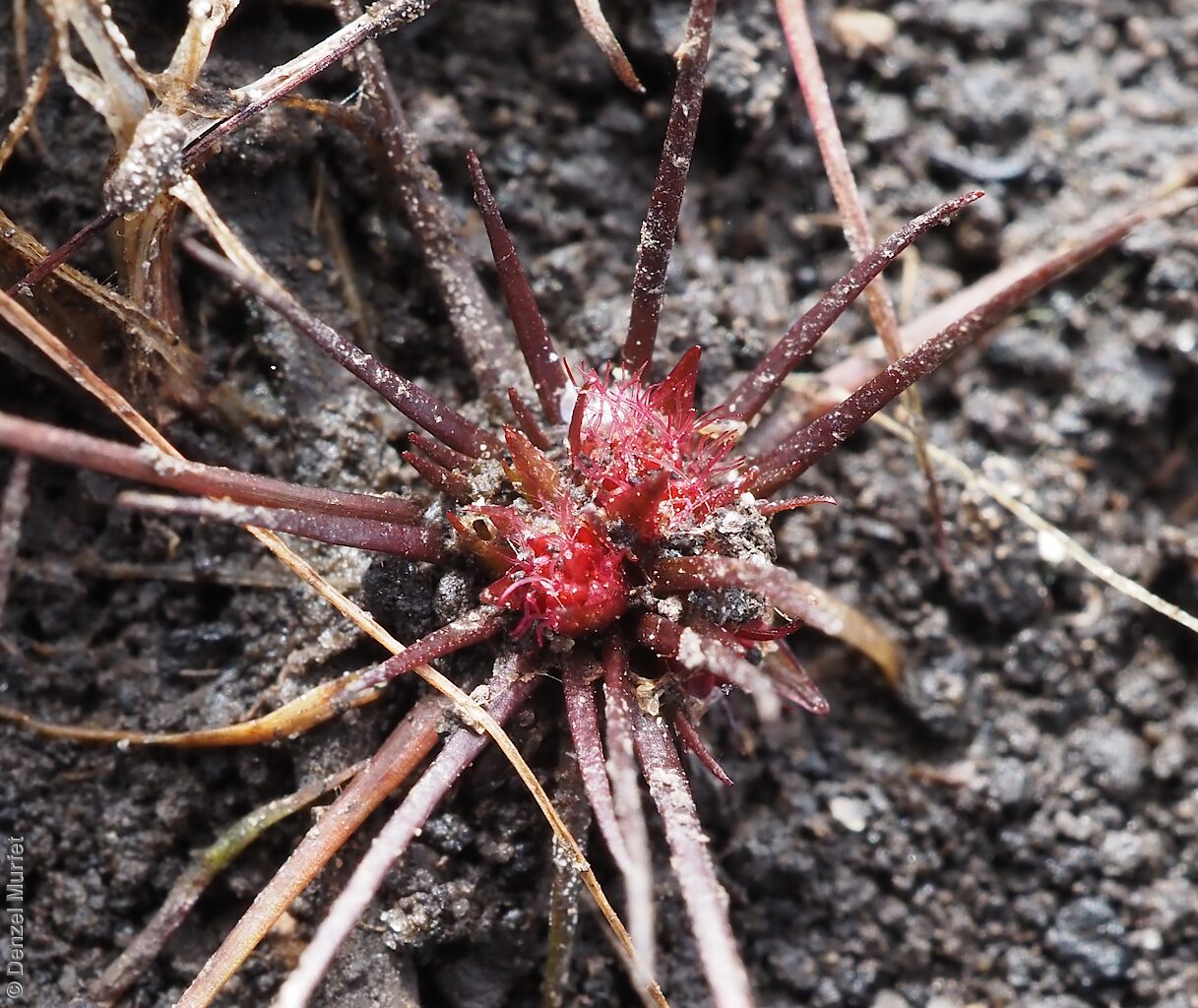
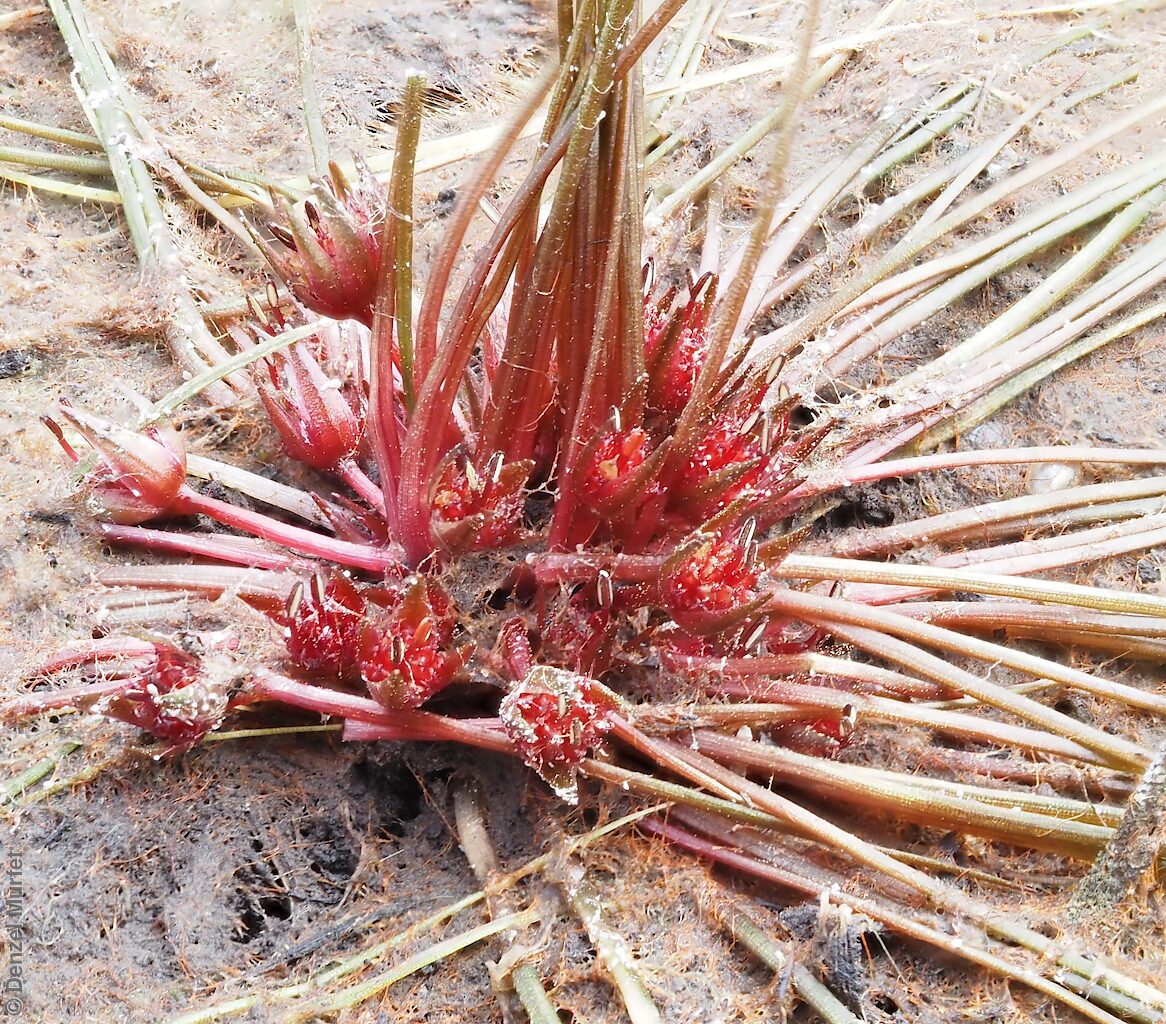
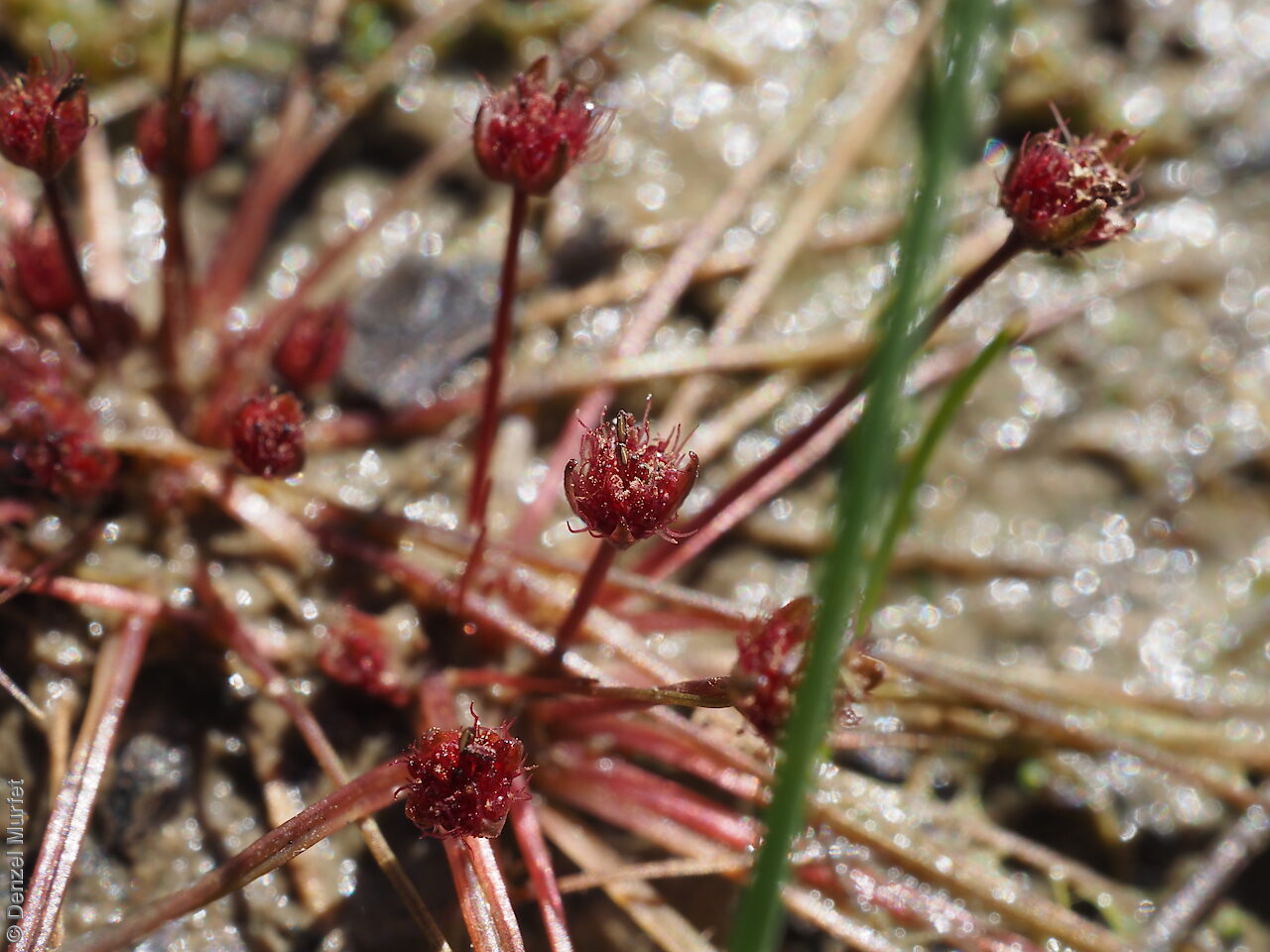
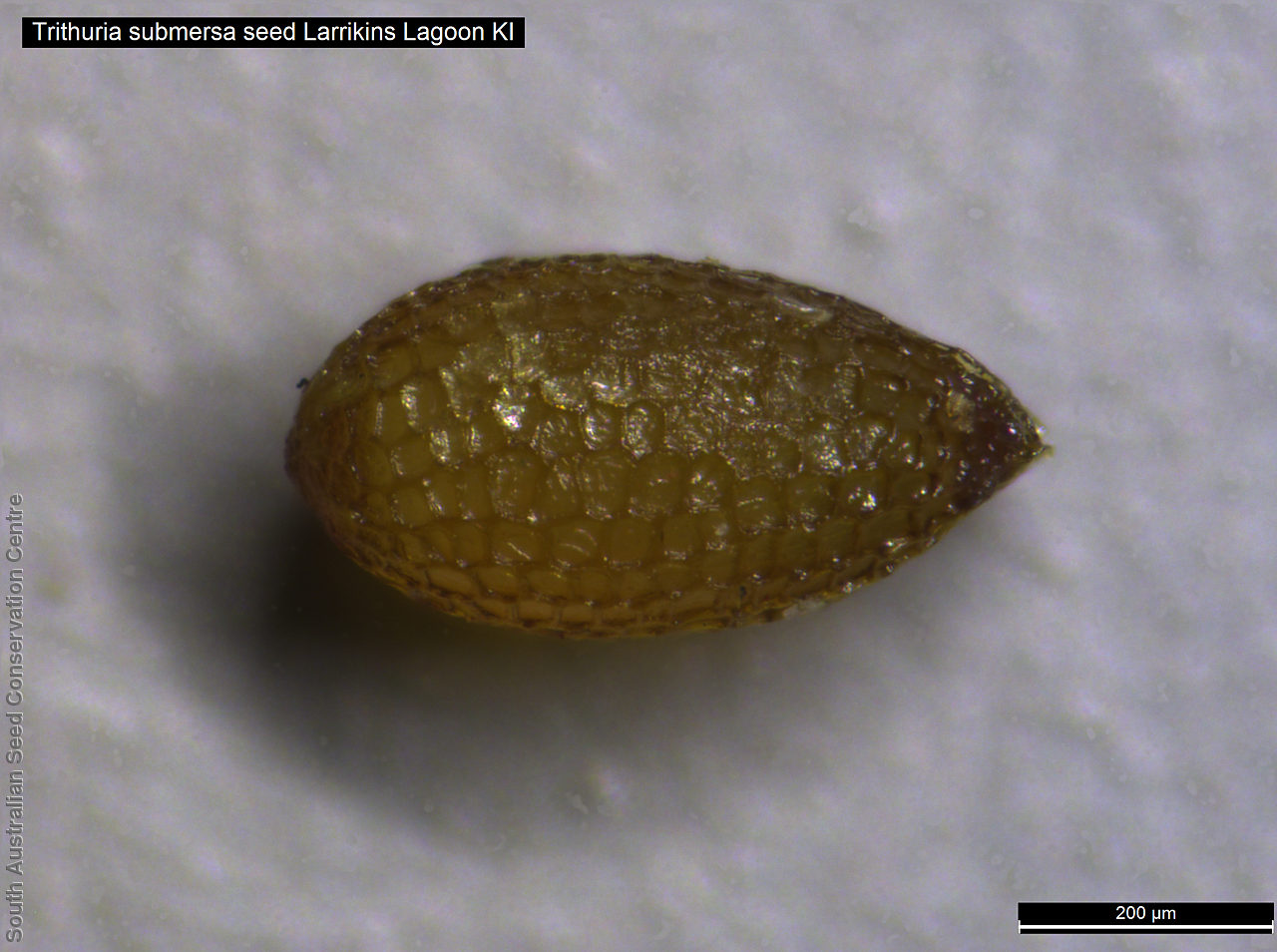
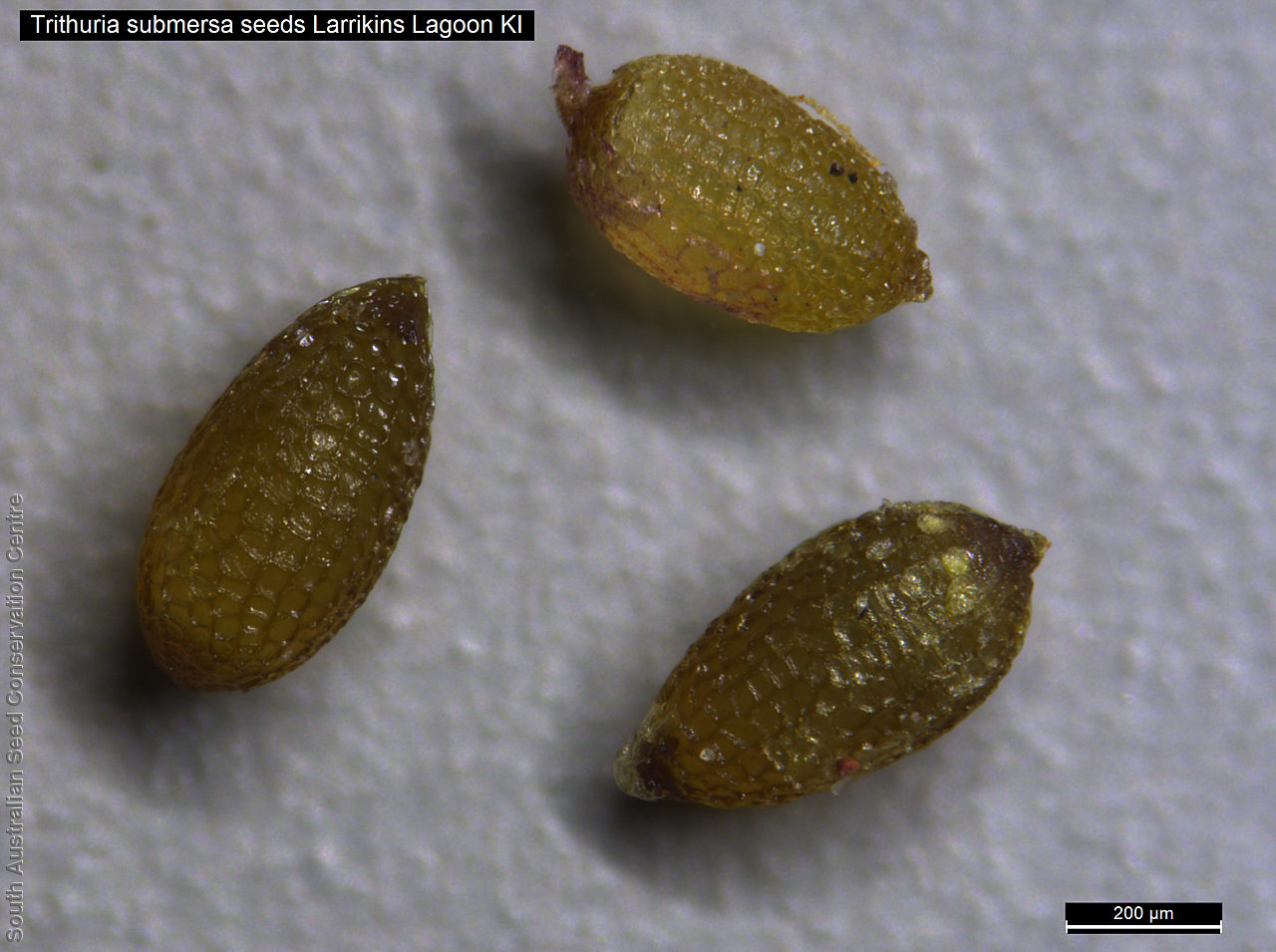
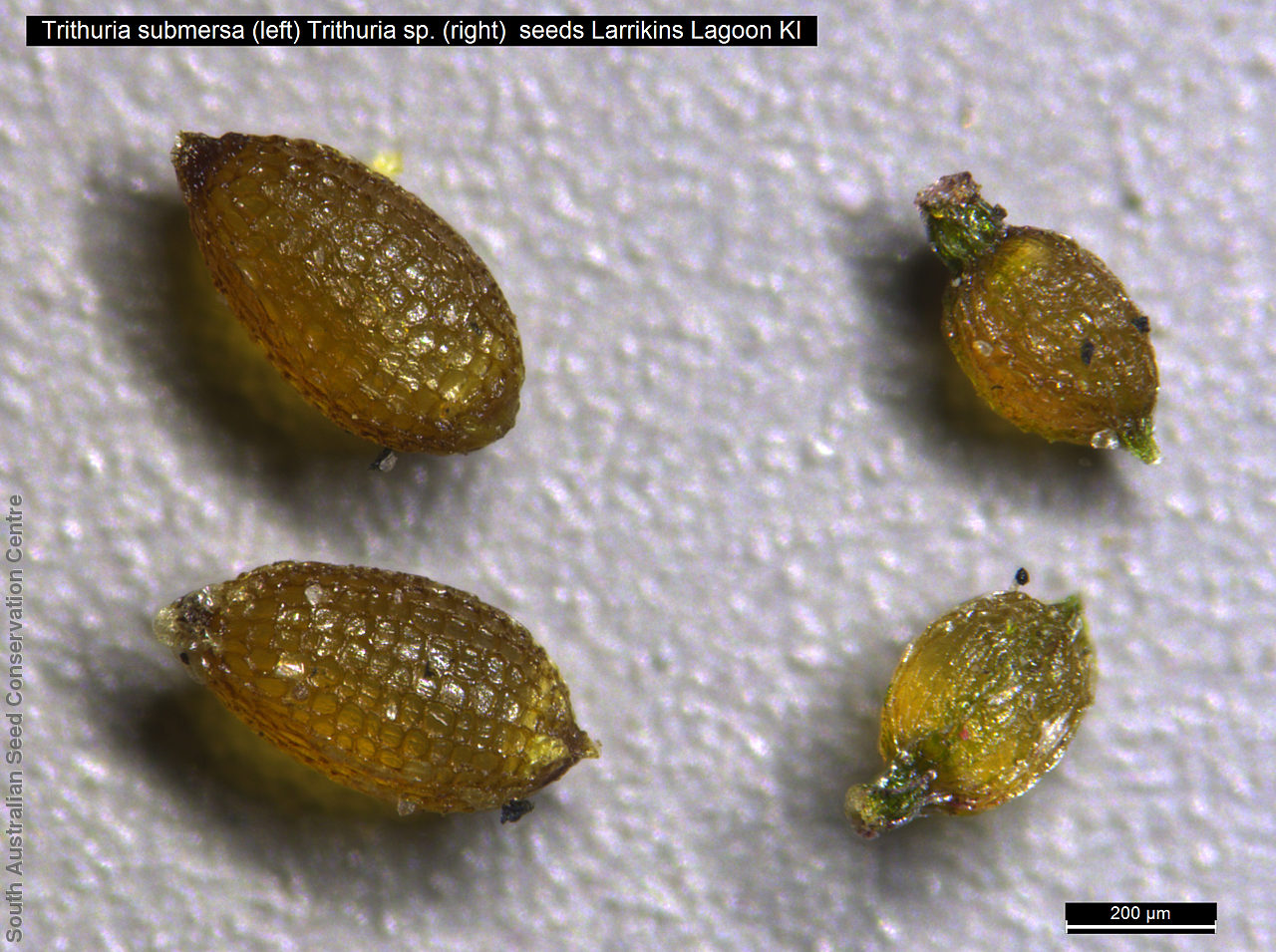
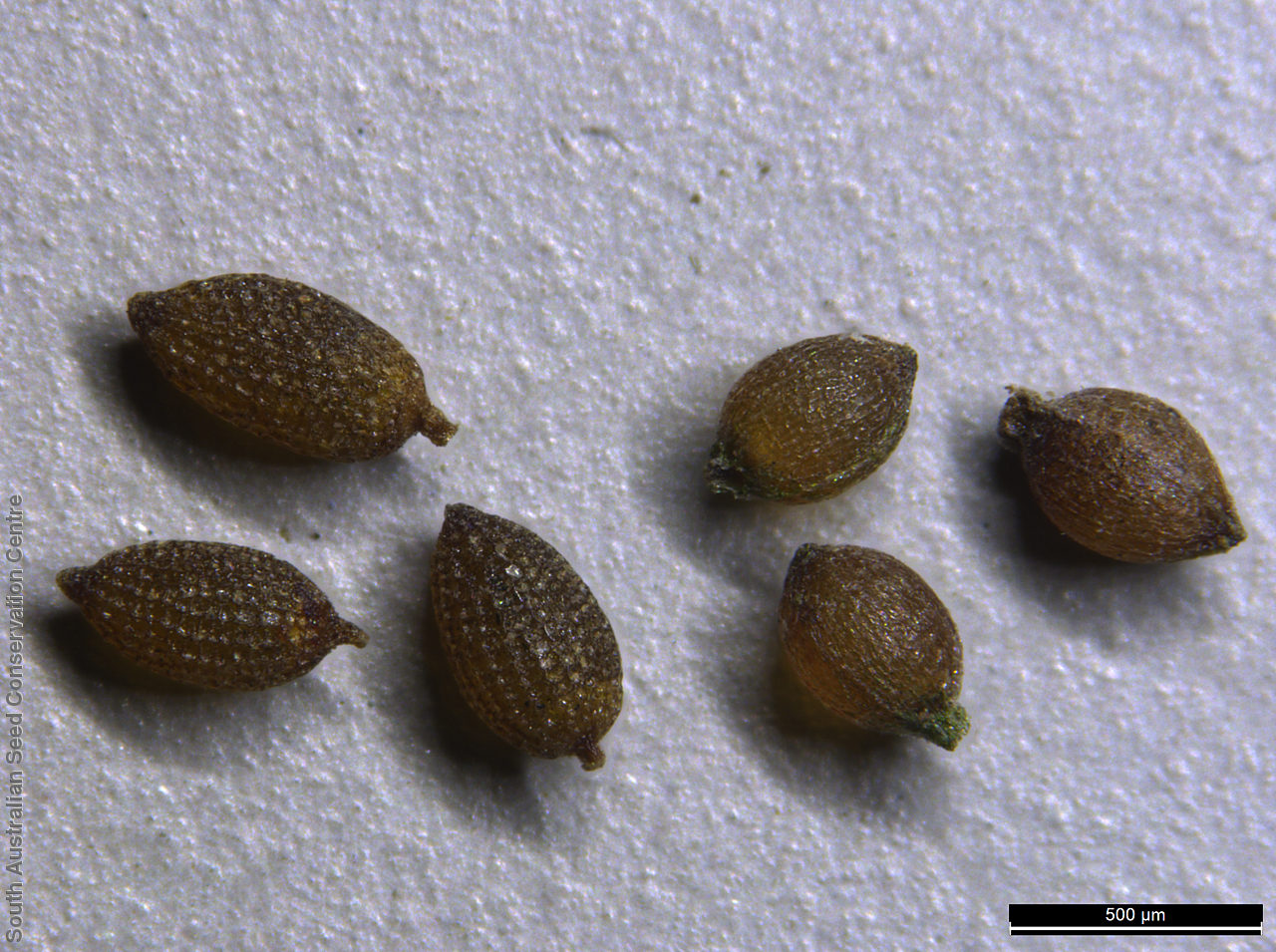
