













Botanical art
Common names
Small-flower Tobacco
Smooth-flower Tobacco
Etymology
Nicotiana, named after Jean Nicot (1530-1600), a French Ambassador for the King of France to Lisbon in 1560, who sent the first tobacco plant to France. Goodspeedii, named after Thomas Harper Goodspeed (1887-1966), an American botanist specialising in the intra-generic relationships in Nicotiana, and director of the University of California Botanic Gardens.
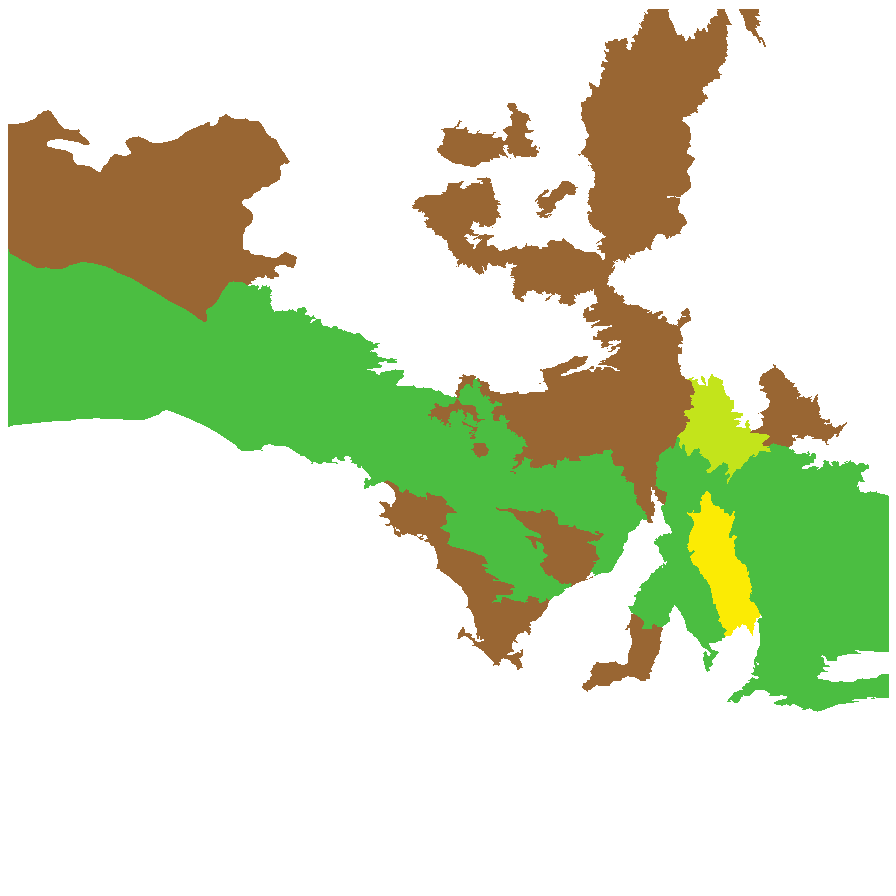
Distribution and status
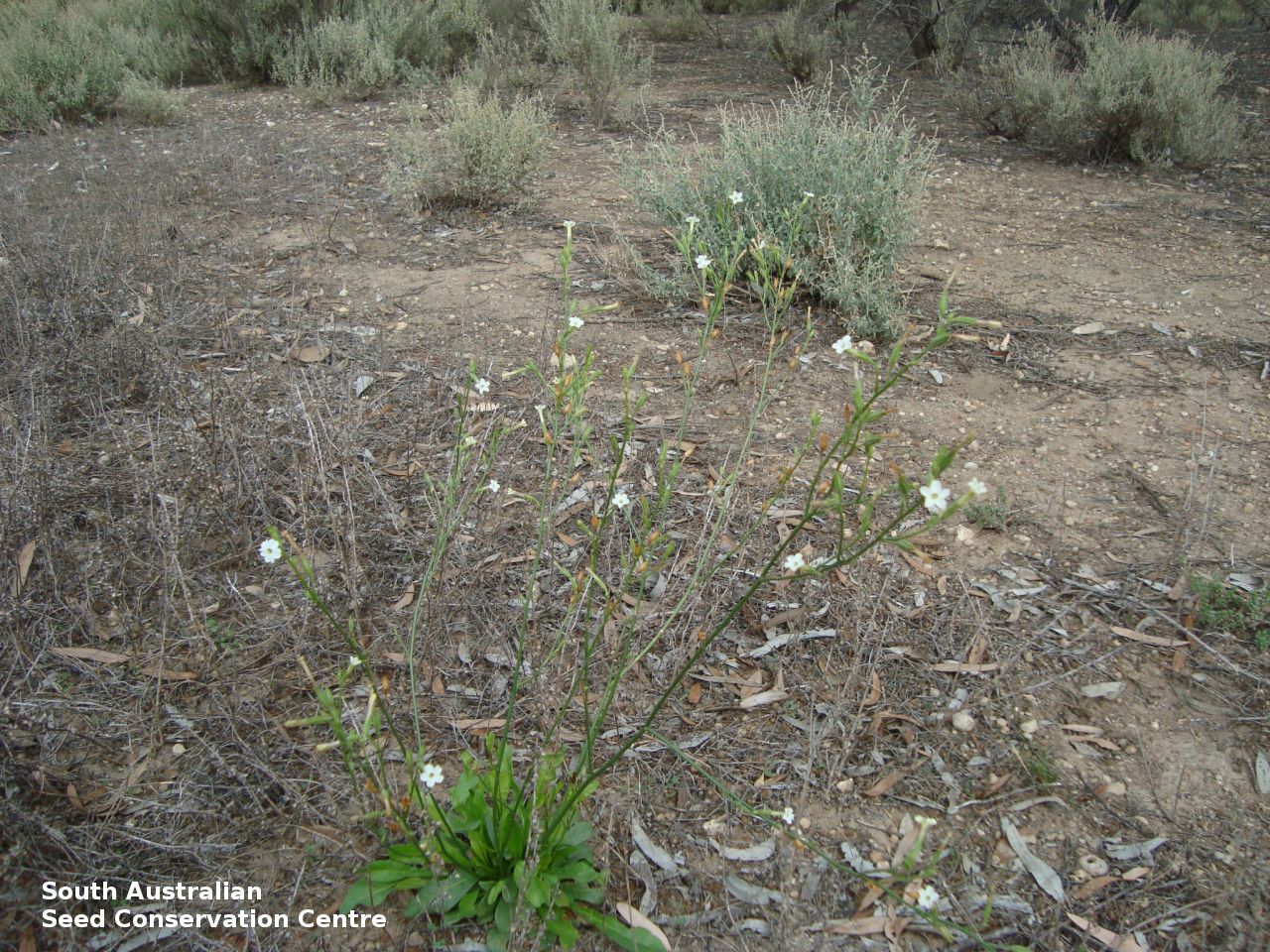
Found across central South Australia from the west coast to the eastern border; growing in open areas, often disturbed, usually on alkaline soils. Also found in