Australian Boxthorn
Display all 14 images














Regional Species Conservation Assessments per IBRA subregion.

Least concern
Near threatened
Rare
Vulnerable
Endangered
Critically endangered
Extinct
Data deficient
Adelaide
Arkaroola
Ceduna
Coober Pedy
Hawker
Innamincka
Marla
Marree
Mount Gambier
Oodnadatta
Renmark
Wudinna
Keith
Yunta
Display IBRA region text
| Fleurieu (KAN02) | Kanmantoo | Endangered (IUCN: EN B2ab(i,ii,iii)) (Probable Decline) [a few scattered pops at Hartley, Waitpinga, Wirrinna; no recruitment; often mistaken for African boxthrorn & sprayed] |
| Mount Lofty Ranges (FLB01) | Flinders Lofty Block | Endangered (IUCN: EN B2ab(i,ii,iii)) (Probable Decline) [a few scattered pops; Hallett Cove, Gawler, few others; often mistaken for African boxthrorn & sprayed] |
| Broughton (FLB02) | | Least Concern |
| Olary Spur (FLB03) | | Least Concern |
| Southern Flinders (FLB04) | | Least Concern |
| Northern Flinders (FLB05) | | Data Deficient [no vouchered records] |
| Central Flinders (FLB06) | | Near Threatened |
| Southern Yorke (EYB01) | Eyre Yorke Block | Least Concern |
| St Vincent (EYB02) | | Least Concern |
| Eyre Hills (EYB03) | | Least Concern |
| Talia (EYB04) | | Least Concern |
| Eyre Mallee (EYB05) | | Least Concern |
| South Olary Plain (MDD01) | Murray Darling Depression | Least Concern |
| Murray Mallee (MDD02) | | Least Concern |
| Braemer (MDD07) | | Least Concern |
| Murray Scroll Belt (RIV06) | Riverina | Near Threatened [not typical habitat] |
| Myall Plains (GAW01) | Gawler | Least Concern |
| Gawler Volcanics (GAW02) | | Least Concern |
| Gawler Lakes (GAW03) | | Least Concern |
| Arcoona Plateau (GAW04) | | Least Concern |
| Kingoonya (GAW05) | | Least Concern |
| Torrens (GAW06) | | Least Concern |
| Roxby (GAW07) | | Least Concern |
| Commonwealth Hill (GAW08) | | Least Concern |
| Maralinga (GVD03) | Great Victoria Desert | Least Concern |
| Tallaringa (GVD05) | | Near Threatened [edge of range] |
| Yellabinna (GVD06) | | Least Concern |
| Carlisle (NUL01) | Nullarbor | Least Concern |
| Nullarbor Plain (NUL02) | | Least Concern |
| Yalata (NUL03) | | Least Concern |
| Hampton (HAM01) | Hampton | Least Concern |
| Barrier Range (BHC01) | Broken Hill Complex | Least Concern |
| Bimbowrie (BHC05) | | Least Concern |
| Warriner (SSD04) | Simpson Strzelecki Dunefields | Rare (IUCN: RA d(ii)) |
| Breakaways (STP01) | Stony Plains | Least Concern |
| Baltana (STP07) | | Rare (IUCN: RA d(ii)) |
| Sturt Stony Desert (CHC02) | Channel Country | Data Deficient |
| Fleurieu (KAN02) | Kanmantoo | Endangered (IUCN: EN B2ab(i,ii,iii)) (Probable Decline) [a few scattered pops at Hartley, Waitpinga, Wirrinna; no recruitment; often mistaken for African boxthrorn & sprayed] |
| 6 of 6 subregions | Flinders Lofty Block | Least Concern , Near Threatened , Endangered , Data Deficient |
| 5 of 5 subregions | Eyre Yorke Block | Least Concern |
| 3 of 6 subregions | Murray Darling Depression | Least Concern |
| Murray Scroll Belt (RIV06) | Riverina | Near Threatened [not typical habitat] |
| 8 of 8 subregions | Gawler | Least Concern |
| 3 of 4 subregions | Great Victoria Desert | Least Concern , Near Threatened |
| 3 of 3 subregions | Nullarbor | Least Concern |
| Hampton (HAM01) | Hampton | Least Concern |
| 2 of 4 subregions | Broken Hill Complex | Least Concern |
| Warriner (SSD04) | Simpson Strzelecki Dunefields | Rare (IUCN: RA d(ii)) |
| 2 of 7 subregions | Stony Plains | Least Concern , Rare |
| Sturt Stony Desert (CHC02) | Channel Country | Data Deficient |
Botanical art
Kath Alcock paintings: 2
Common names
Australian Boxthorn
Etymology
Lycium, from the Greek 'lykion', the name of a medicinal thorny shrub believed to be a native of Lycia (Asia Minor). Australe means of or from the south; referring to the distribution of the species in Australia.
