














Botanical art
Prior names
Stipa semibarbata var. mollis
Stipa plagiopogon
Stipa mollis
Common names
Supple Spear-grass
Soft Spear-grass
Etymology
Austrostipa from the Latin 'auster' meaning south and the genus Stipa, referring to the genus being allied to Stipa but restricted to Australia. Mollis from Latin meaning soft, referring to its leaf-blades or inflorescence being softly hairy.
Distribution and status
Found in the southern part of South Australia, south of Port Augusta growing on limestone, sand, sandy loam and clay in open forest, woodland and mallee. Also found in Western Australia, New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania. Native. Common in South Australia. Common in the other states.
Herbarium regions: Flinders Ranges, Eyre Peninsula, Northern Lofty, Murray, Yorke Peninsula, Southern Lofty, Kangaroo Island, South Eastern, Green Adelaide
NRM regions: Adelaide and Mount Lofty Ranges, Eyre Peninsula, Kangaroo Island, Northern and Yorke, South Australian Arid Lands, South Australian Murray-Darling Basin, South East
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
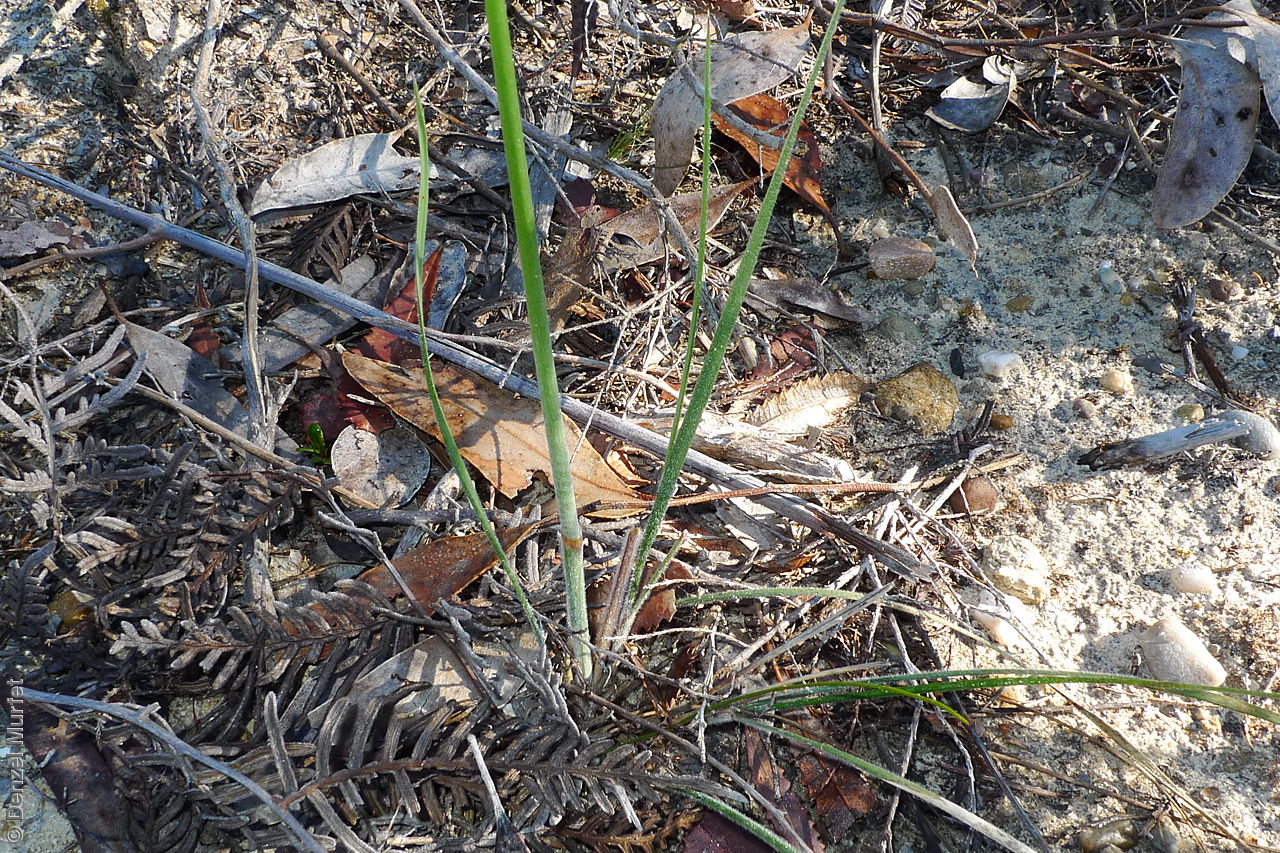
Plant description
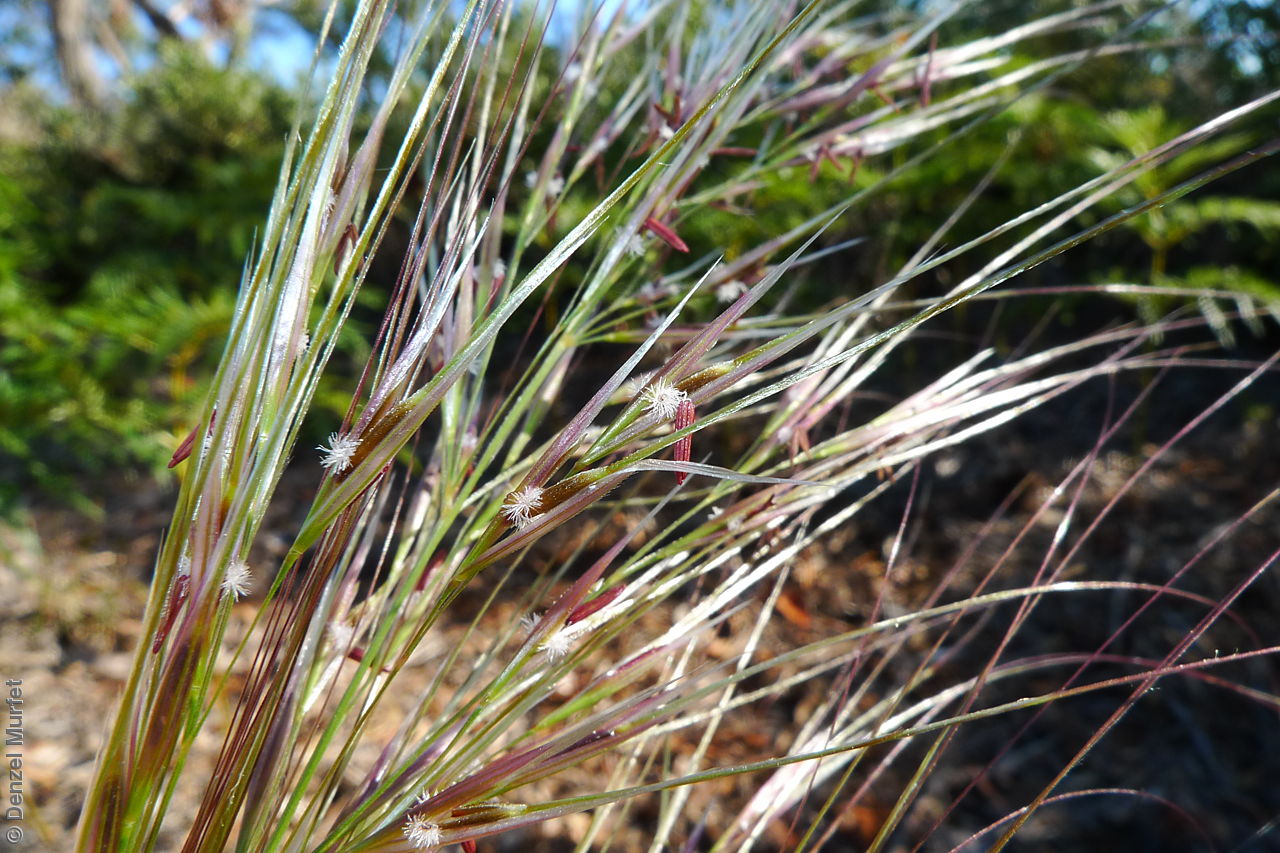
Tufted perennial grass to 1.2 m high, with culms unbranched and pubescent or rarely glabrous nodes. Leaves usually glabrous, sometimes scabrous, rarely pubescent, with blade weakly to strongly inrolled to 30 cm long and 4 mm wide. Inflorescence a densely contracted panicle to 30 cm long with purplish or green glumes to 22 mm long, upper glumes to 20 mm long. Flowering between September to December.