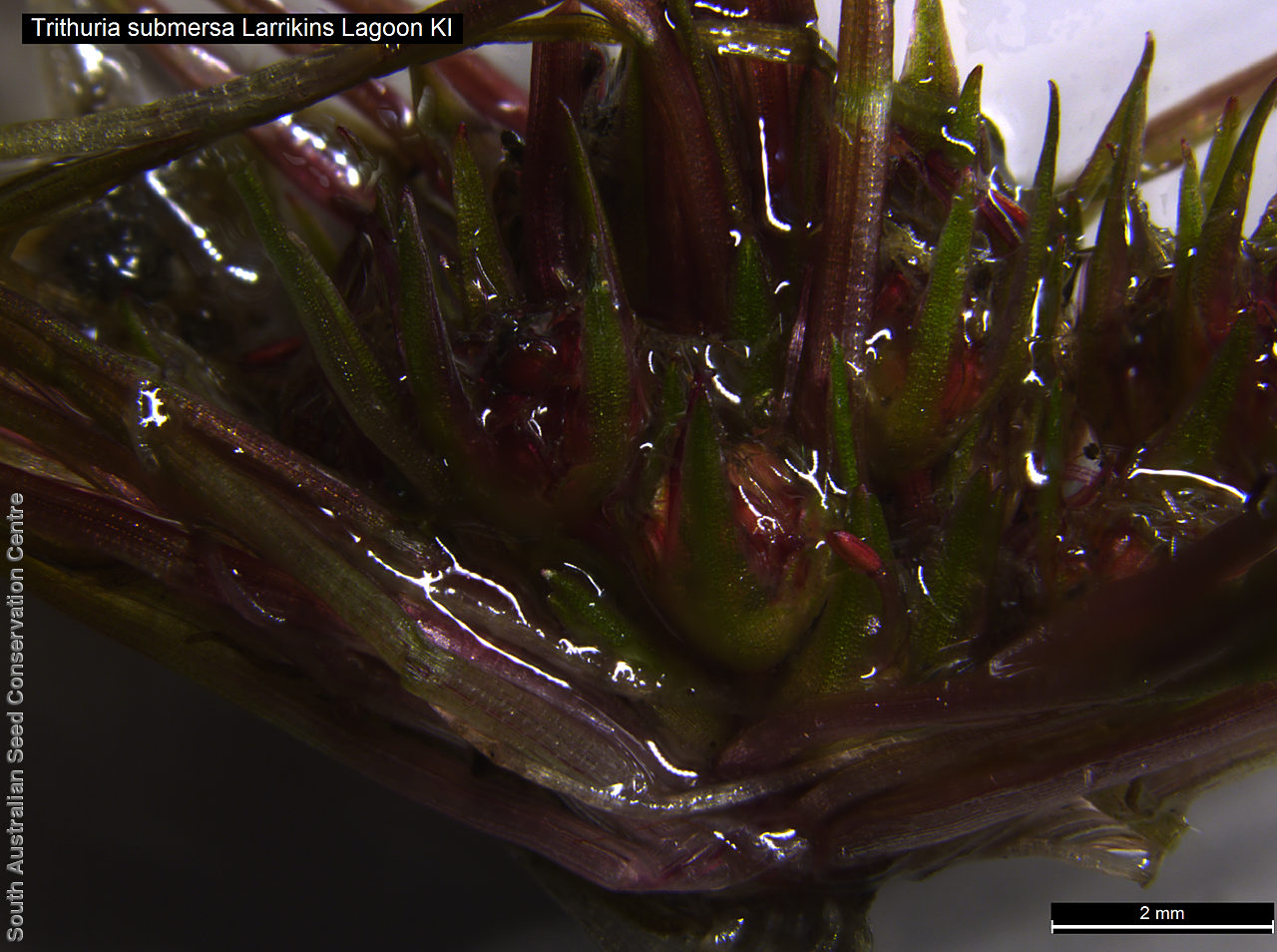
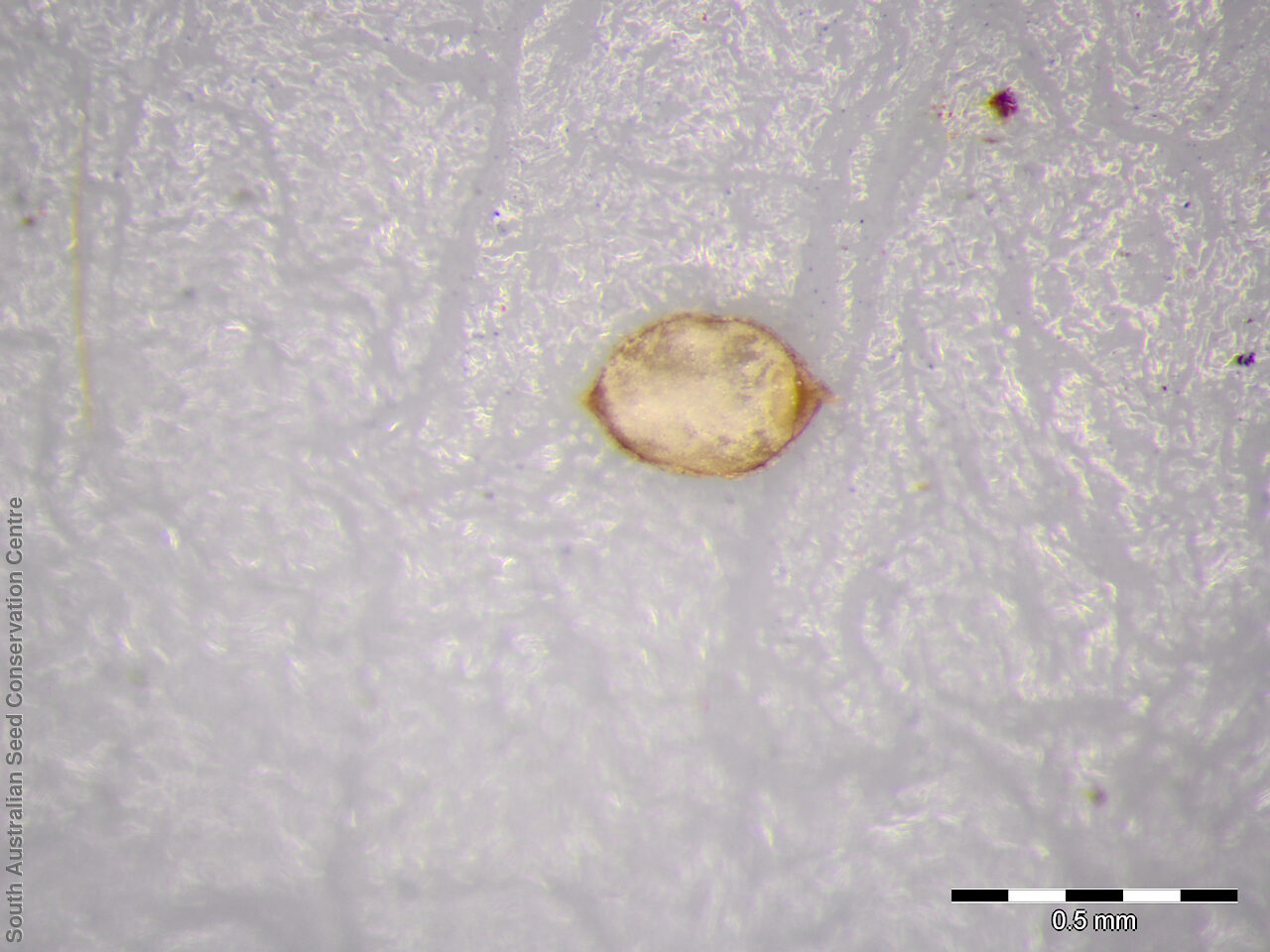
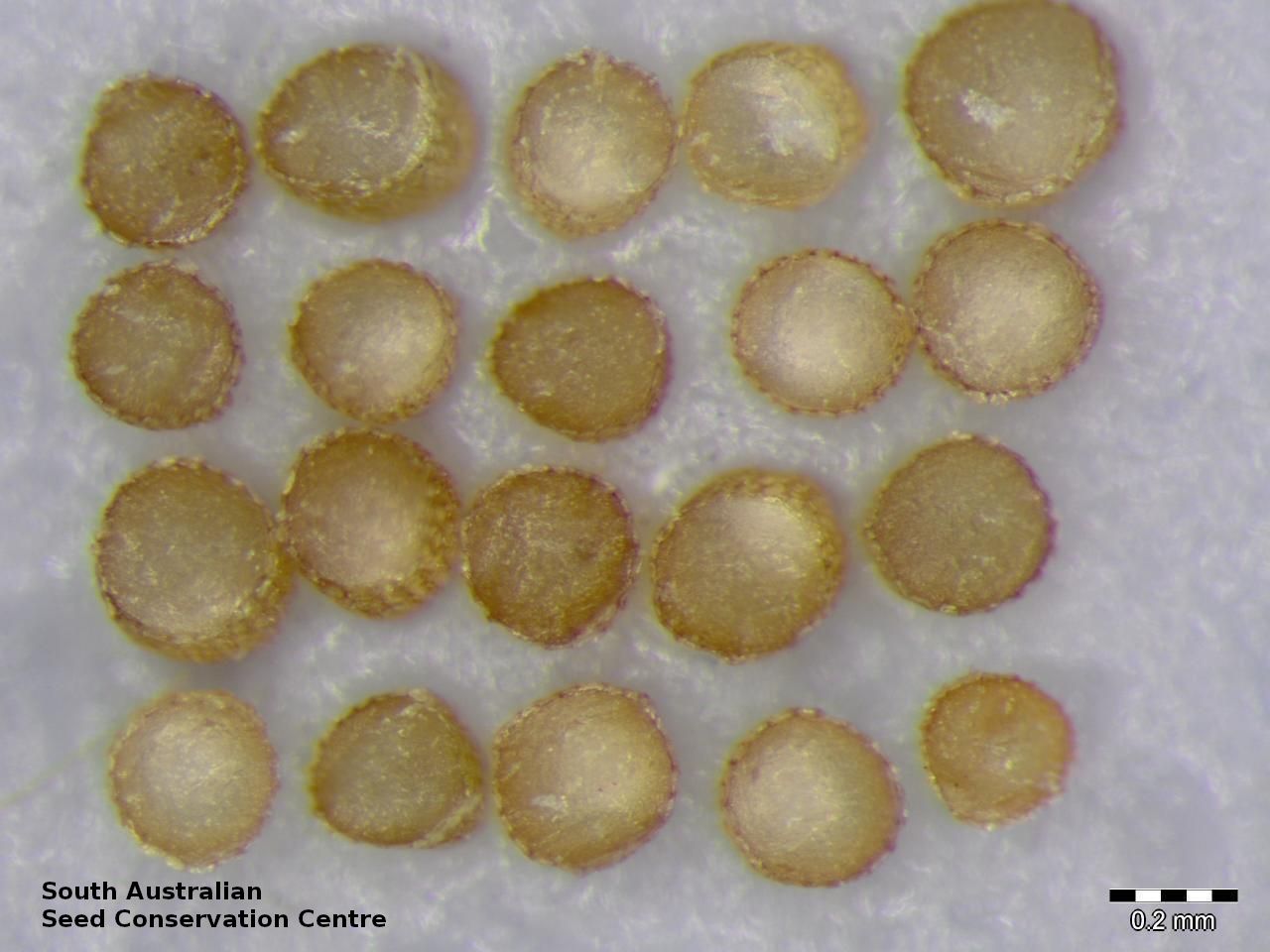
Annual herb, usually becoming reddish. Leaves glabrous, straight, narrow-linear, acute, to 4 cm long and 1 mm wide. Capitula numerous, scapose rarely sessile, scapes