Distribution and status
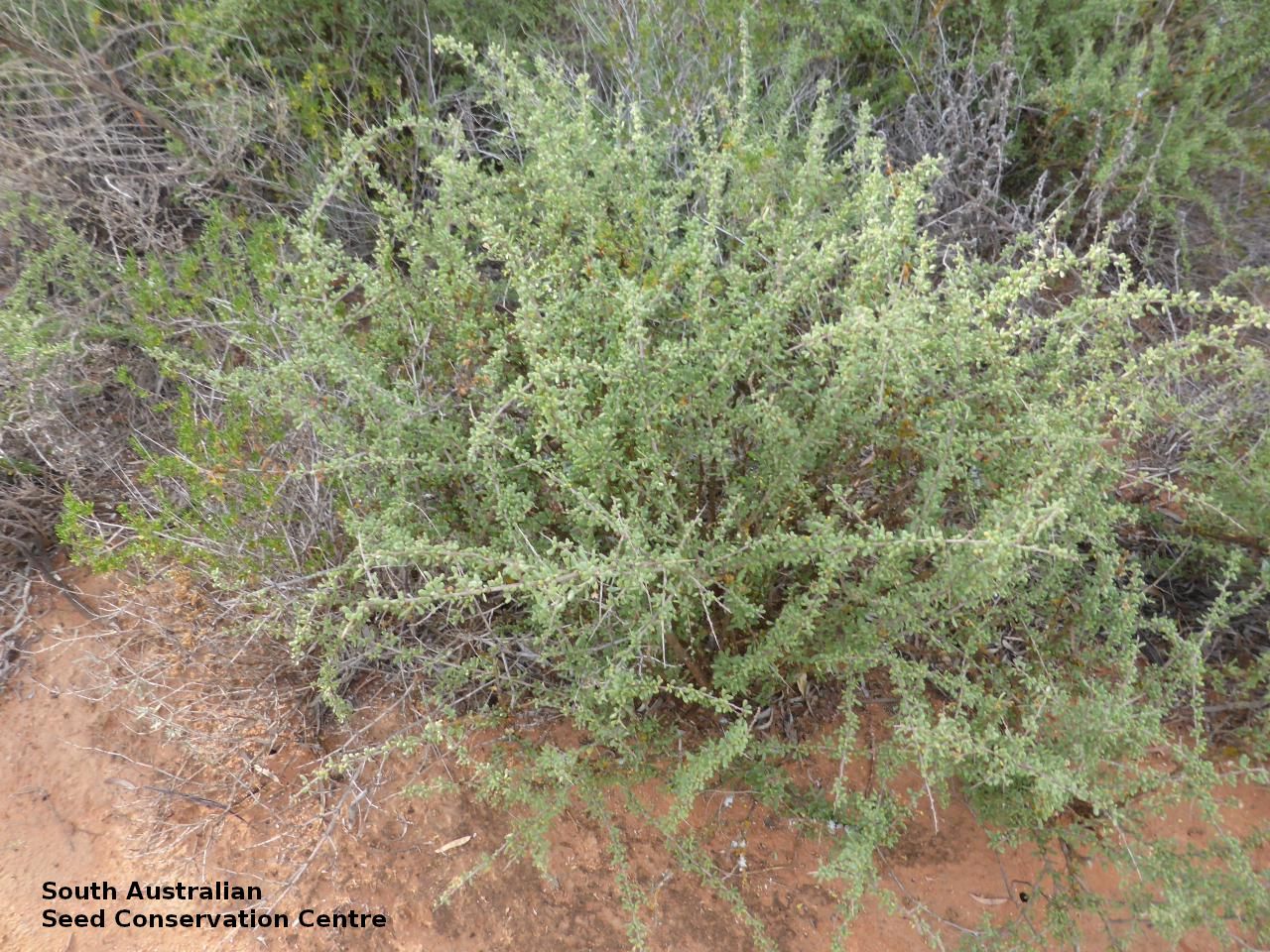
Found across the central part of South Australia, growing in open arid shrublands, mallee and woodland, often in depressions in sub-saline, usually clayey soils. Also found in Western Australia, New South Wales and Victoria, Native. Common in South Australia. Common in the other States.
