


















Botanical art
Prior names
Aristida ramosa var. speciosa
Etymology
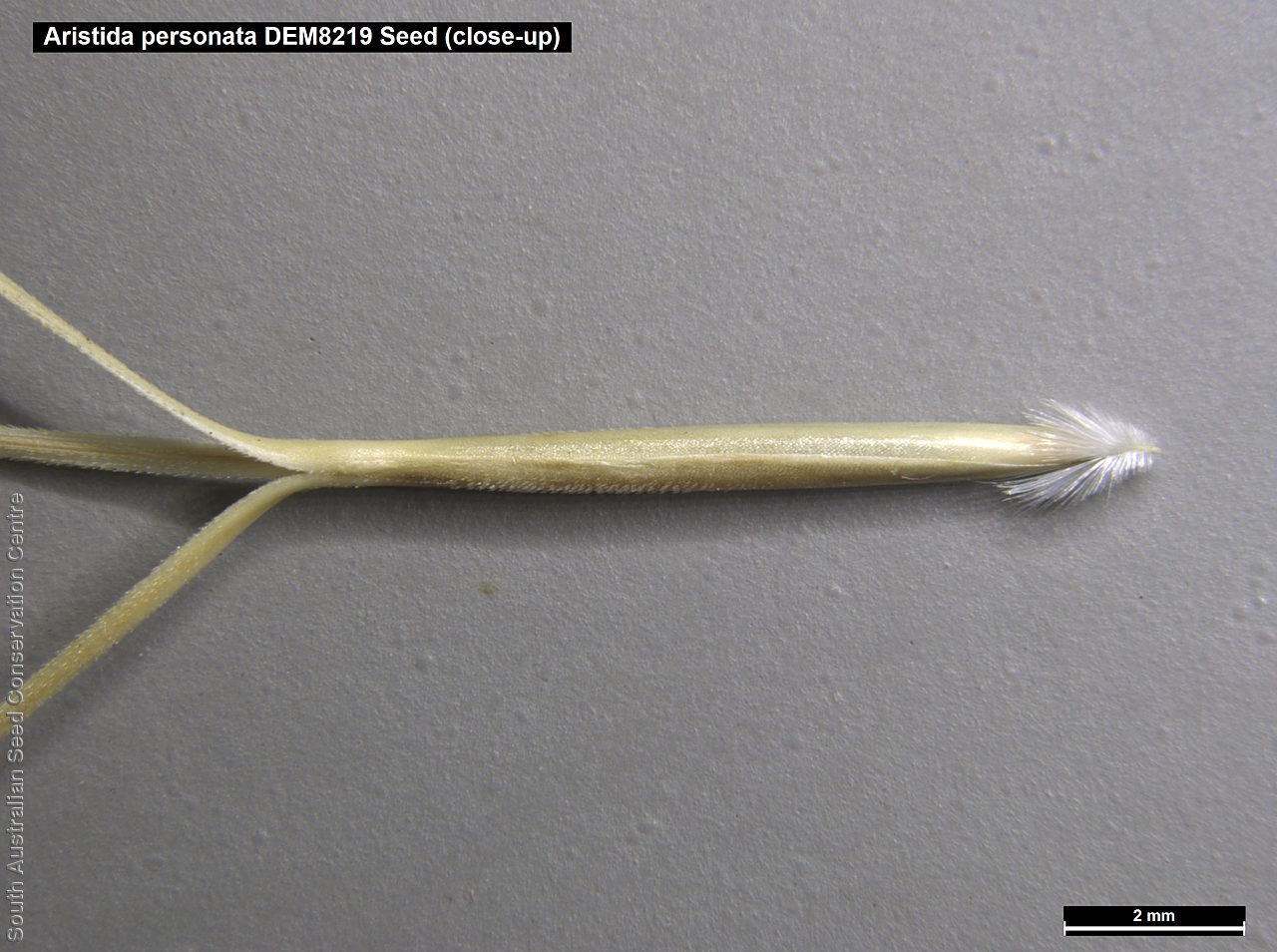
Aristida from the Latin 'arista' meaning awned, alluding to the awned lemma. Personata from the Latin 'personatus' meaning masked, counterfeit, referring to its resemblance to another Aristida species, possibly A. ramosa.
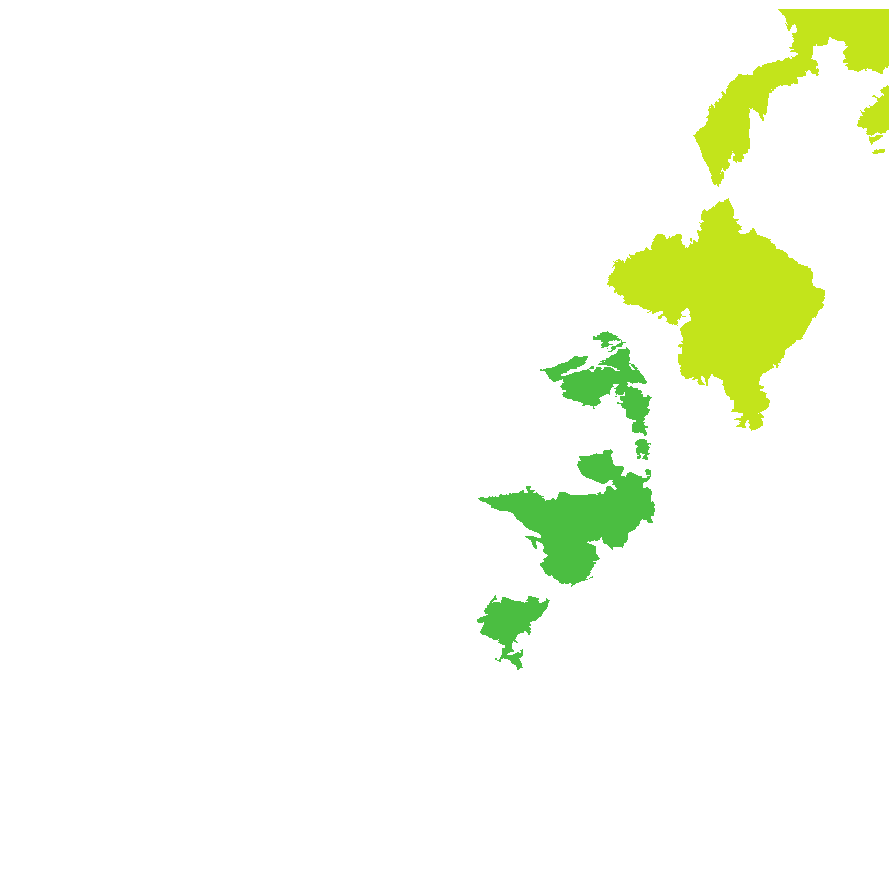
Distribution and status