erect, filiform, unbranched, accrescent, to 5 cm high, leafless, glabrous; involucre spreading; bracts 4-6, acuminate, 1-veined, subequal, 3-4 mm long, glabrous; male florets 2-5; anther oblong, c. 0.6 mm long, purple; filament 1-2 mm long, rigid; female florets 10-25, c. 2 mm long, densely packed in a hemispherical cluster; stigmatic hairs 3-6. Fruits are tiny ovoid capsule to 0.6 mm long, splitting along the 3 ribs, with 3 panels attached at the apex and opening outwards from the base after falling from the pedicel. Seeds are tiny, brown, ovoid seed to 0.5 mm long and 0.3 mm wide. Seed embryo type is broad.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between September and October. Collect mature capsules, those that are turning a pale straw colour and contain brown seeds. Can collect individual capsules or break off the whole plant. Place the capsules/plant in a tray and leave to dry for two weeks. Then rub the capsules gently by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Be very careful as the seeds are very small. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Good seed viability. One collection of 4000 seeds had 100% viability. Seeds are non-dormant, viable seed should germinate readily when sown in winter.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA | 8,000 (0.17 g) | 100+ | 28-Oct-2009 | DJD1631 | 1-Jun-2010 | 100% | -18°C |
| BGA | 3,800 (0.11 g) | 100+ | 16-Nov-2010 | DJD2018 South Eastern | 1-Jan-2012 | 100% | -18°C |
| BGA | 1,800 (0.047 g) | 50+ | 11-Nov-2016 | DJD3567 Kangaroo Island | 1-Nov-2017 | 100% | -18°C |
| BGA | 26,500 (0.87 g) | 100+ | 23-Nov-2018 | DJD3828 South Eastern | 24-Apr-2019 | 100% | -18°C, -80°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.