Herbarium regions: North Western, Lake Eyre, Nullarbor, Gairdner-Torrens, Flinders Ranges, Eastern, Eyre Peninsula, Northern Lofty, Murray, Yorke Peninsula, Southern Lofty, Green Adelaide
AVH map: SA distribution map (external link)
Plant description
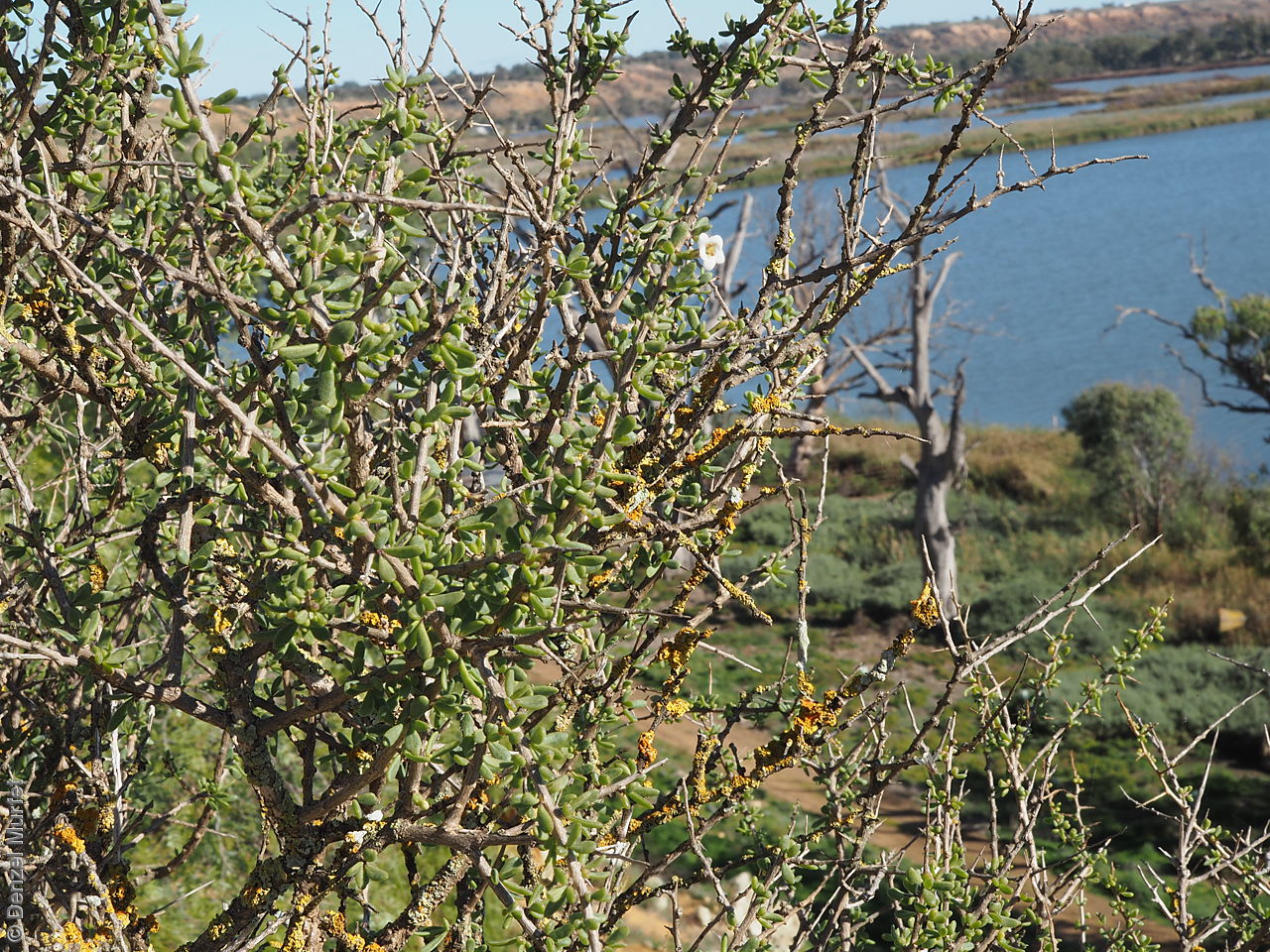