Western Australia, New South Wales and Victoria. Native. Common in South Australia. Rare in Victoria. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: North Western, Nullarbor, Gairdner-Torrens, Flinders Ranges, Eastern, Eyre Peninsula, Northern Lofty, Murray, Yorke Peninsula
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
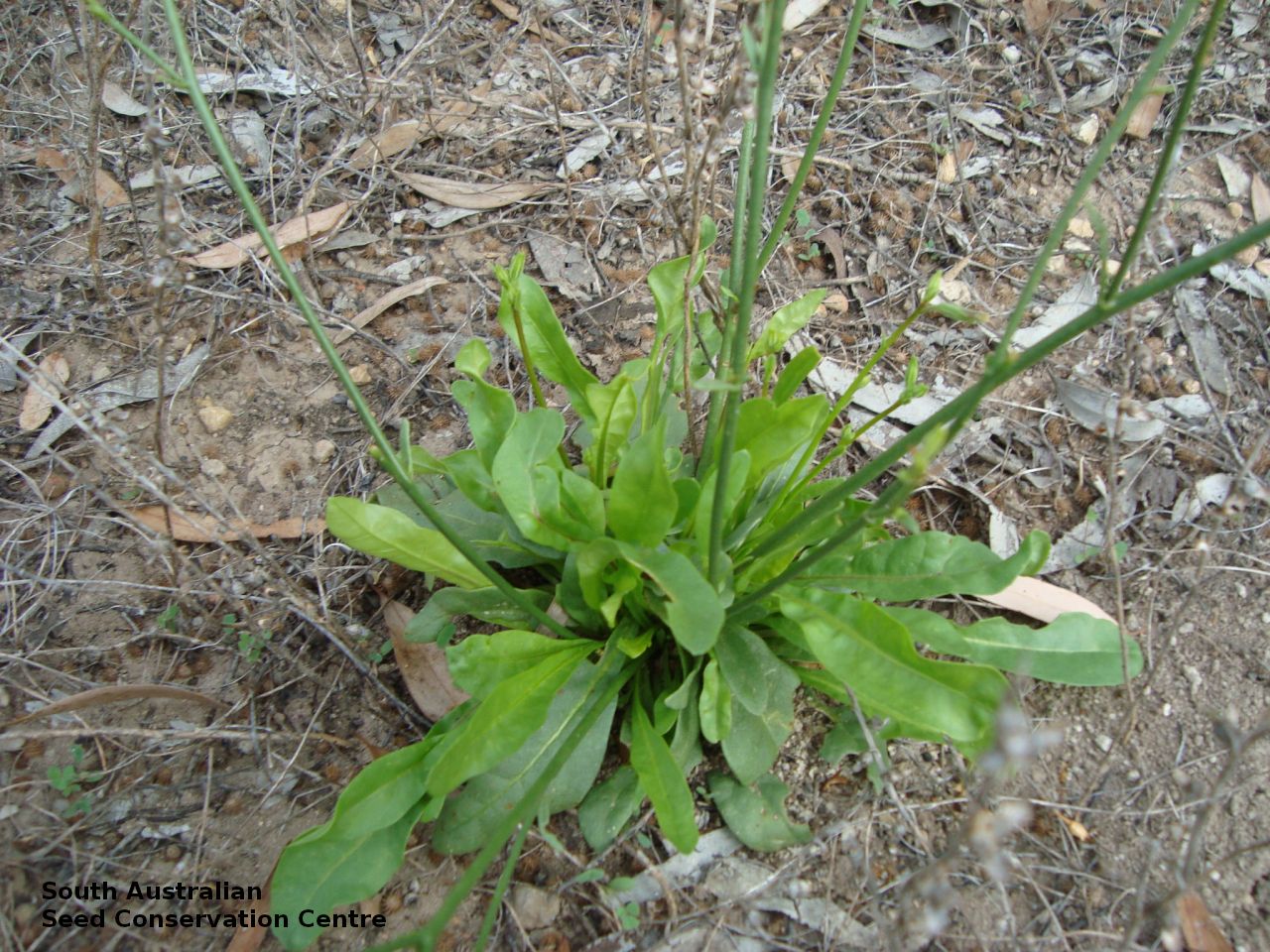