Found scattered across the north-eastern part of South Australia and on the Eyre Peninsula and Mount Lofty Ranges, growing in dry grassland or open shrubland and woodland on poor soils. Also found in Queensland, New South Wales and Victoria. Native. Common in South Australia. Rare in Victoria. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: Nullarbor, Flinders Ranges, Eyre Peninsula, Northern Lofty, Murray, Southern Lofty, Green Adelaide
NRM regions: Adelaide and Mount Lofty Ranges, Alinytjara Wilurara, Eyre Peninsula, Northern and Yorke, South Australian Arid Lands, South Australian Murray-Darling Basin
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
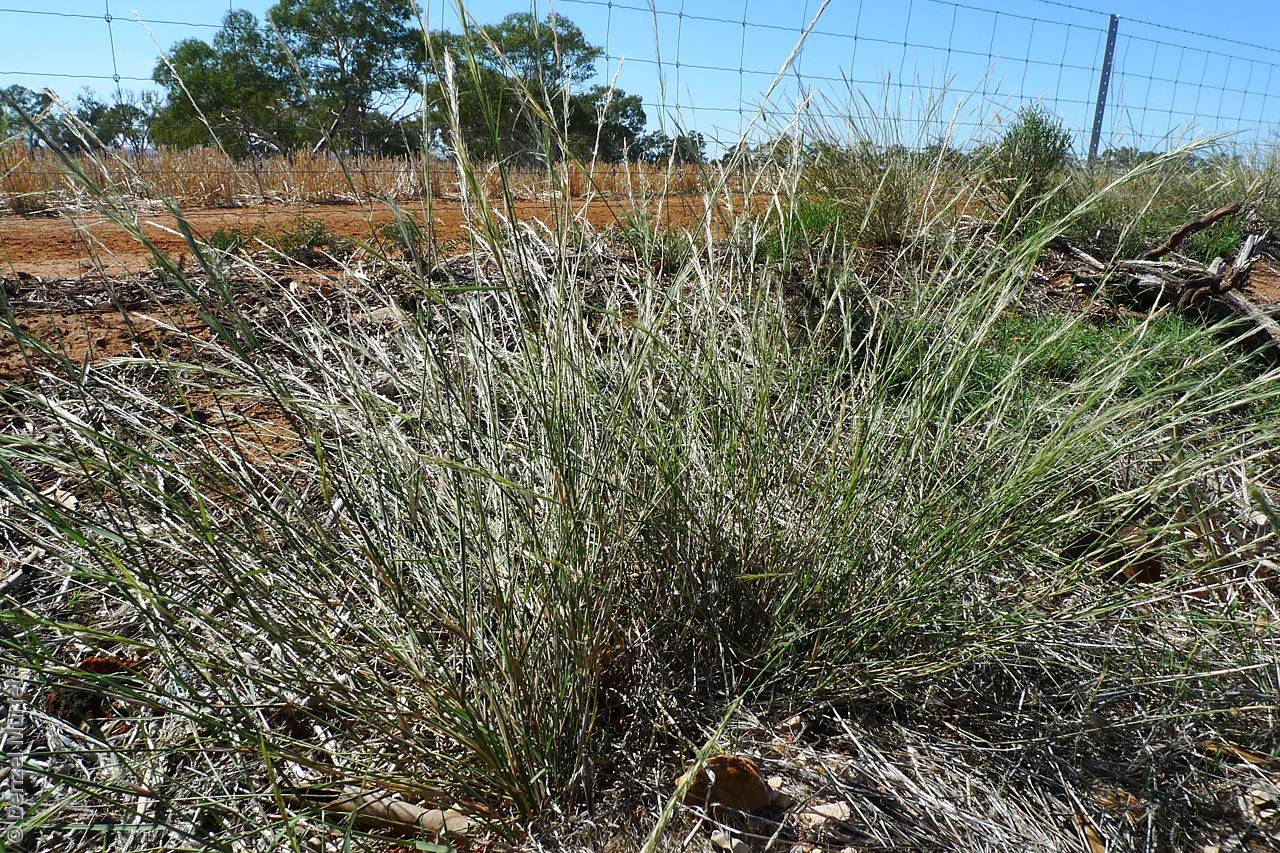
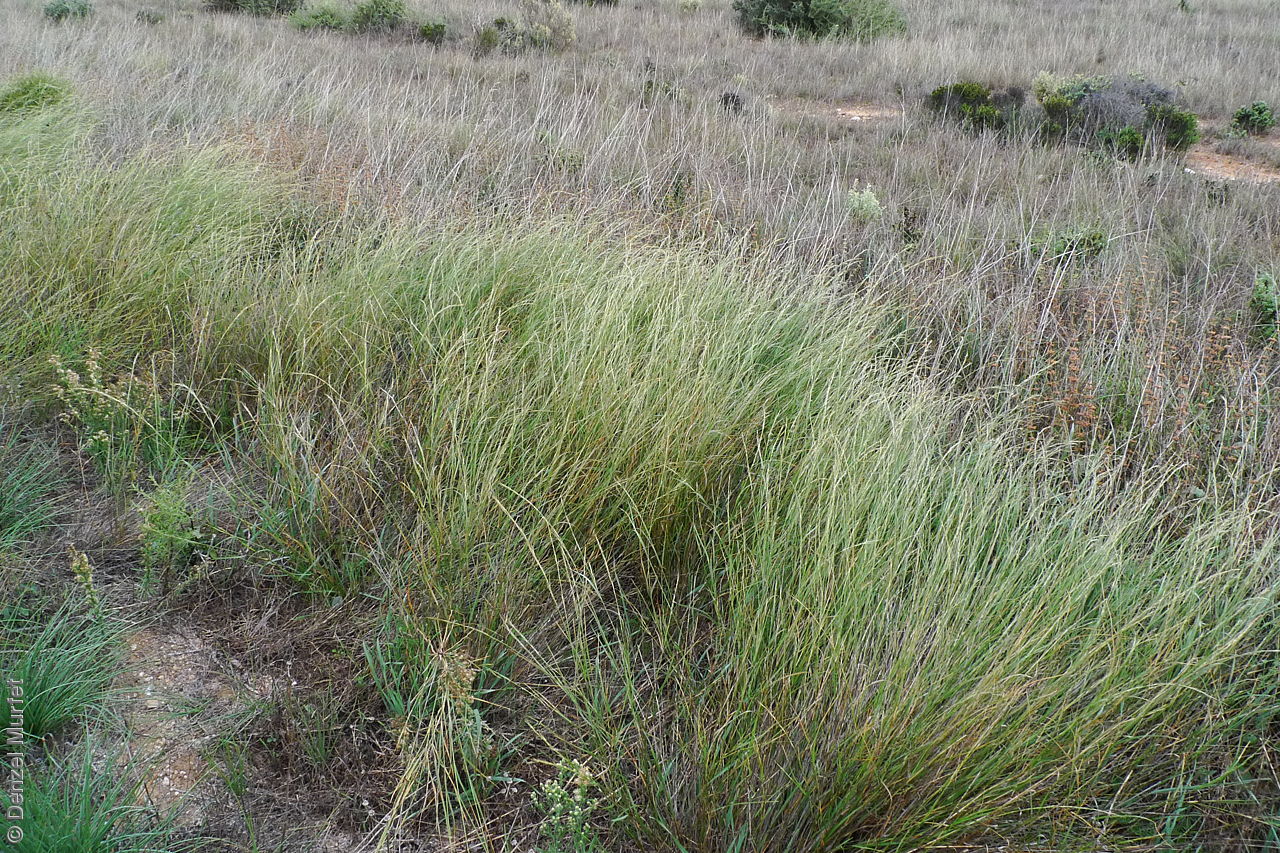
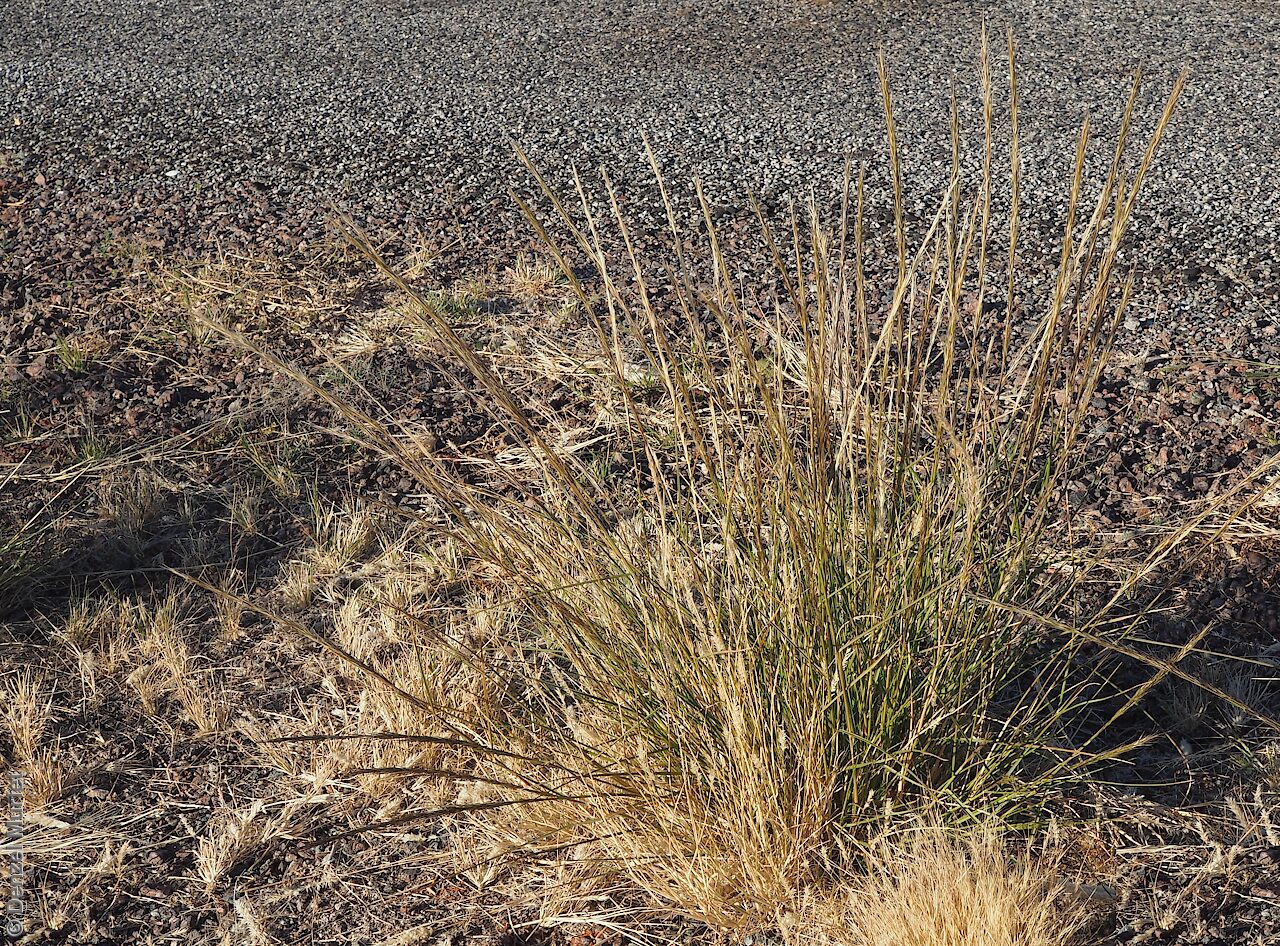
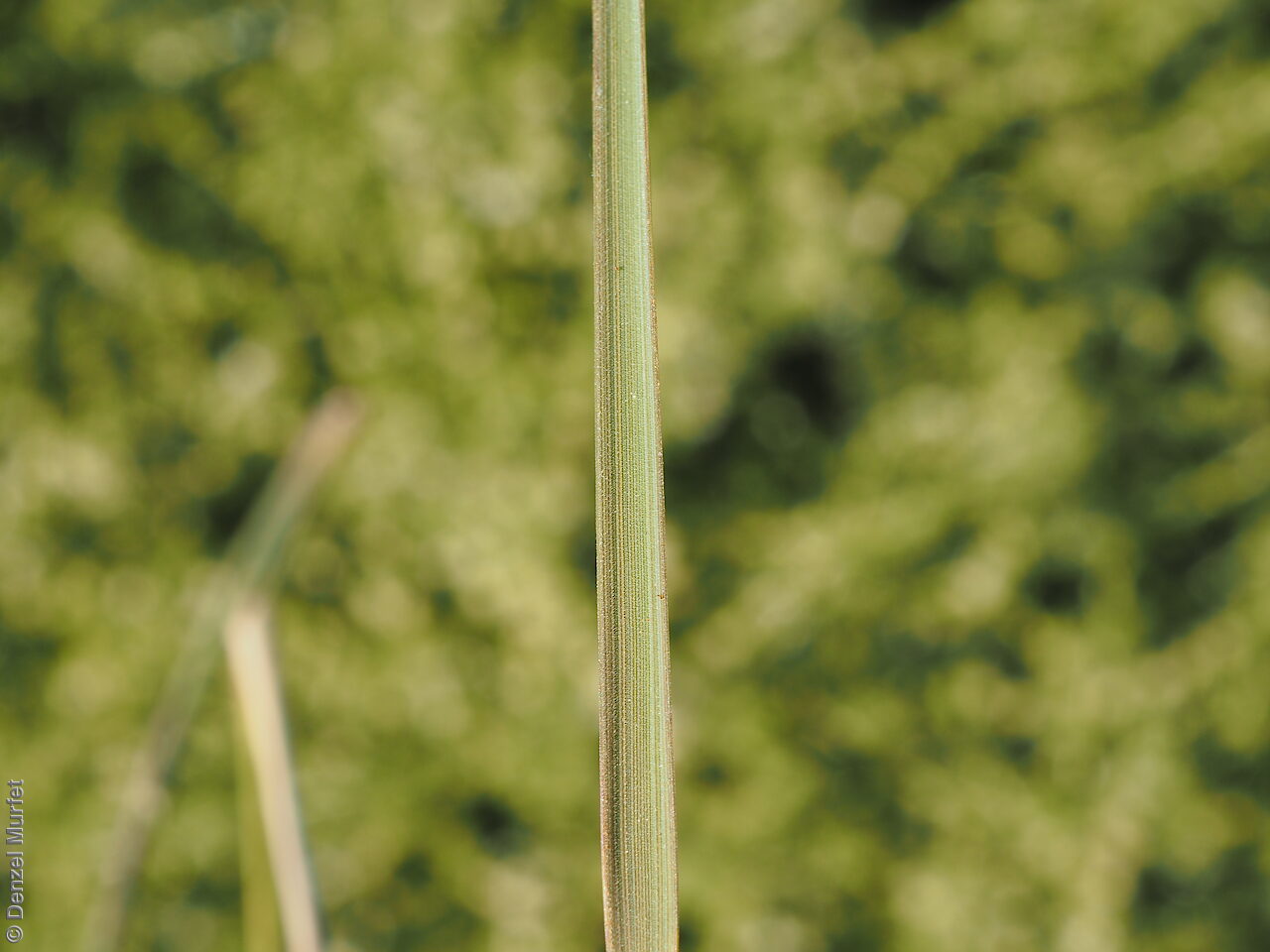
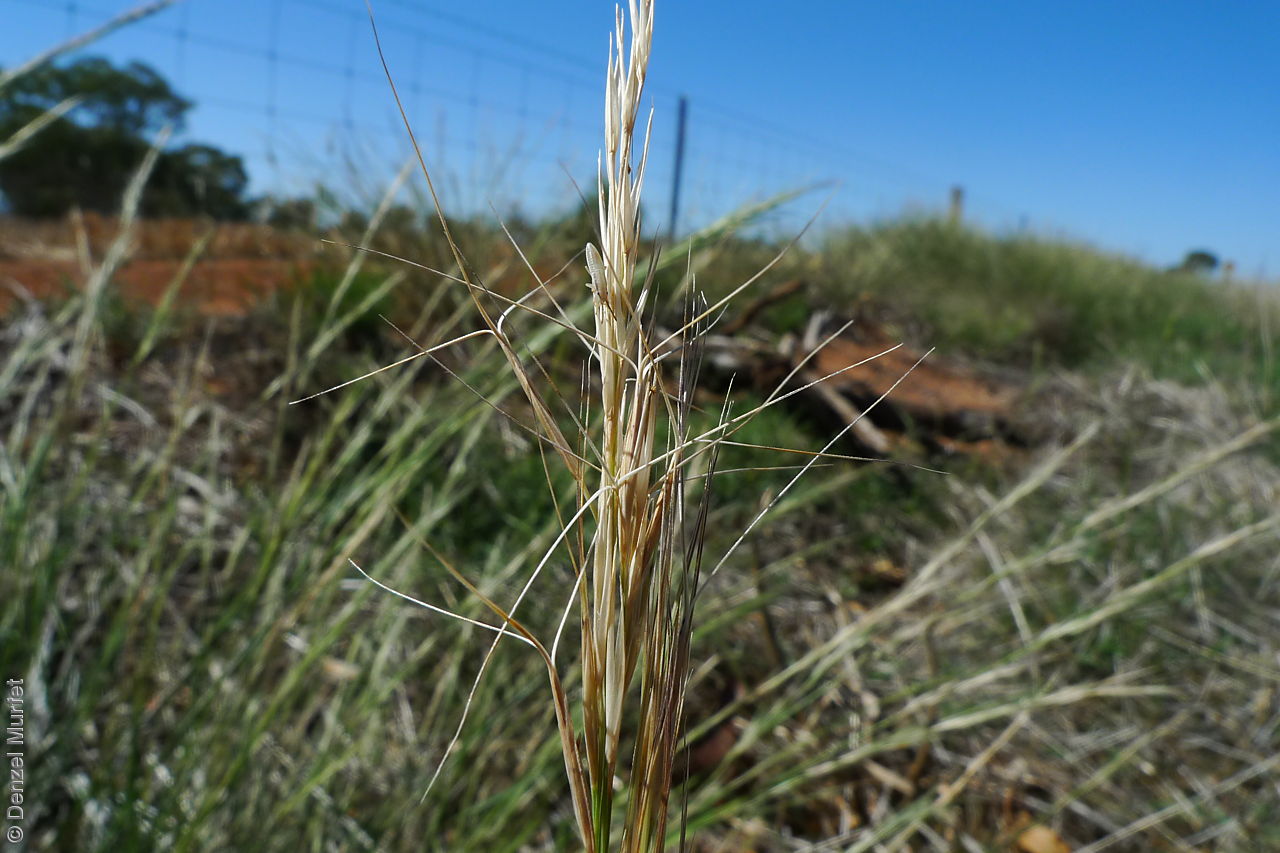