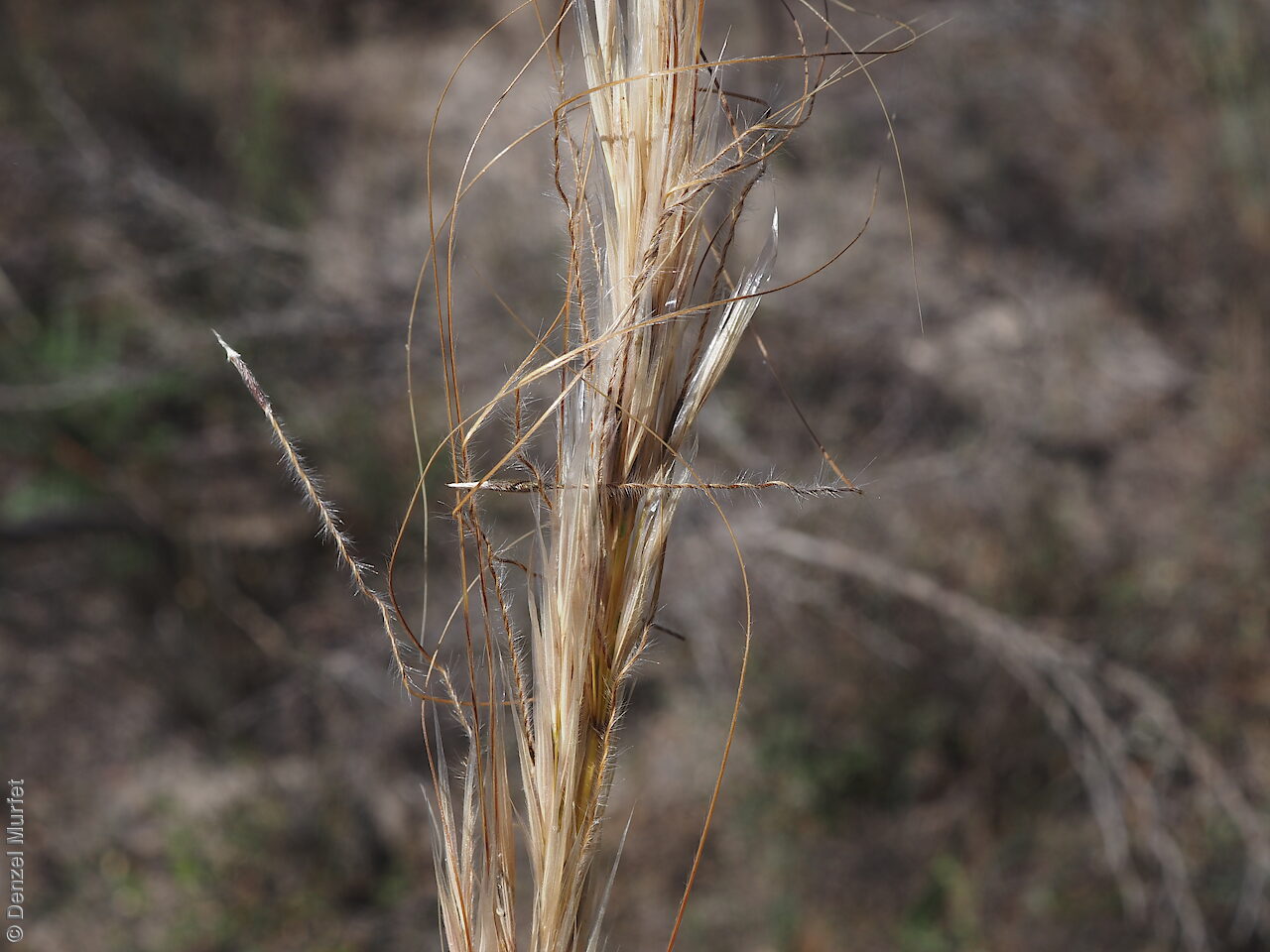
Key to this species: awn twice bent with no coma (no hairs around the lemma apex); awn 60-120 mm; awn hairs 0.6-2 mm spiralling up nerve; lemma 7.5-9 mm with red-brown granular surface; panicle dense; upper glume 15-20 mm. Fruits are red-brown narrow-ellipsoid lemma to 9 mm long, with finely granular surface and covered in white to golden hairs except towards the apex; callus long straight and sharp to 3 mm long; awn twice bent to 100 mm long and column plumose, with a spiralling line of hairs to 2 mm long up the nerve, palea about equal to lemma, with a line of hairs down the centre. Seeds are yellow-brown narrow-ellipsoid grain to 4.5 mm long within the lemma. Seed embryo type is lateral.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between November and February. Use your hands to gently strip the seeds (lemma) off the mature fruiting spike, those that are turning brown. Mature seeds will come off easily compare to the immature seeds that remain on the spike. Alternatively, you can break off the whole fruit spike to allow some of the seeds to mature further. Place the seeds/spike in a tray and leave to dry for two weeks. No further cleaning is required if only seed collected. If seed spikes collected, use hand to strip off the mature seeds. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Viability of grass seeds could be very viable, depending on time of seed collections and seasonal conditions.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSB | 1,800 (13.95 g) | 26-Nov-2006 | DJD704 Southern Lofty | ||||
| BGA | 5,000 (27.21 g) | 100+ | 13-Dec-2007 | DJD983 South Eastern | 1-Jan-2016 | 100% | -18°C |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.