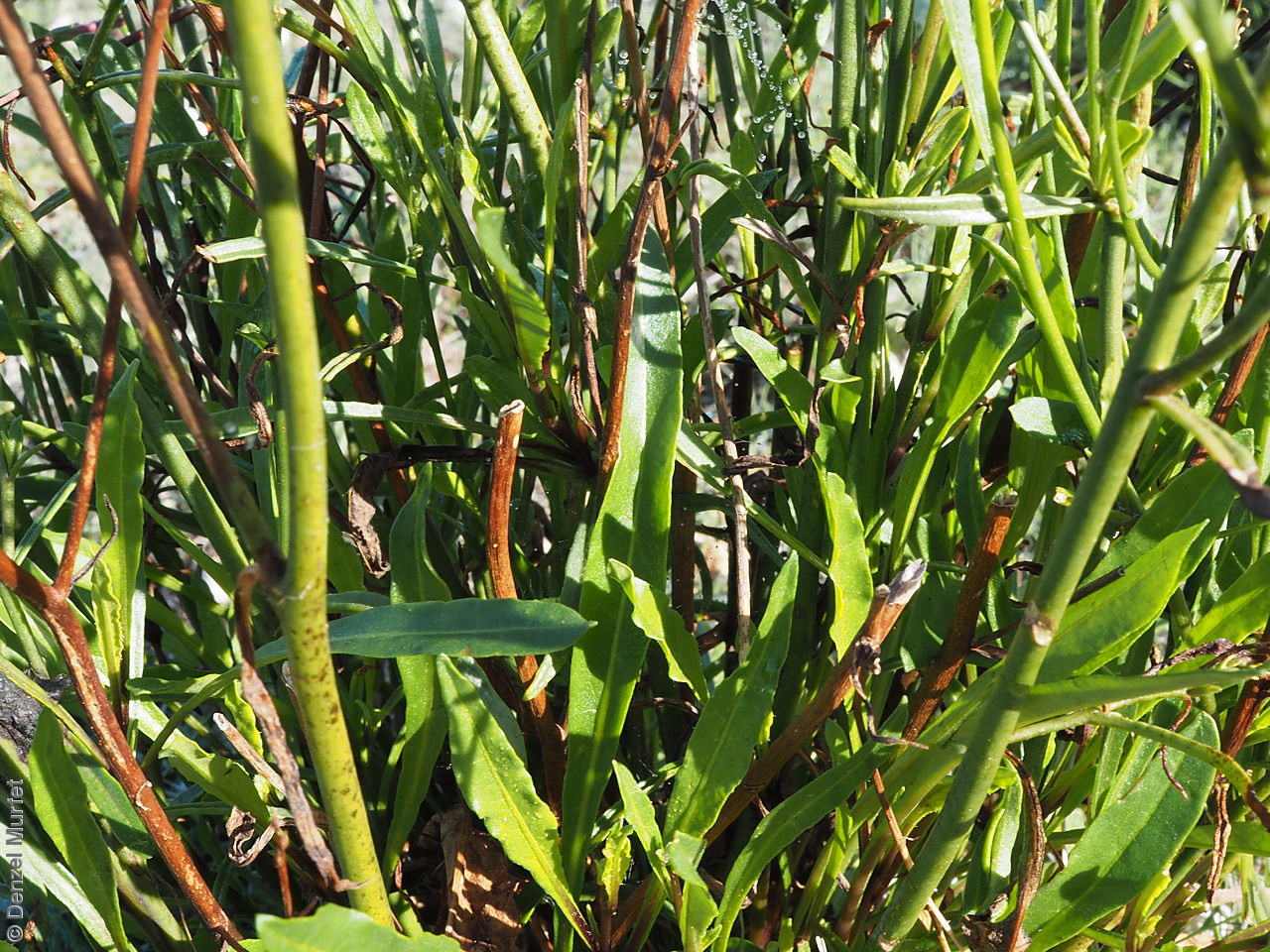
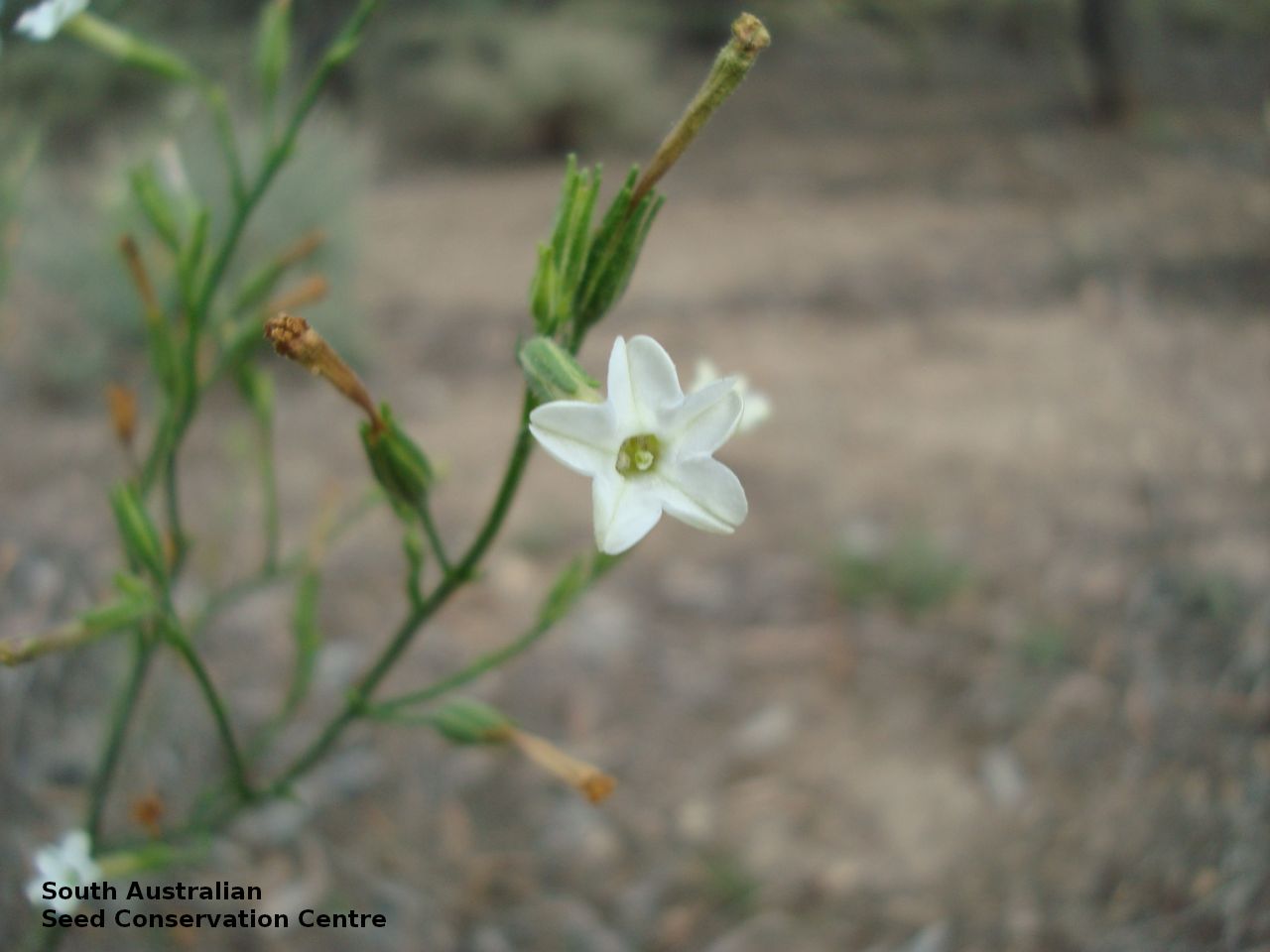
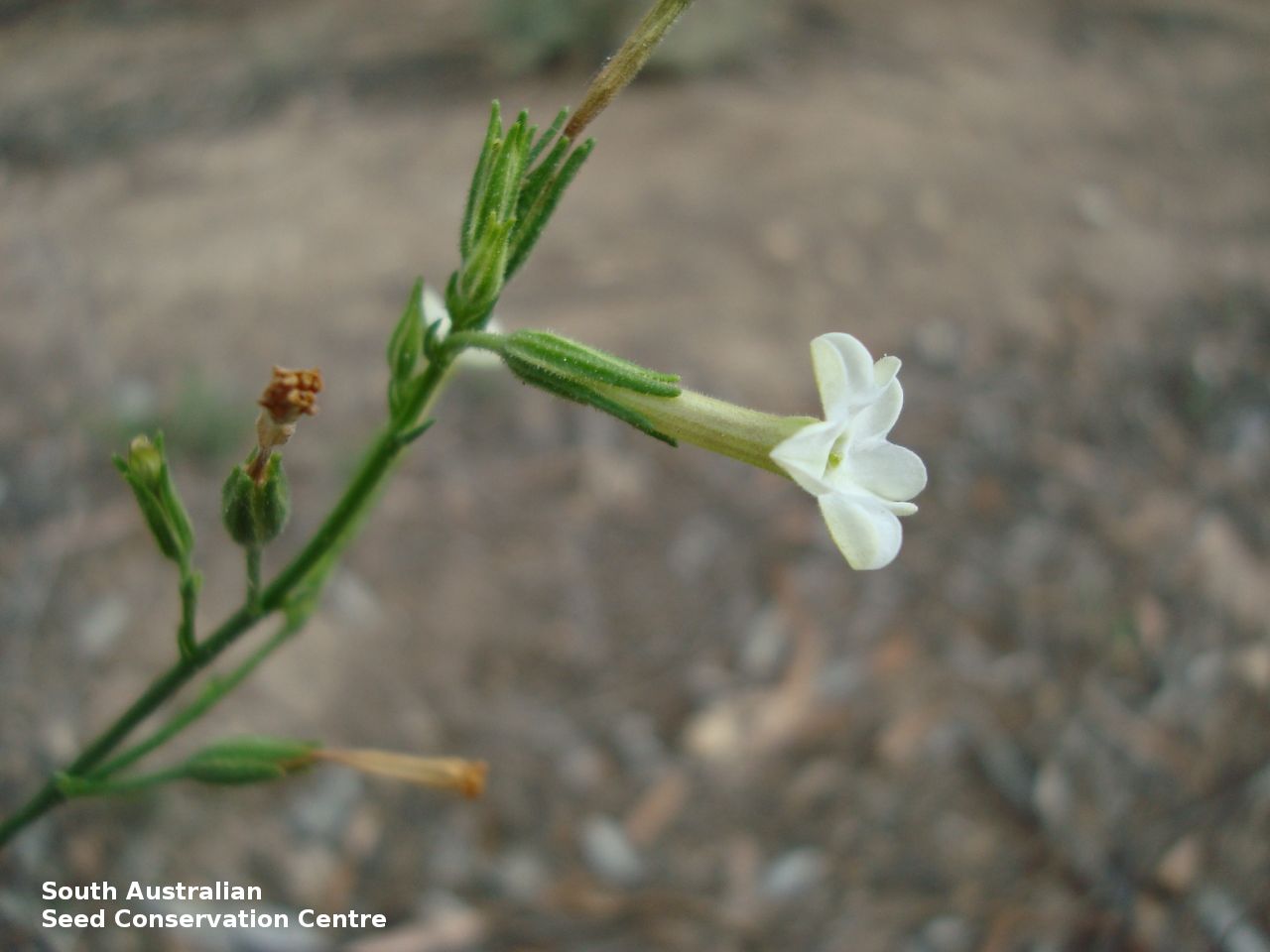
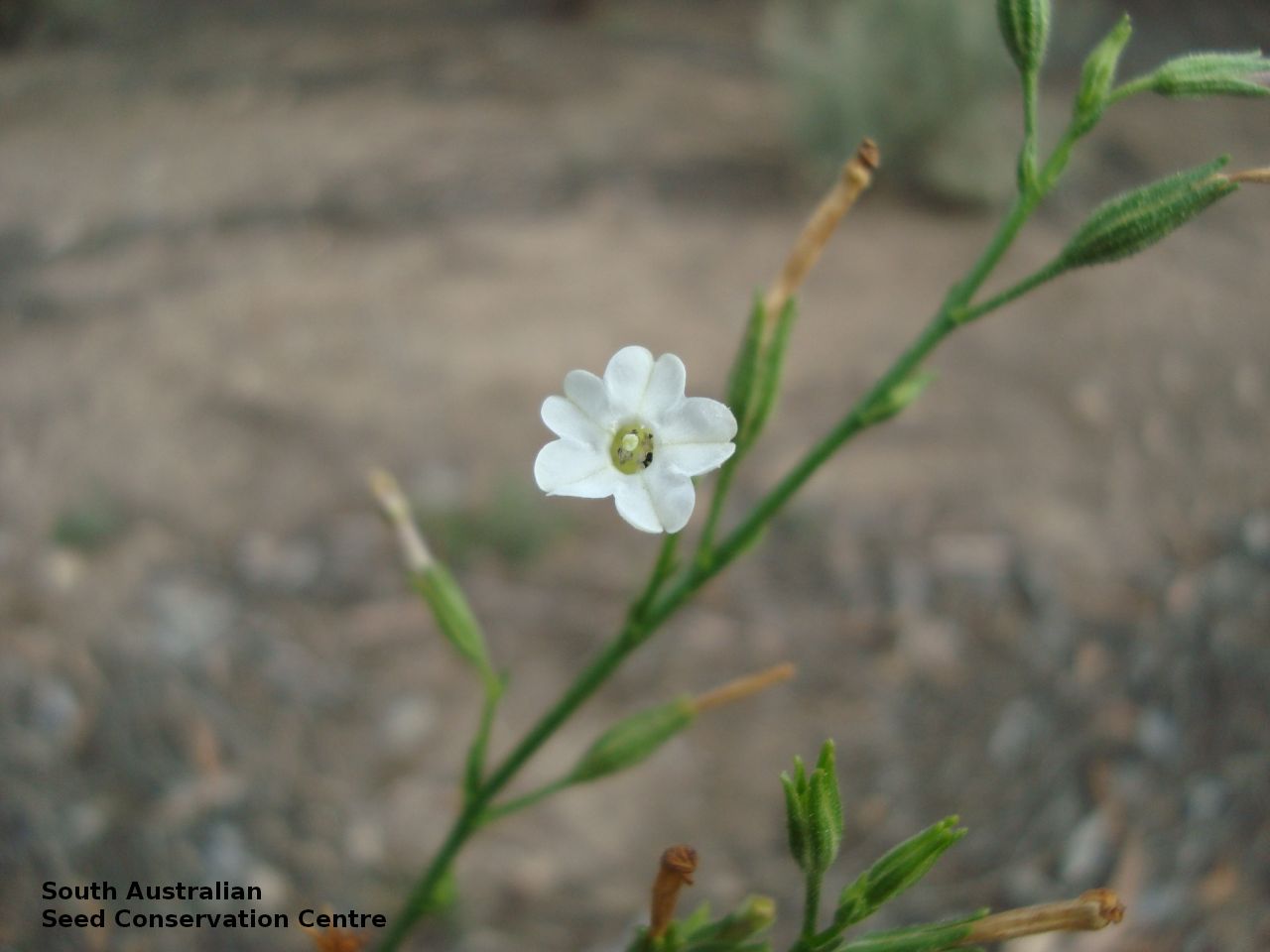
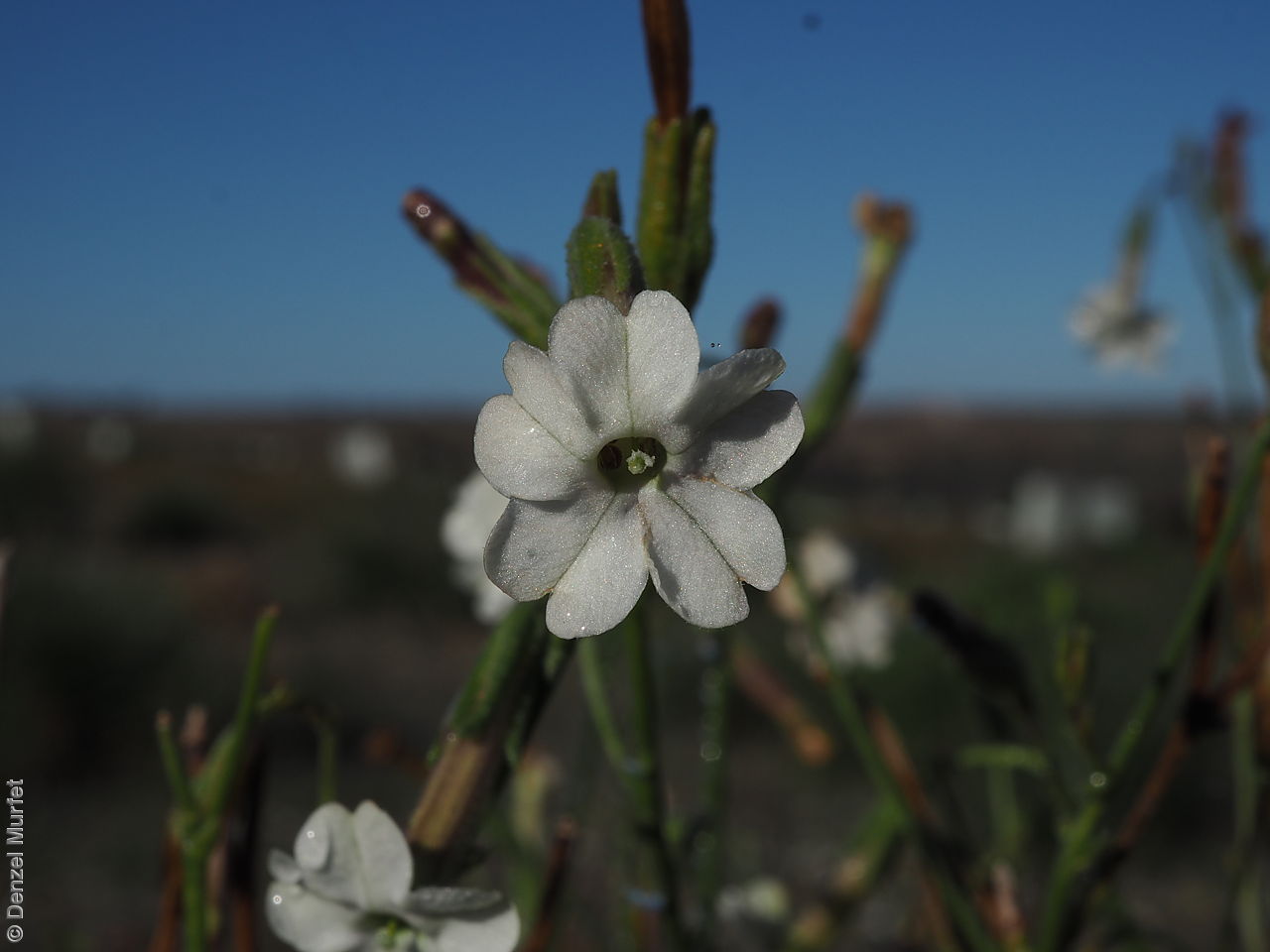
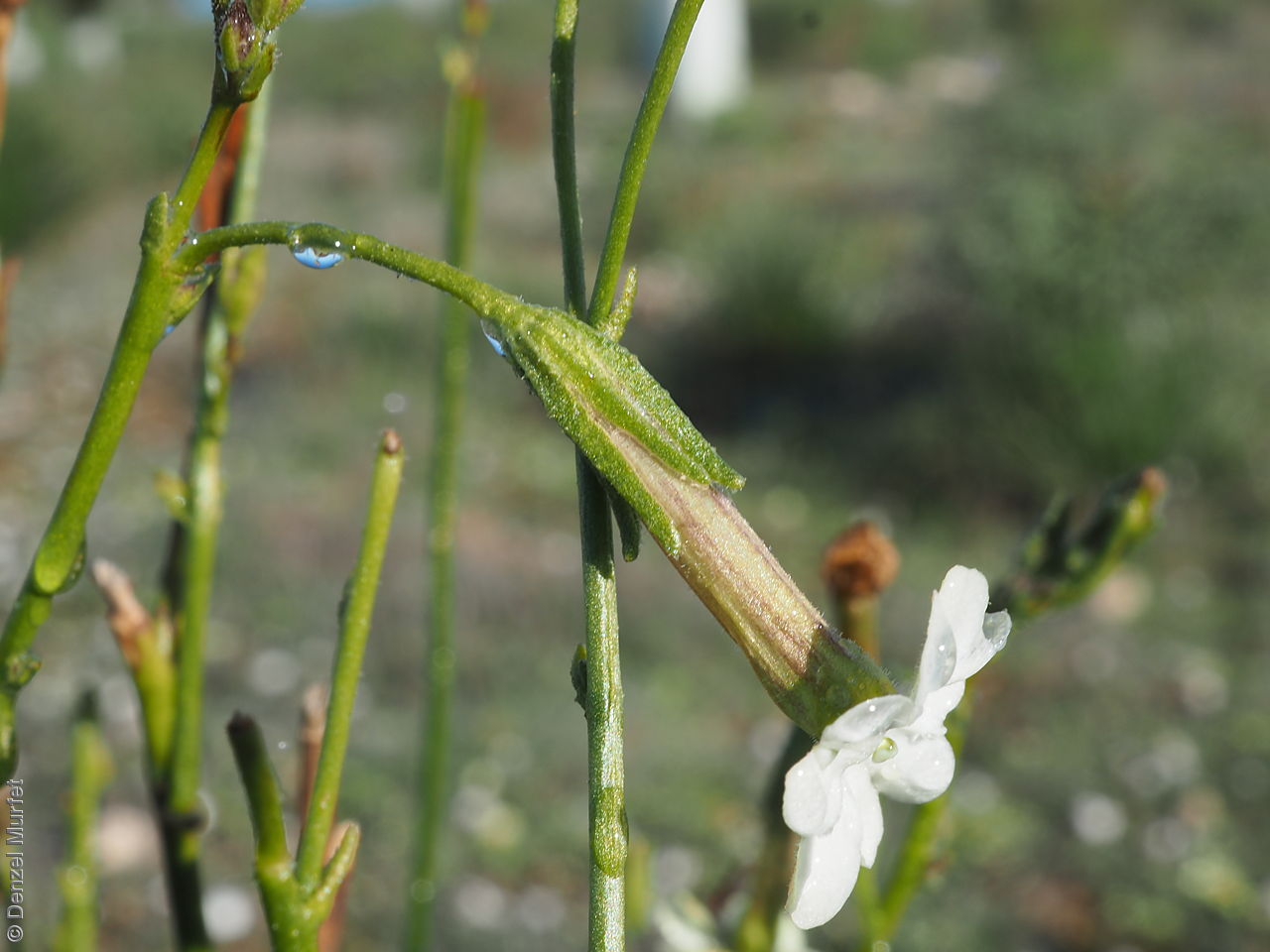
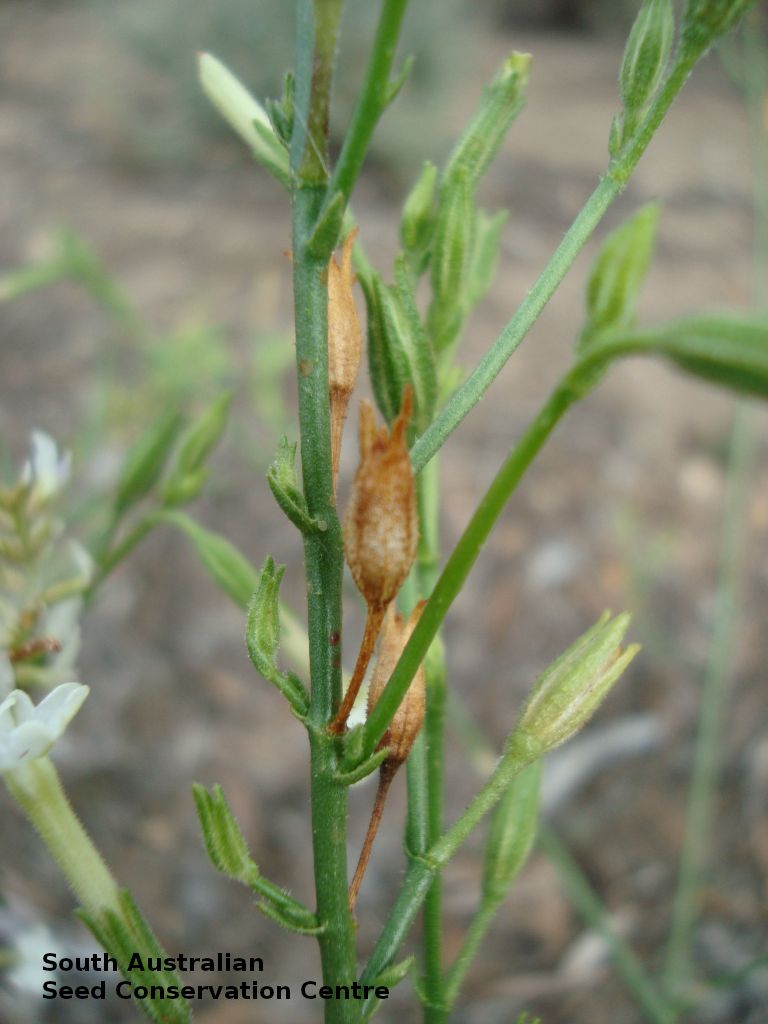
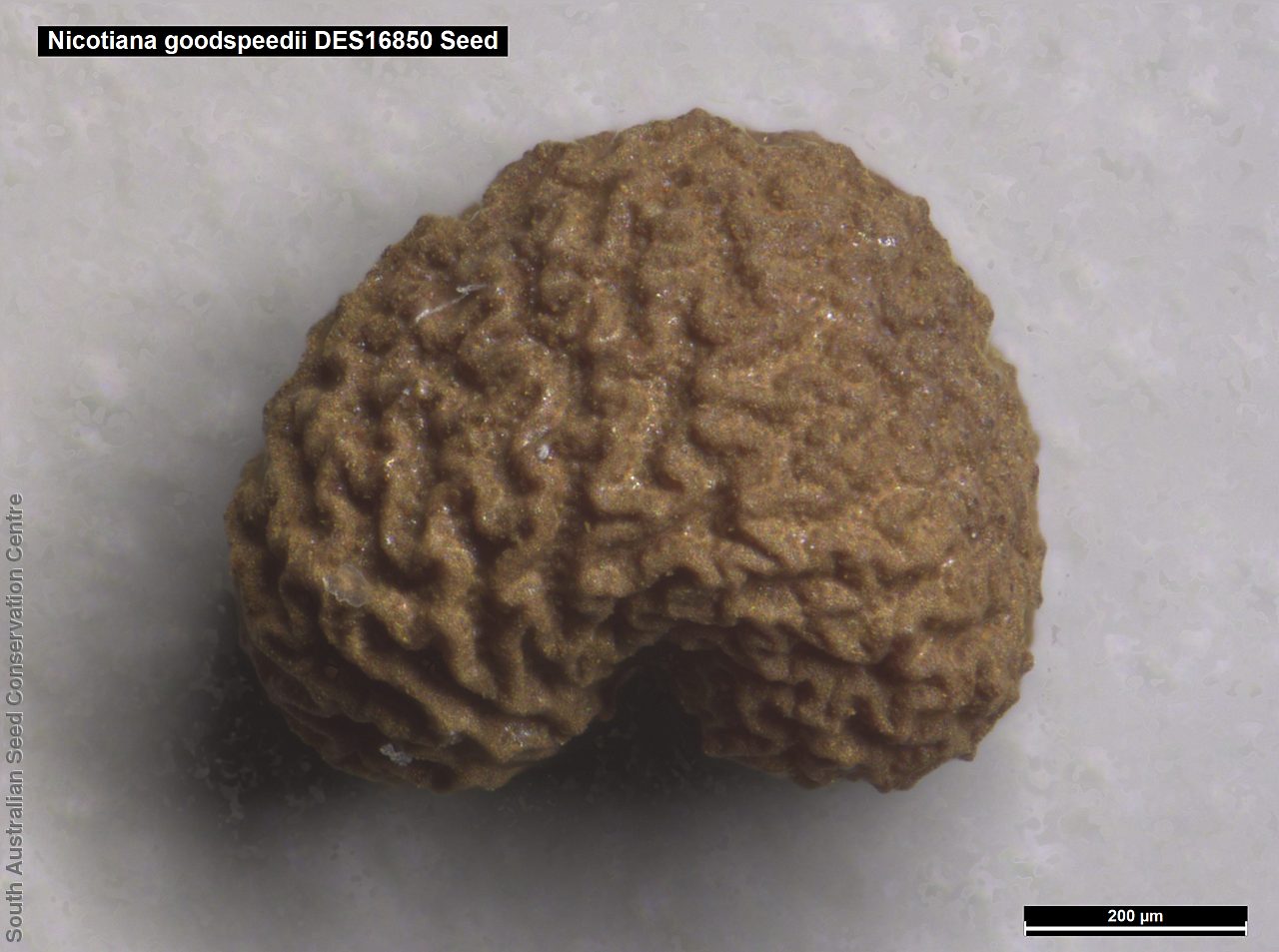