Plant description
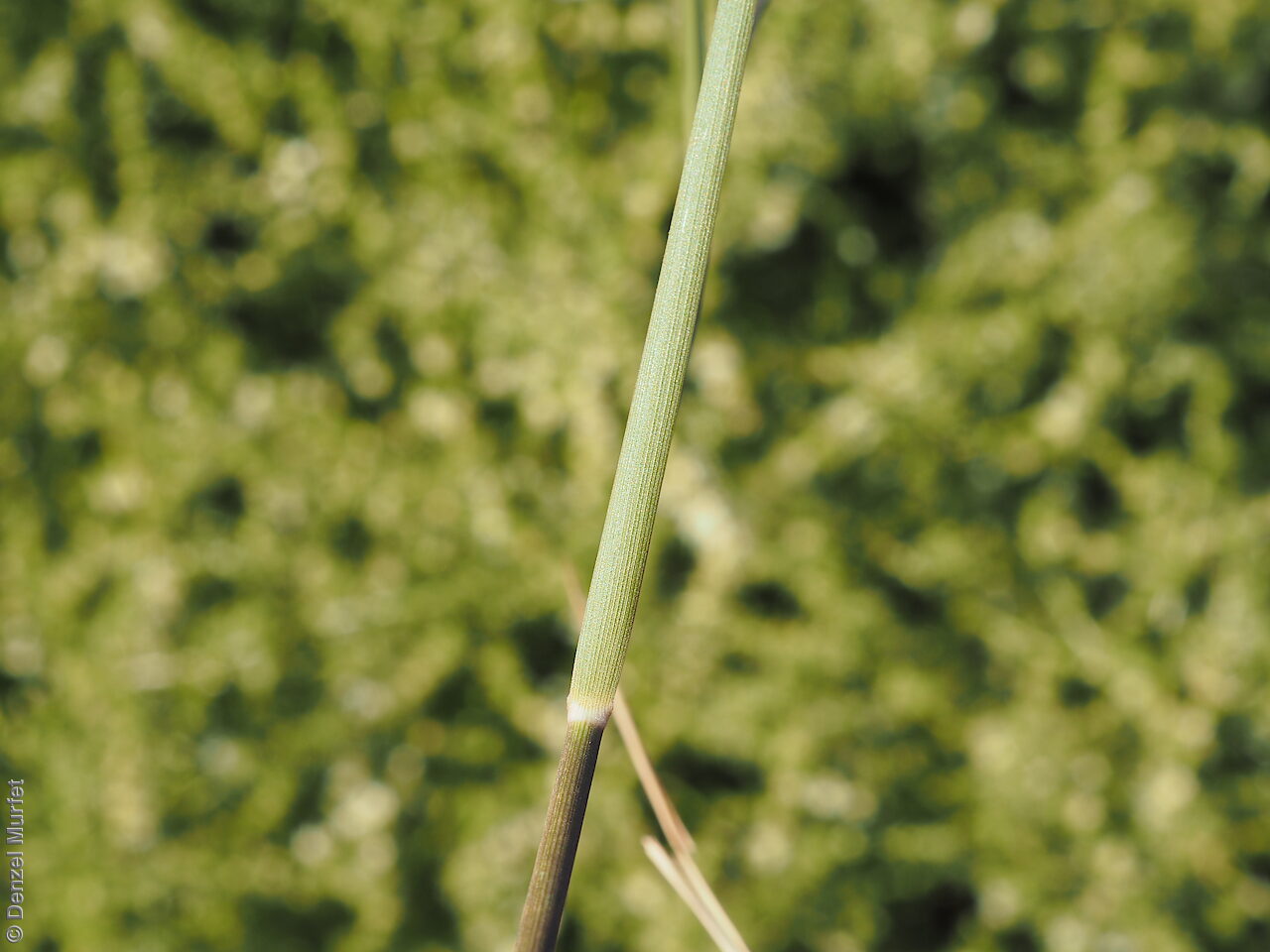
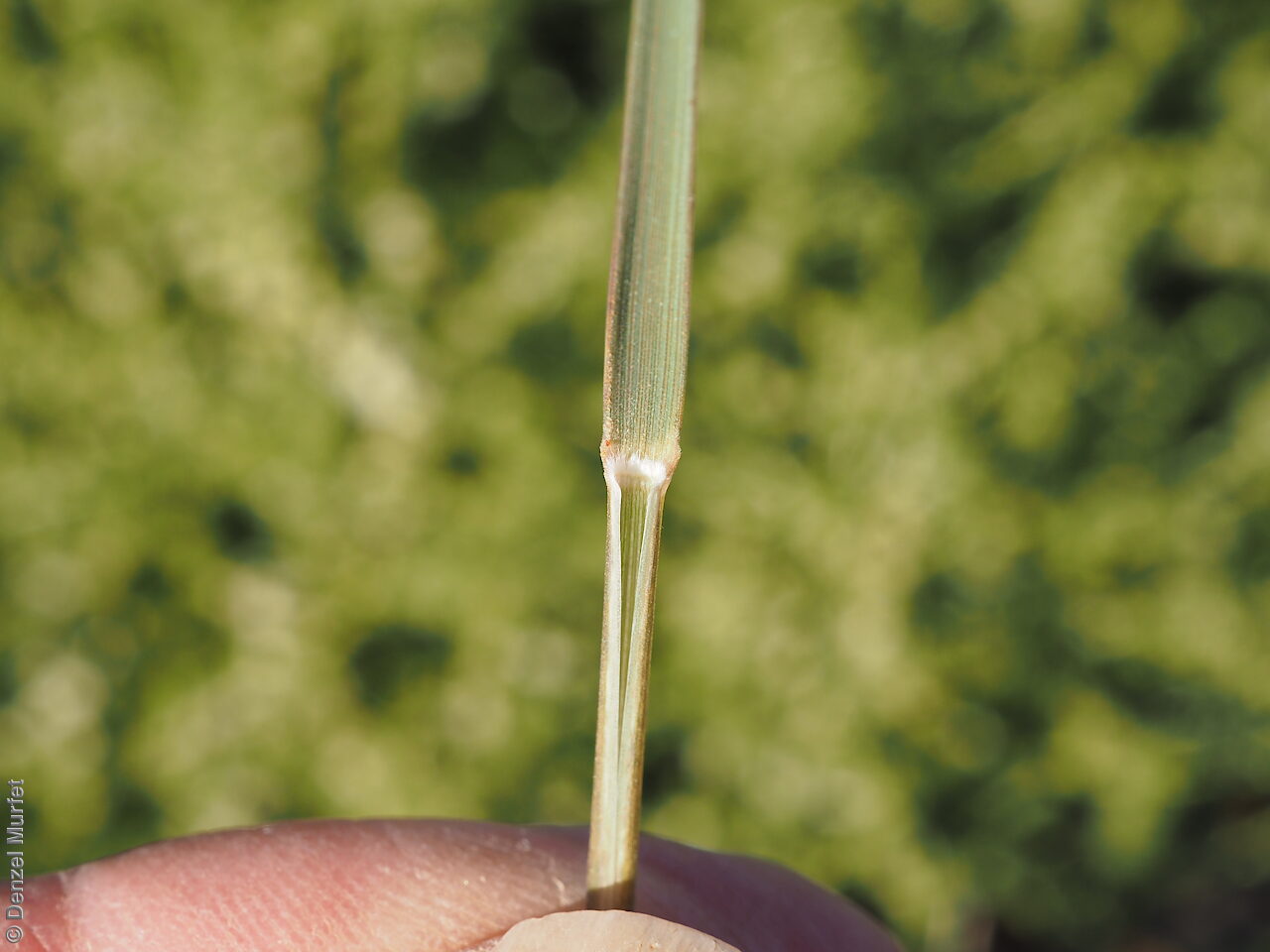
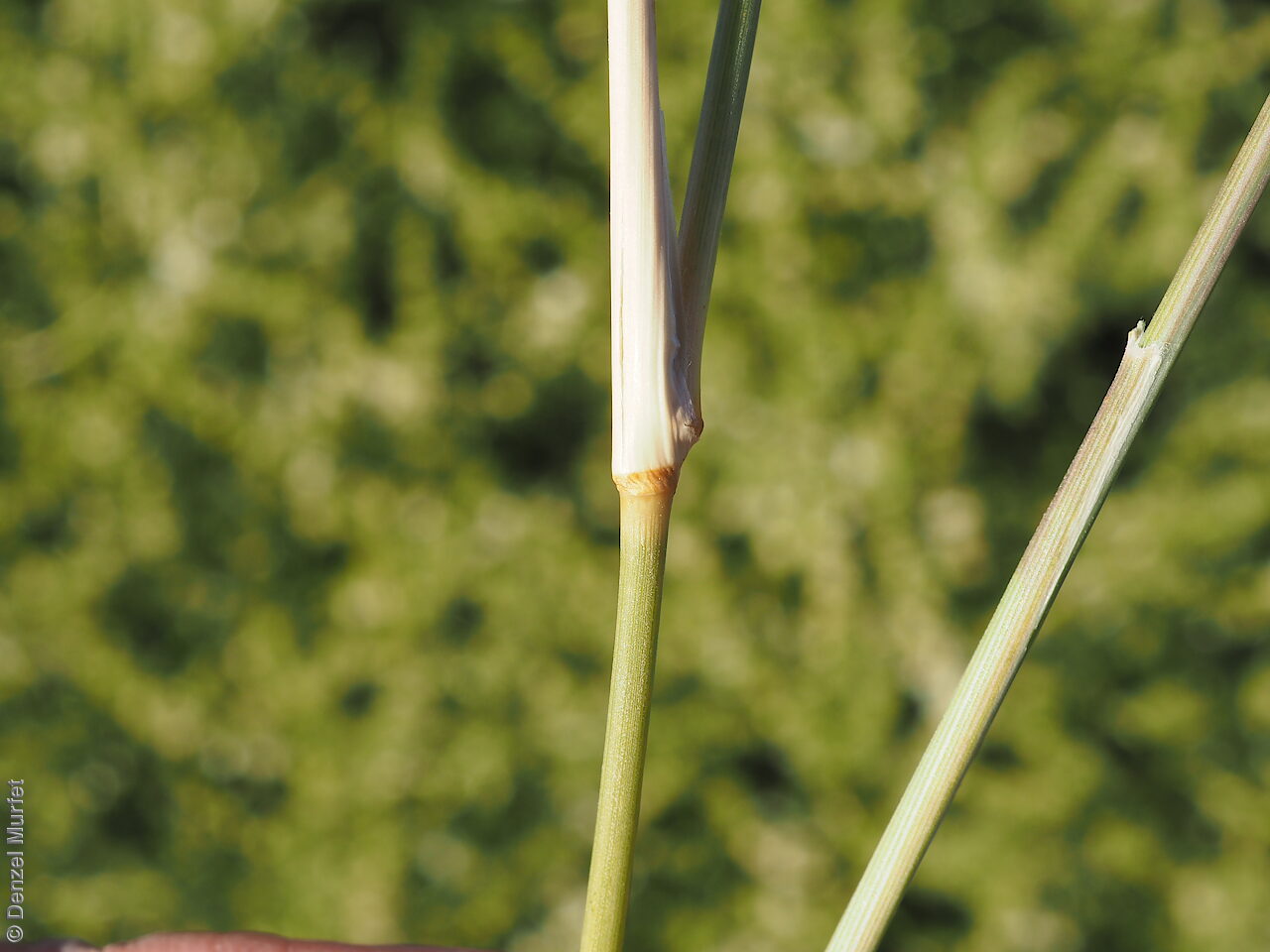
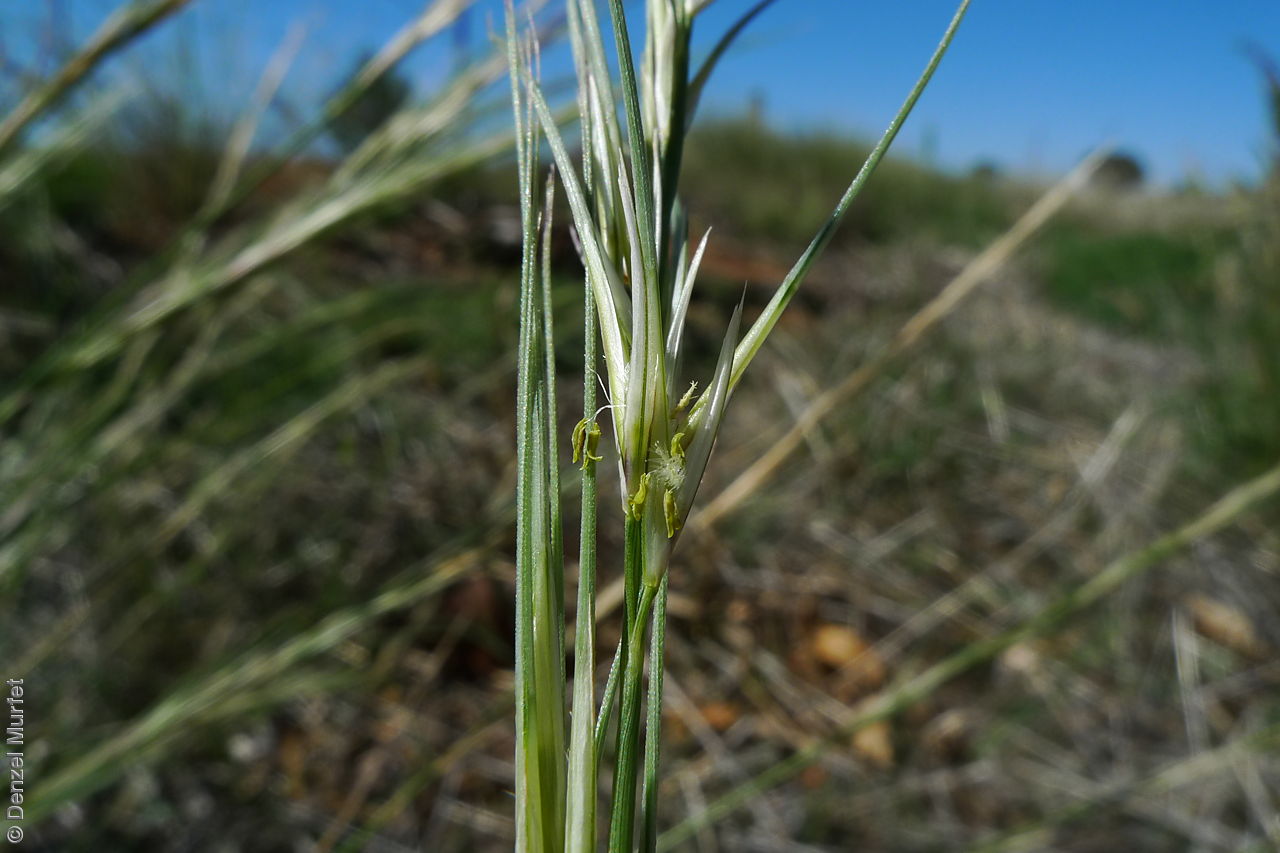
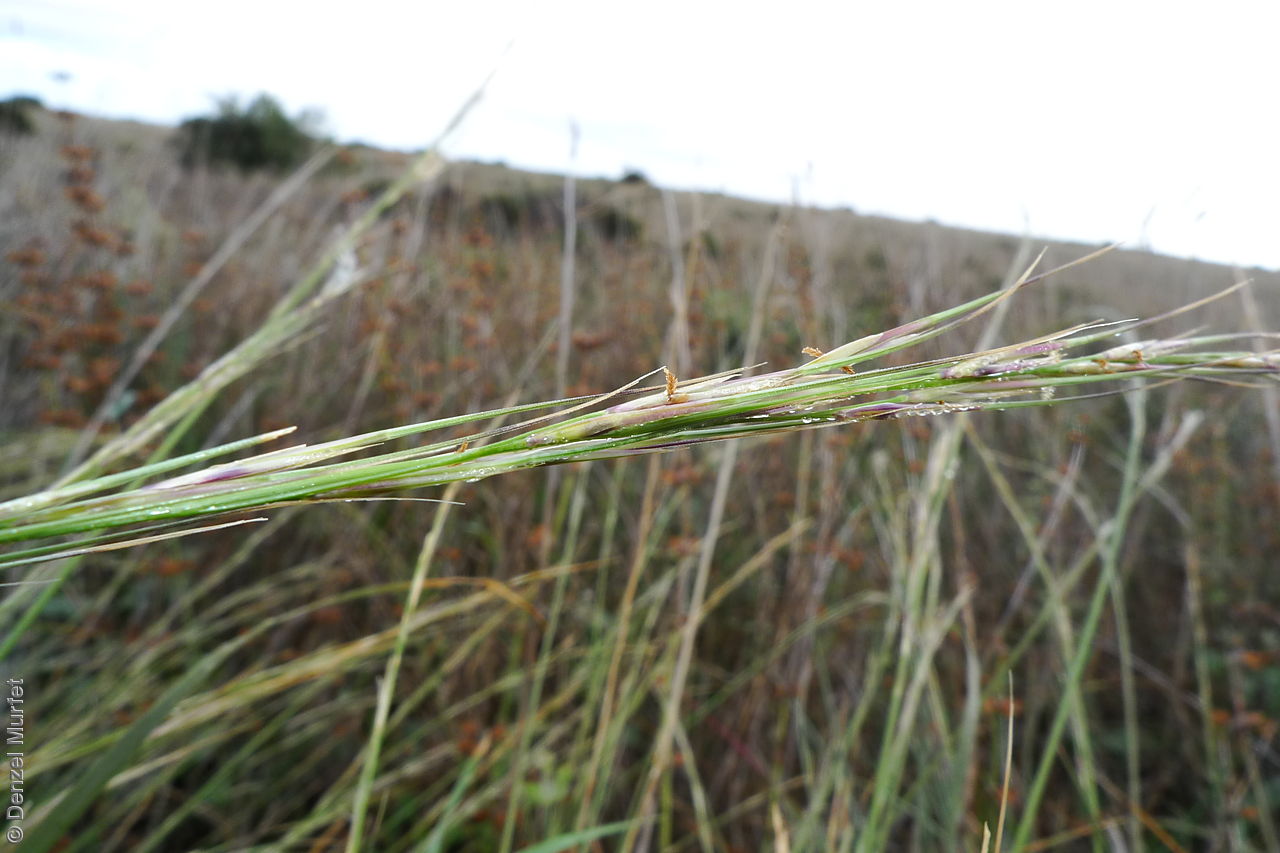
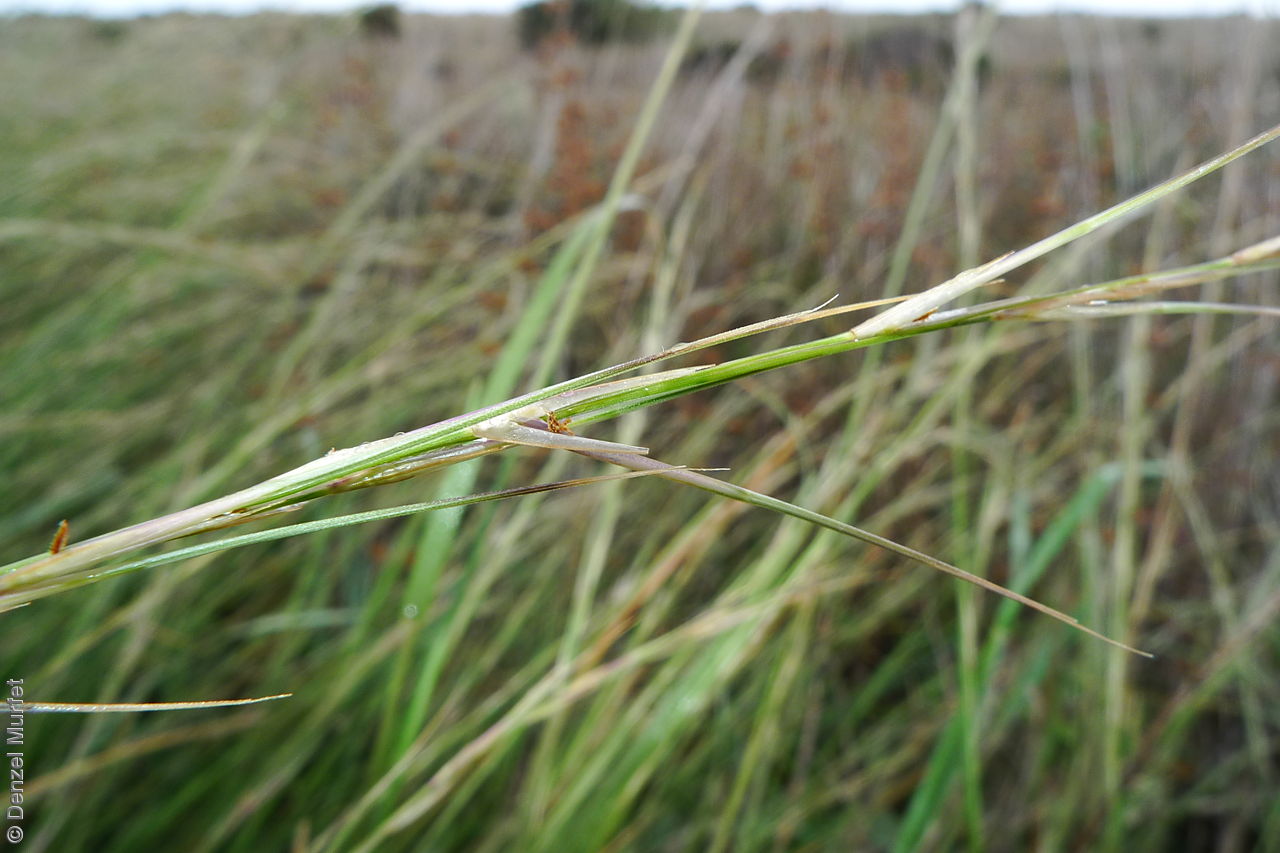
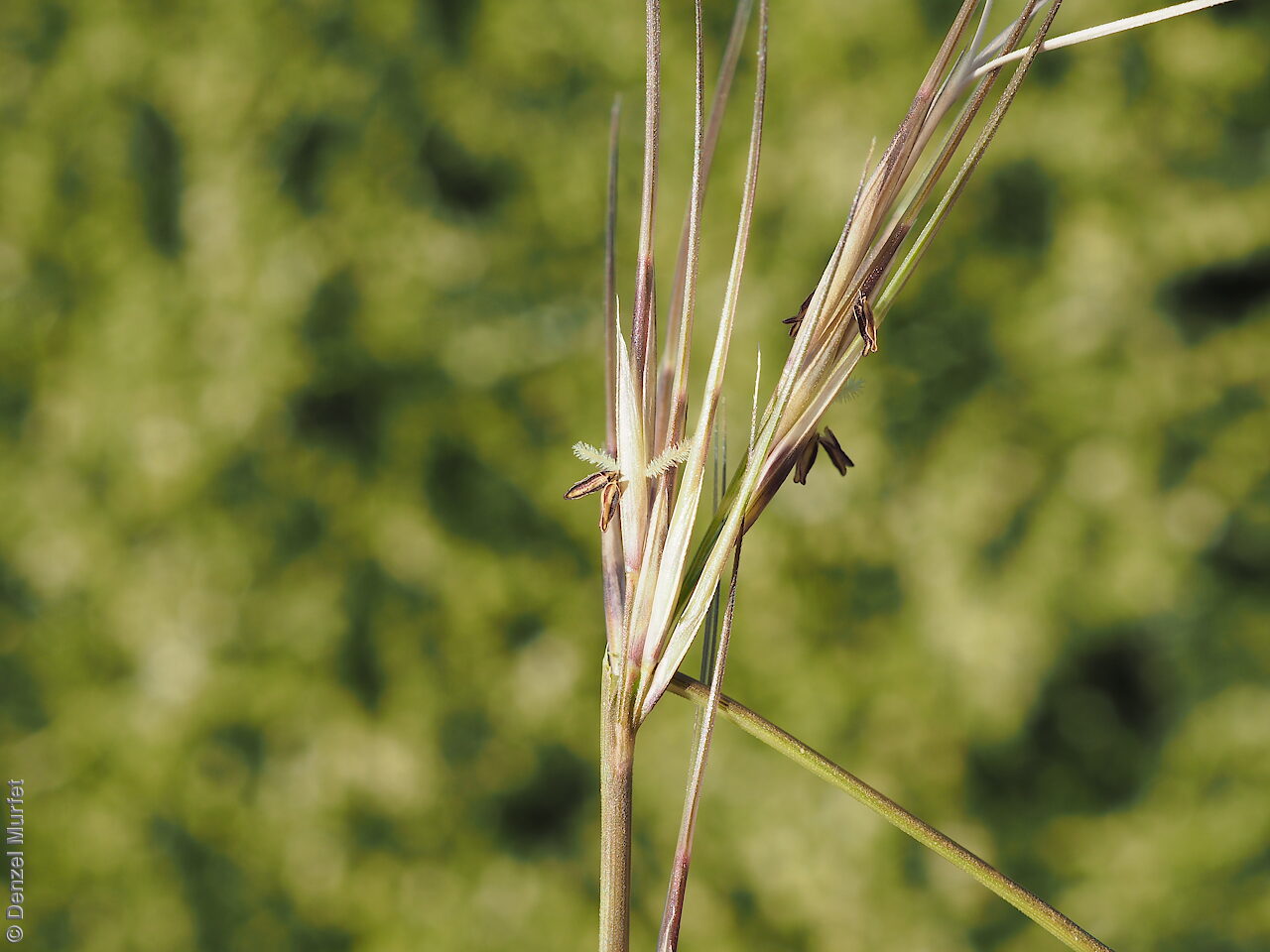
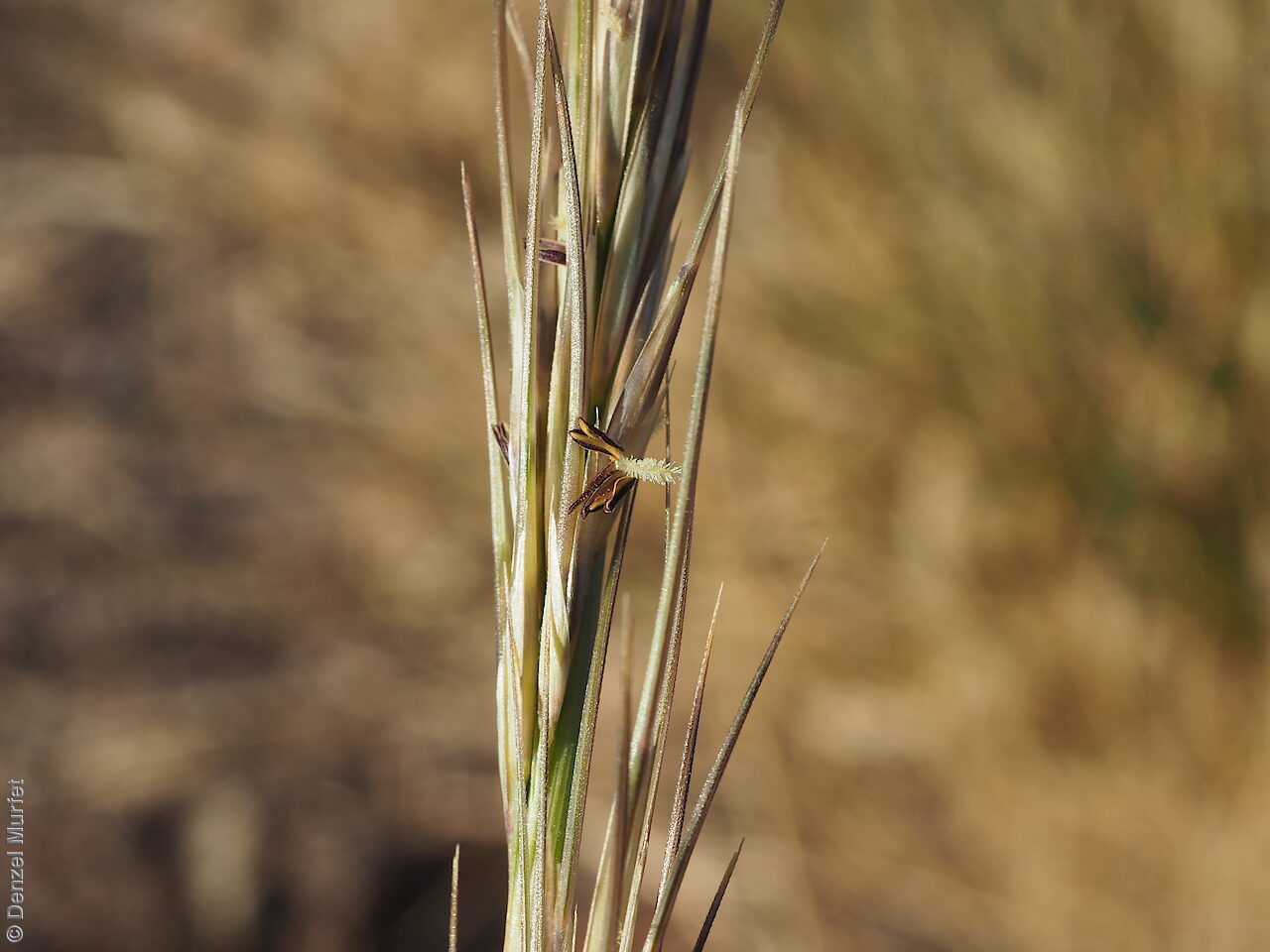
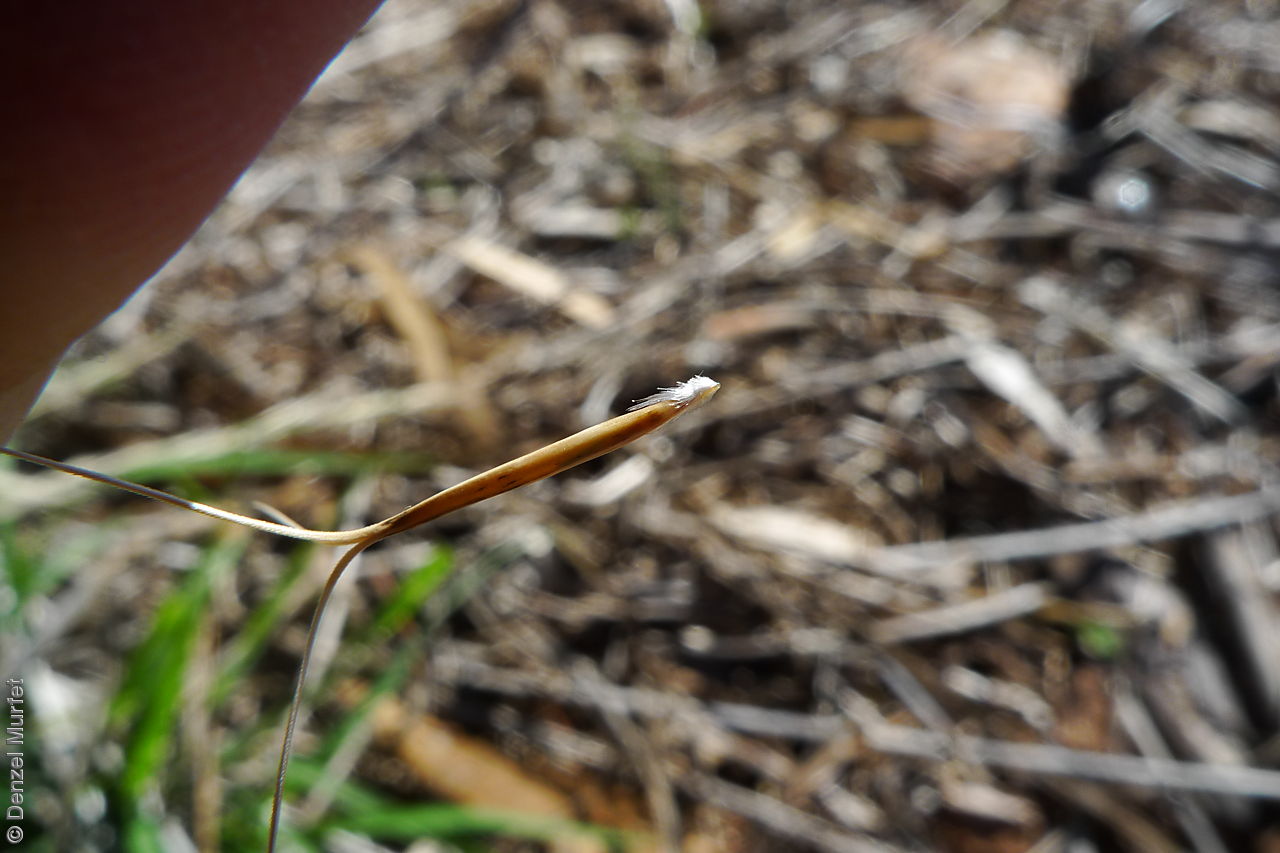
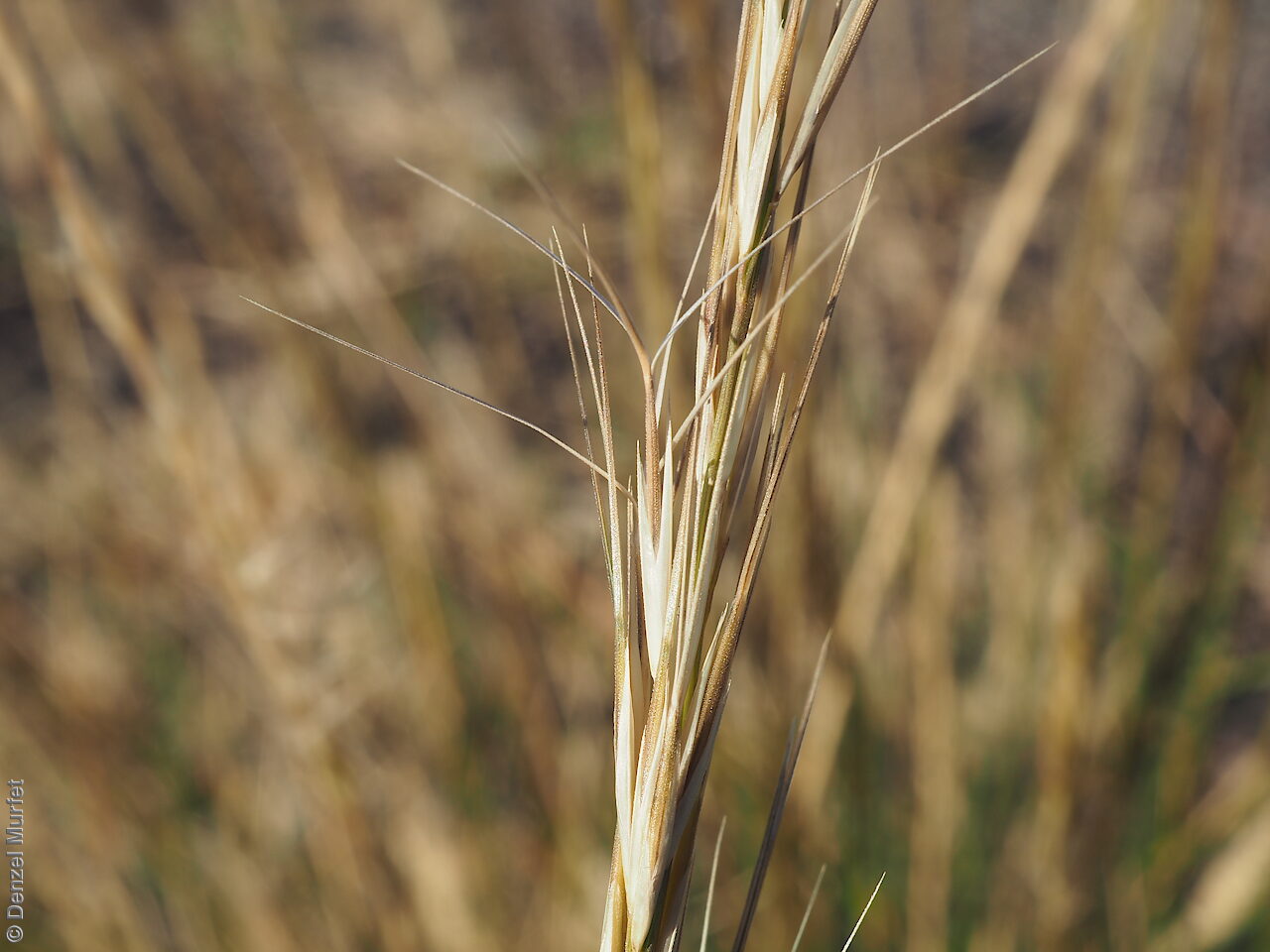