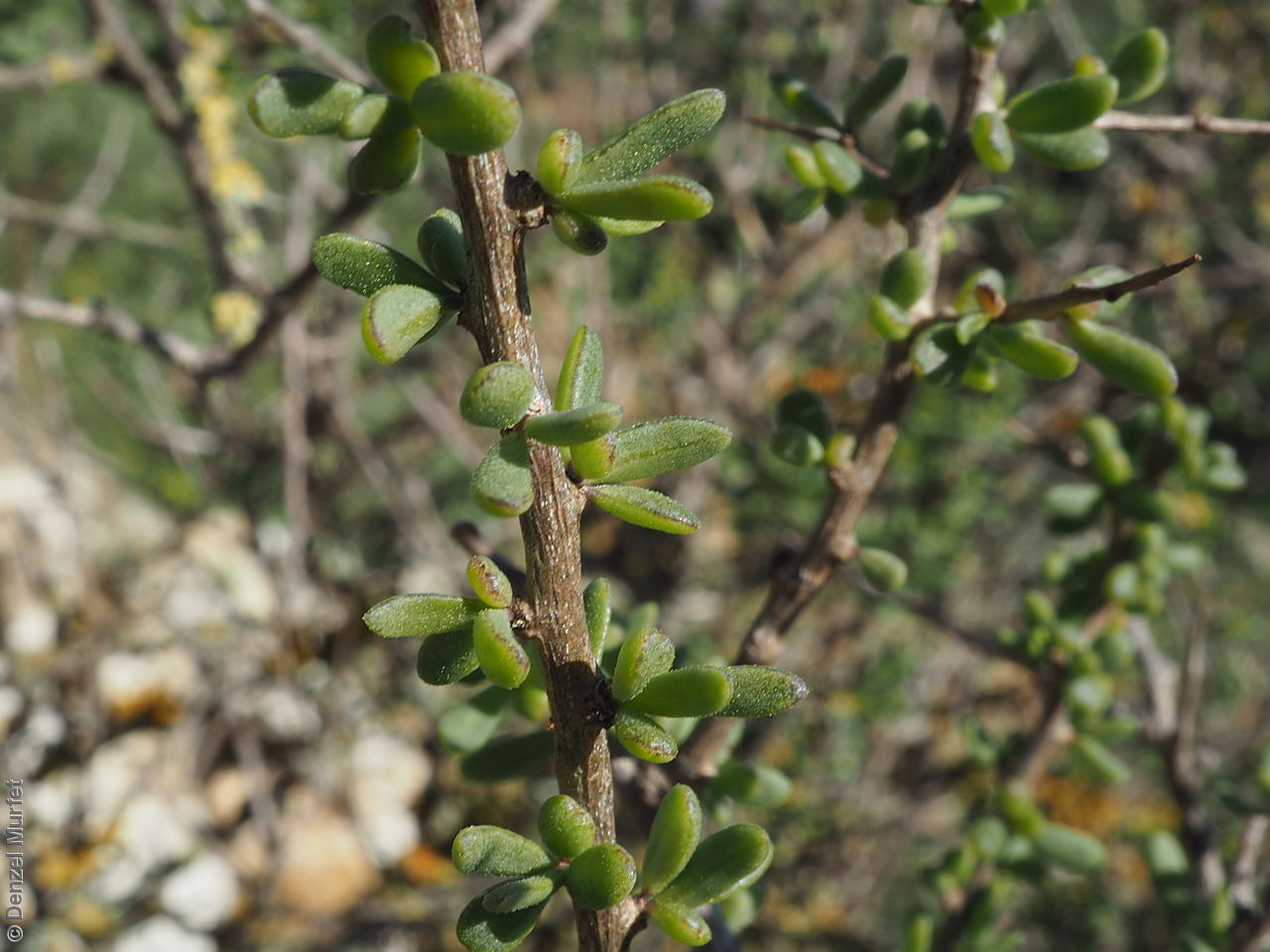
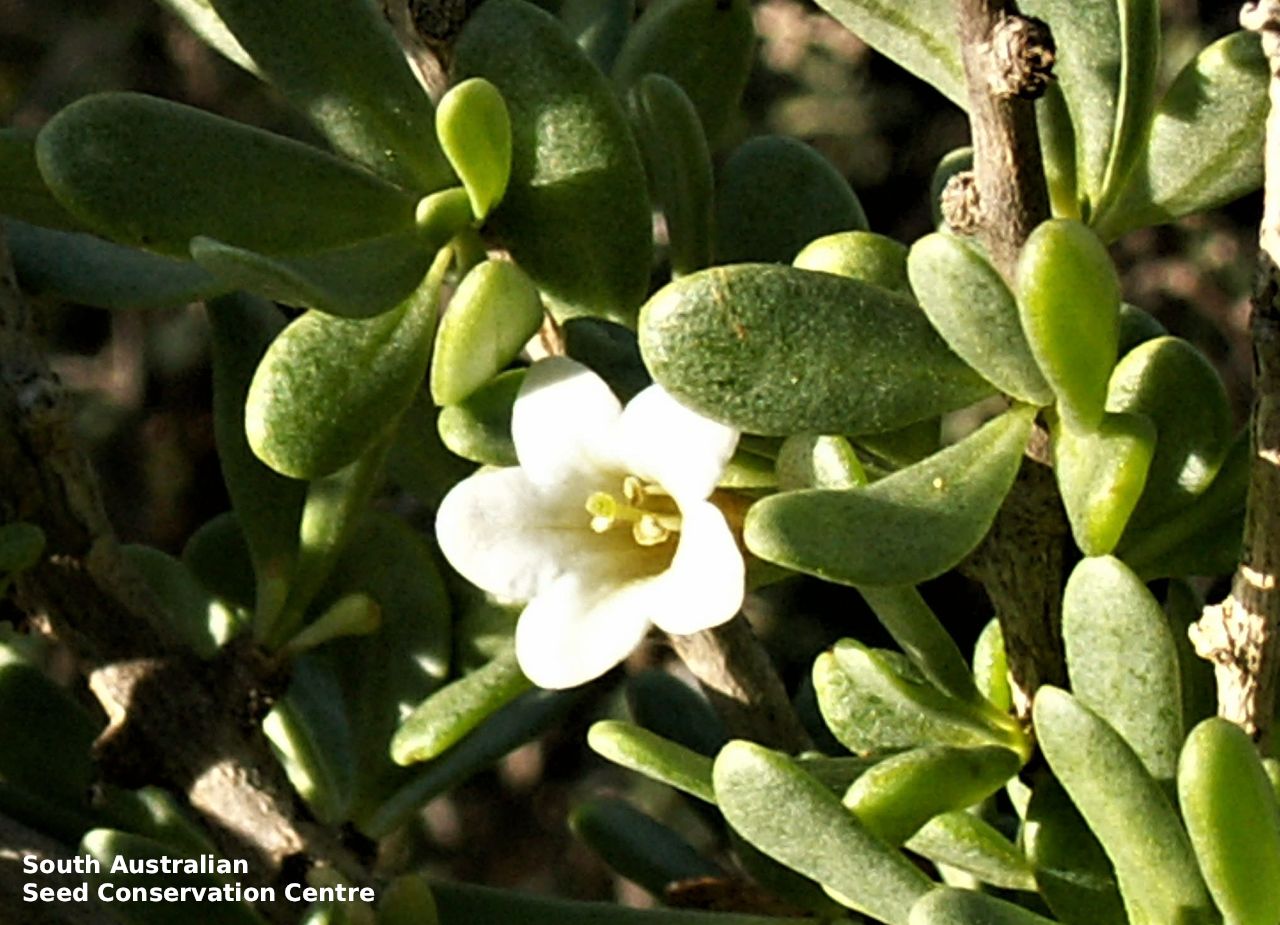