Herb to 70 cm high or more, often with many glabrous stems. Leaves, mostly basal to 5 cm or more long. Stem leaves, subsessile to sessile to 19 cm long; elliptic to spatulate or narrowly so; upper leaves narrower. Inflorescence erect panicle-like spikes, few branching with small tubular white flowers. Flowering most of the year but mainly in spring. Fruits are brown, ellipsoid to ovoid capsule to 10 mm long. Seeds are orange-brown reniform seed to 1 mm long and 0.5 mm wide and covered in wrinkles. Seed embryo type is linear, fully-developed.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between October and January. Collect mature capsules that are brown or turning a pale straw-colour and contain brown seeds. Can collect individual capsules or break off the whole fruit spike. Place the capsules in a tray and leave to dry for one to two weeks, then rub the capsules gently by hand to dislodge the seeds. Use a sieve to separate the unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. From two collections, the seed viability was high, ranging from 95% to 100%.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGA MSB | 15,000 (1.7 g) 15,000 (1.7 g) | 100+ | 22-Nov-2005 | DJD213 Flinders Ranges | 9-Aug-2006 | 95% | -18°C |
| BGA | 32,000 (3.88 g) | 50 | 3-Apr-2007 | RJB71147 Eastern | 19-Sep-2008 | 100% | -18°C |
| MSB | 16,400 (1.26 g) | 100+ | 30-Sep-2008 | DJD1092 Eyre Peninsula | 85% |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.