Tussocky perennial to 1.2 m high, with culms erect and cane-like. Leaves with sheath often tuberculate, ligule to 1 mm long and blade flattened in the lower part or convolute, long-scabrous above, often pilose near the ligule. Inflorescence a rather sparse, often interrupted, slender to somewhat spreading panicle, to 30 cm long; glumes narrow-acuminate, sometimes with an awn to 2 mm long, purplish, the lower to 10 mm long, the upper to 12 mm long and up to 4 mm longer than the lower; lemma convolute, narrow-cylindric, to 12 mm long, glabrous except for short, white callus hairs, surface smooth, pale or purplish; awn branches subequal, to 25 mm long. Flowering during the summer months. Fruits are pale brown with three unequal awns as long or longer than the base. Seed embryo type is lateral.
Seed collection and propagation
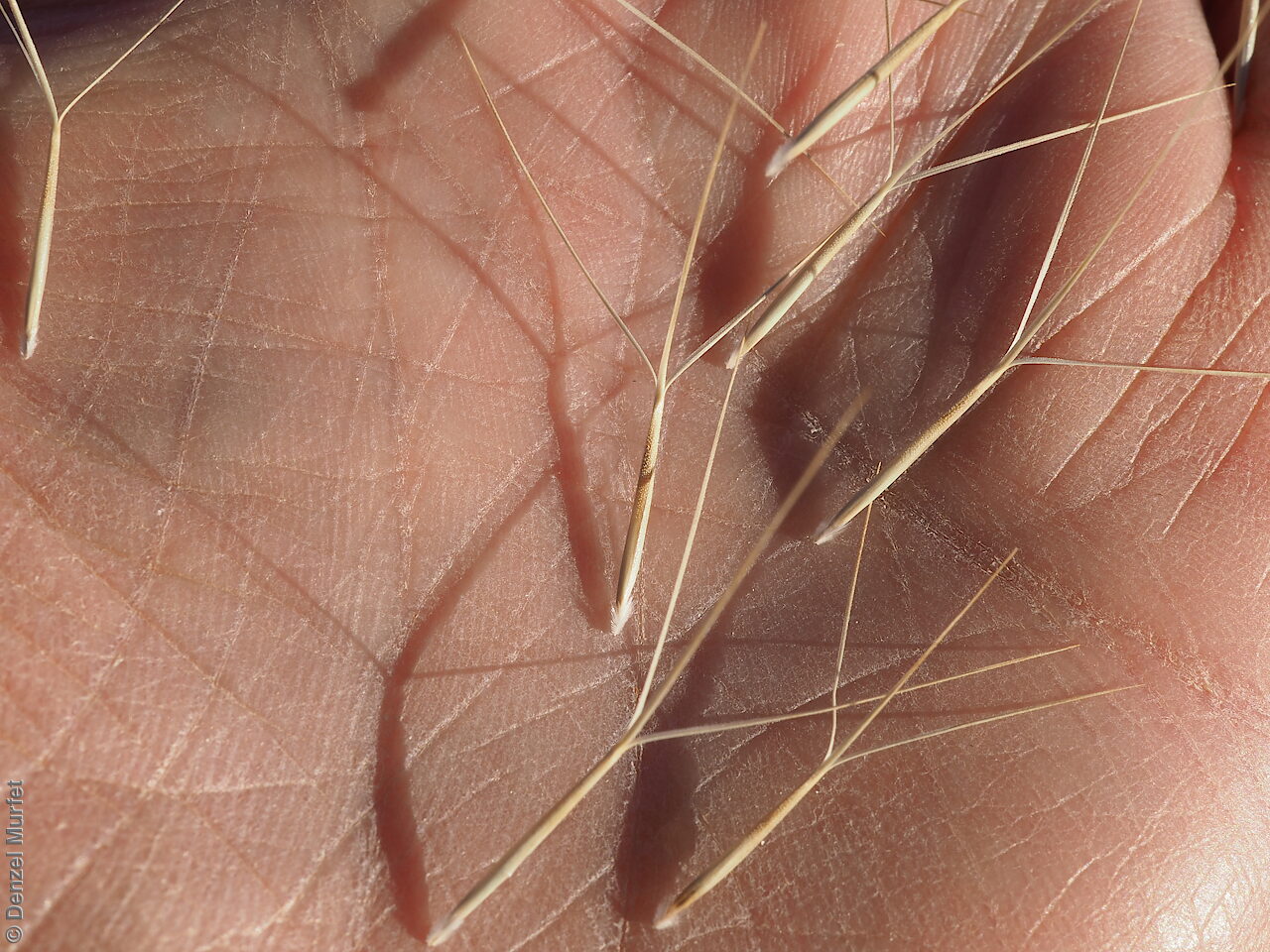
Collect seeds between January and April. Use hands to gently strip seeds off the mature seed spike that are turning straw colour. Mature seeds will come off easily. Alternatively, you can break off the whole seed spike. Place the seeds/spike in a tray and leave to dry for two weeks. No further cleaning is required if only seed collected. If seed spikes collected, use hand to strip off the mature seeds. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place. Seed viability can be low.
| Location | No. of seeds (weight grams) | Number of plants | Date collected | Collection number Collection location | Date stored | % Viability | Storage temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSB | 9,400 (19.79 g) | 50 | 18-Jan-2007 | RJB71281 Northern Lofty |
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.