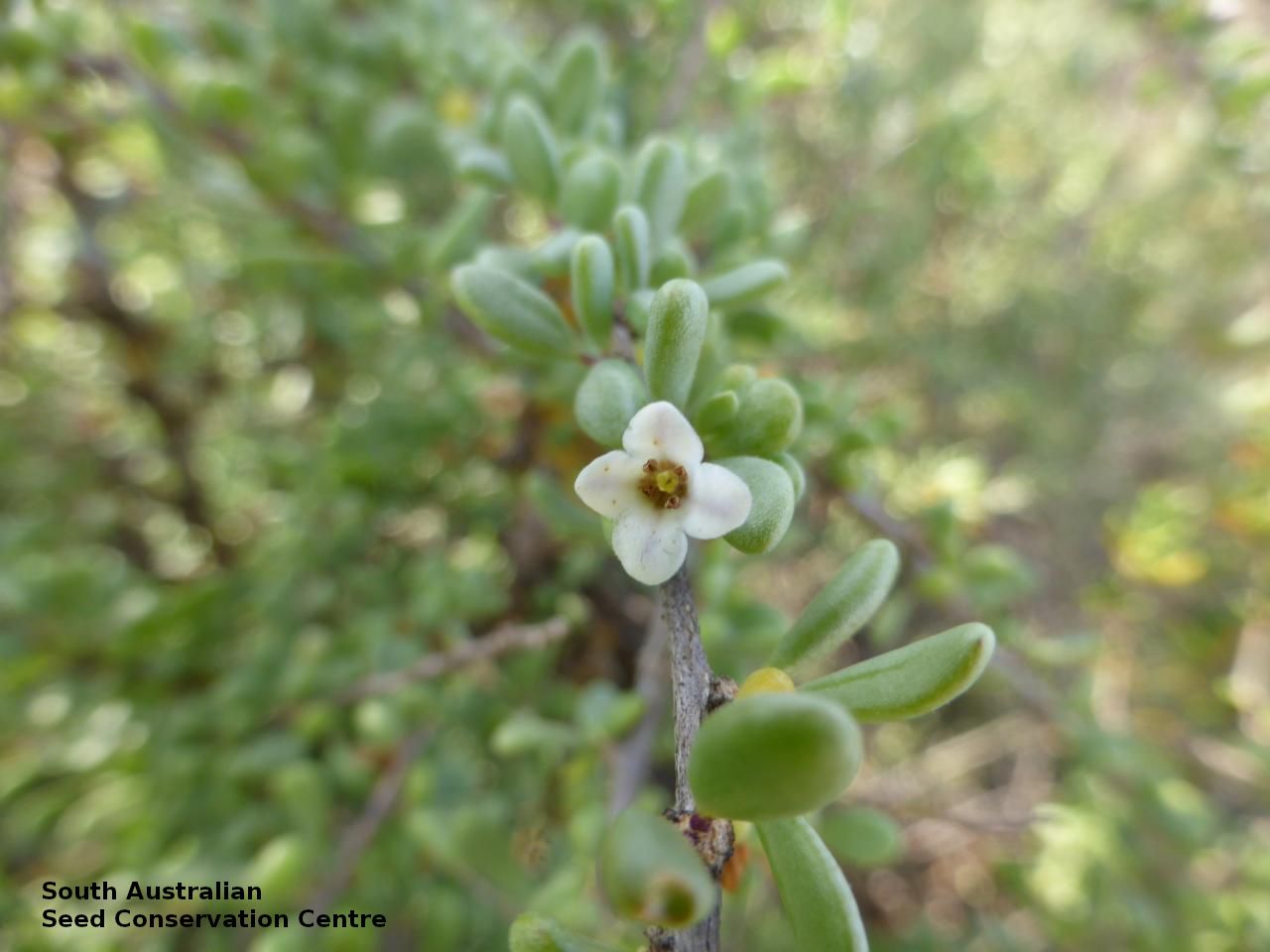
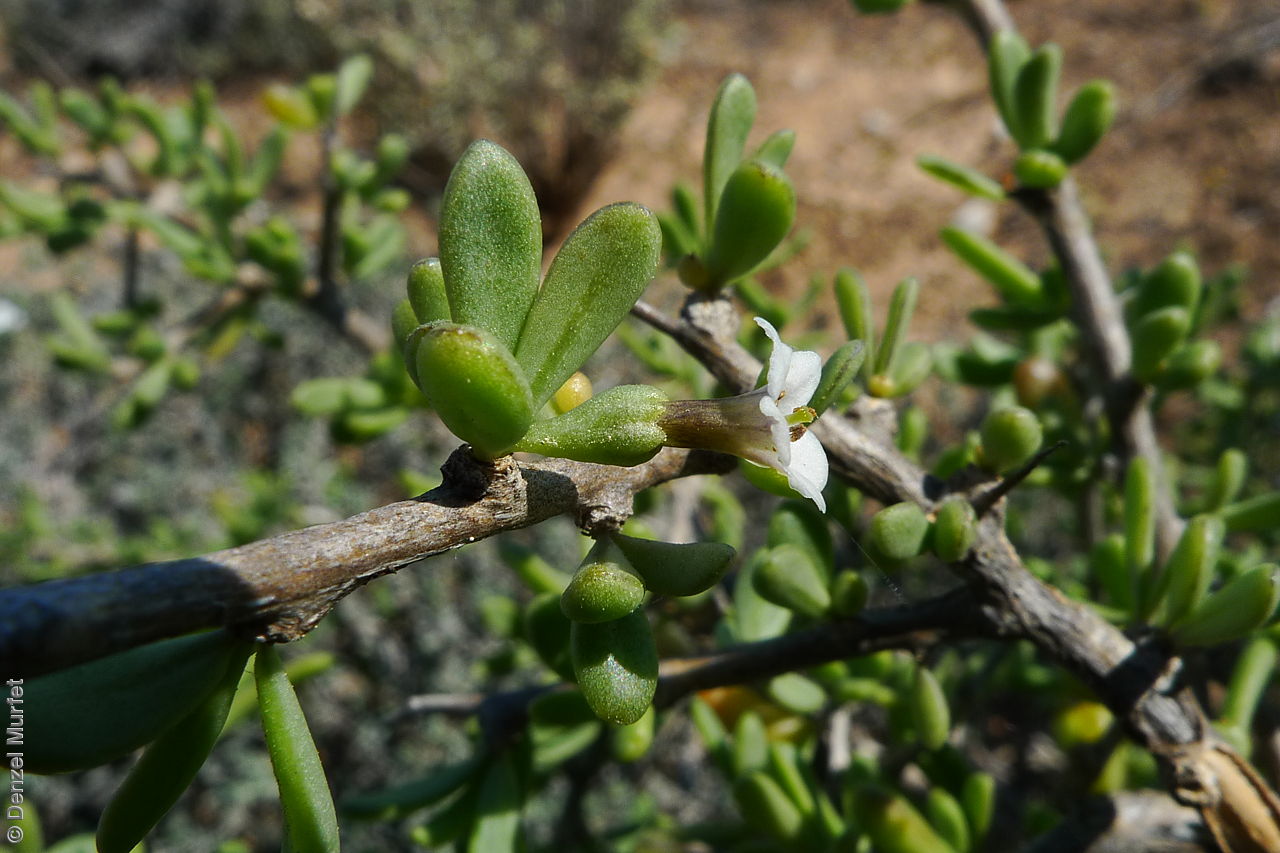
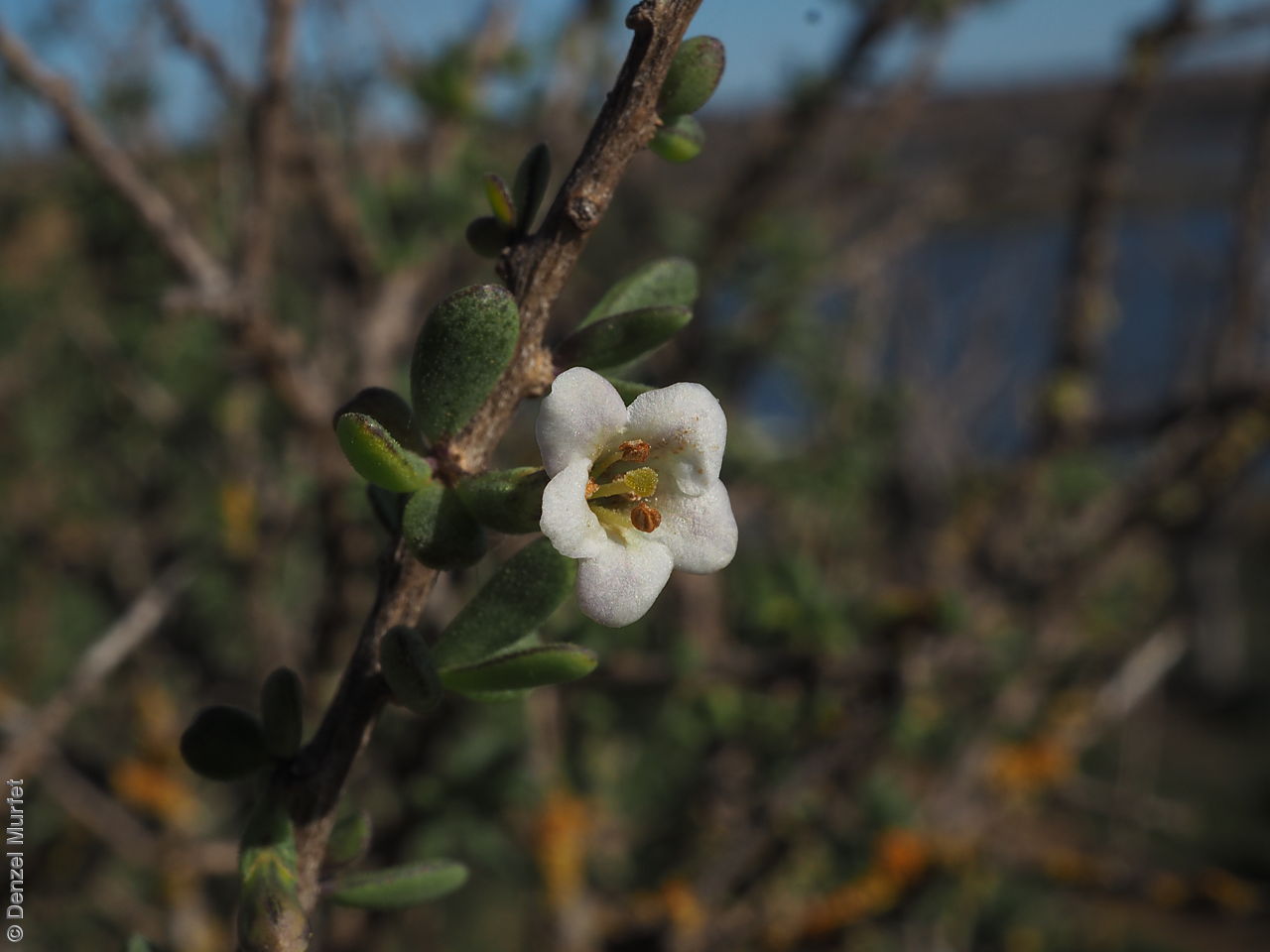
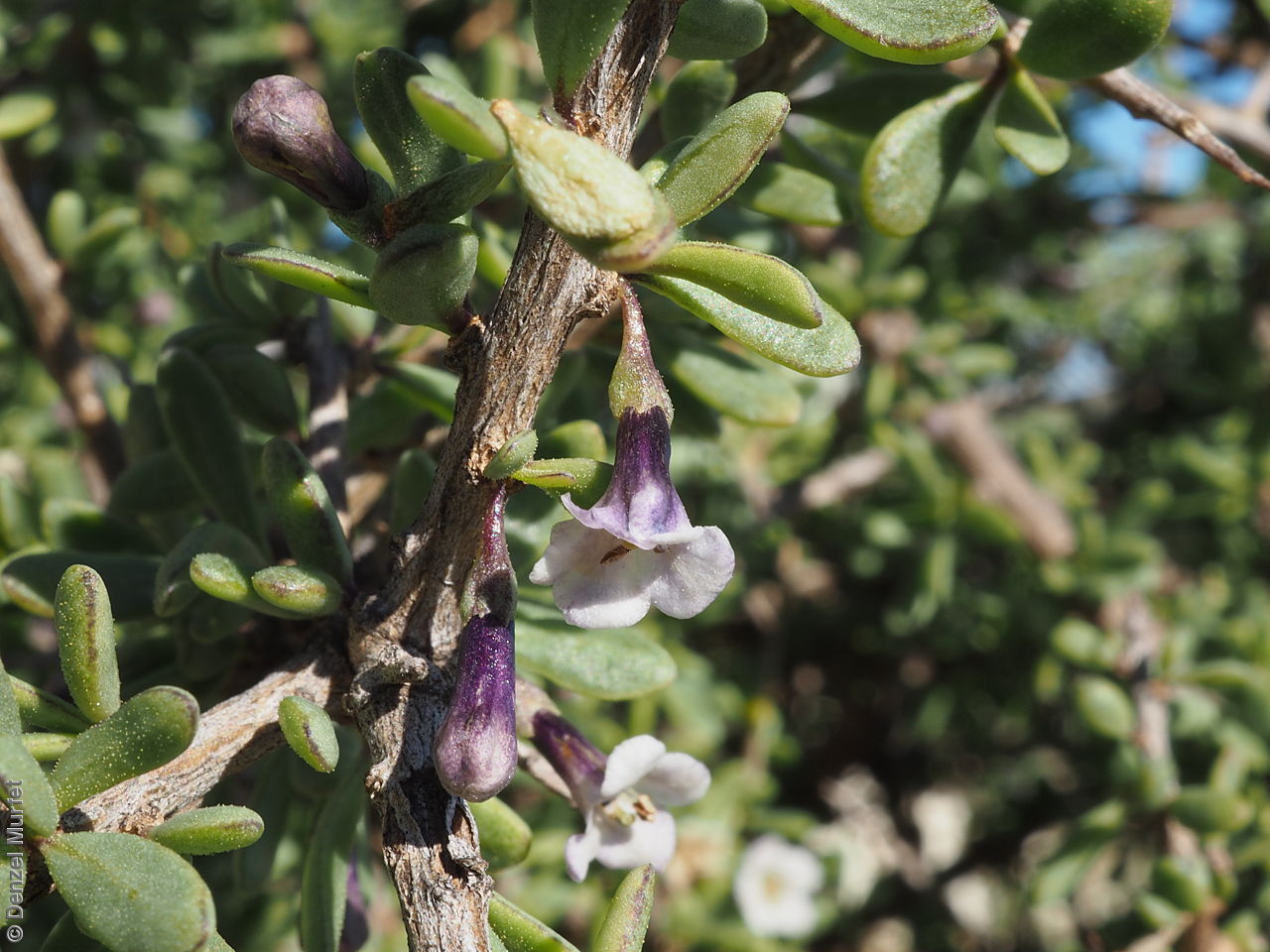
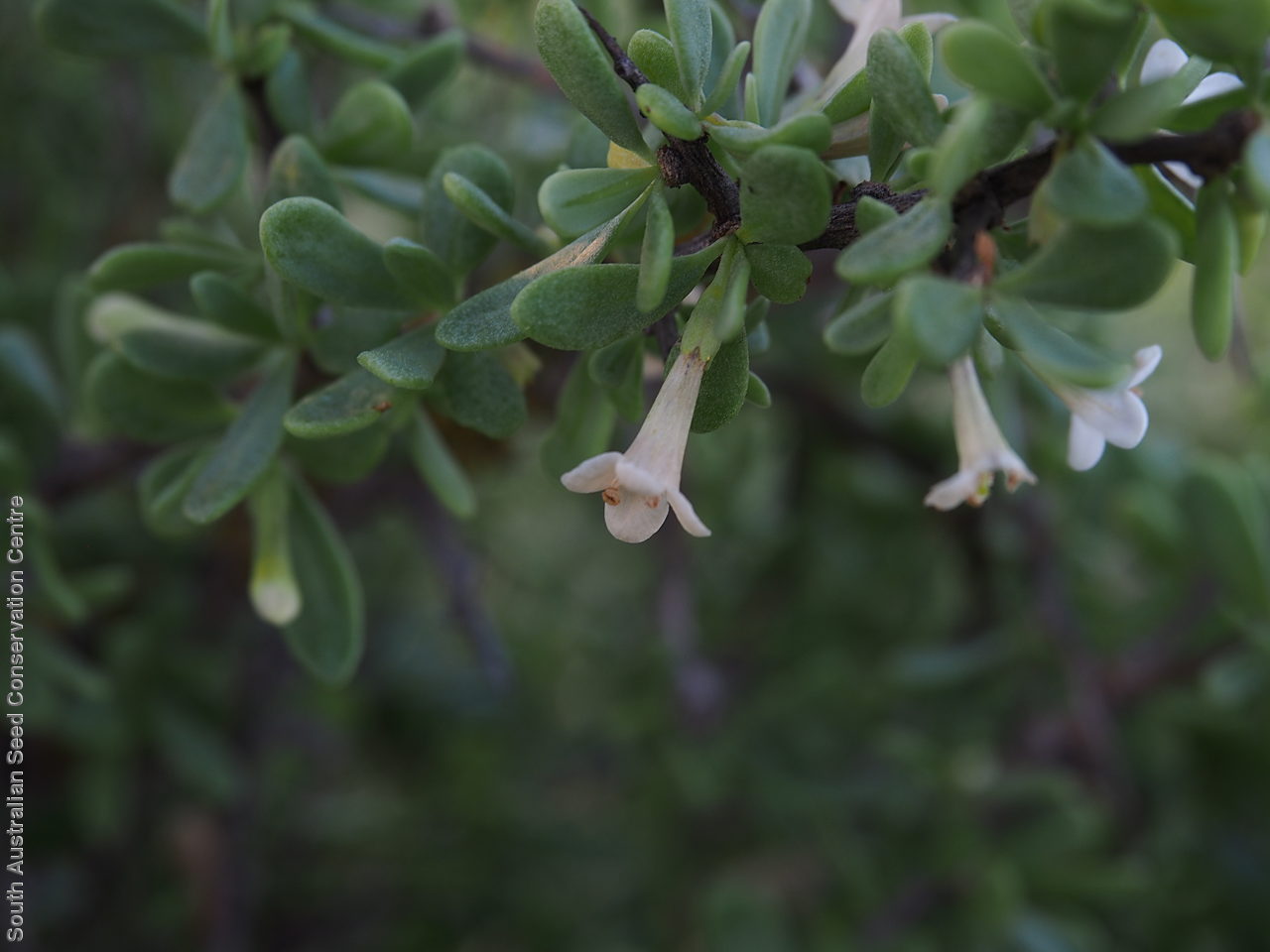
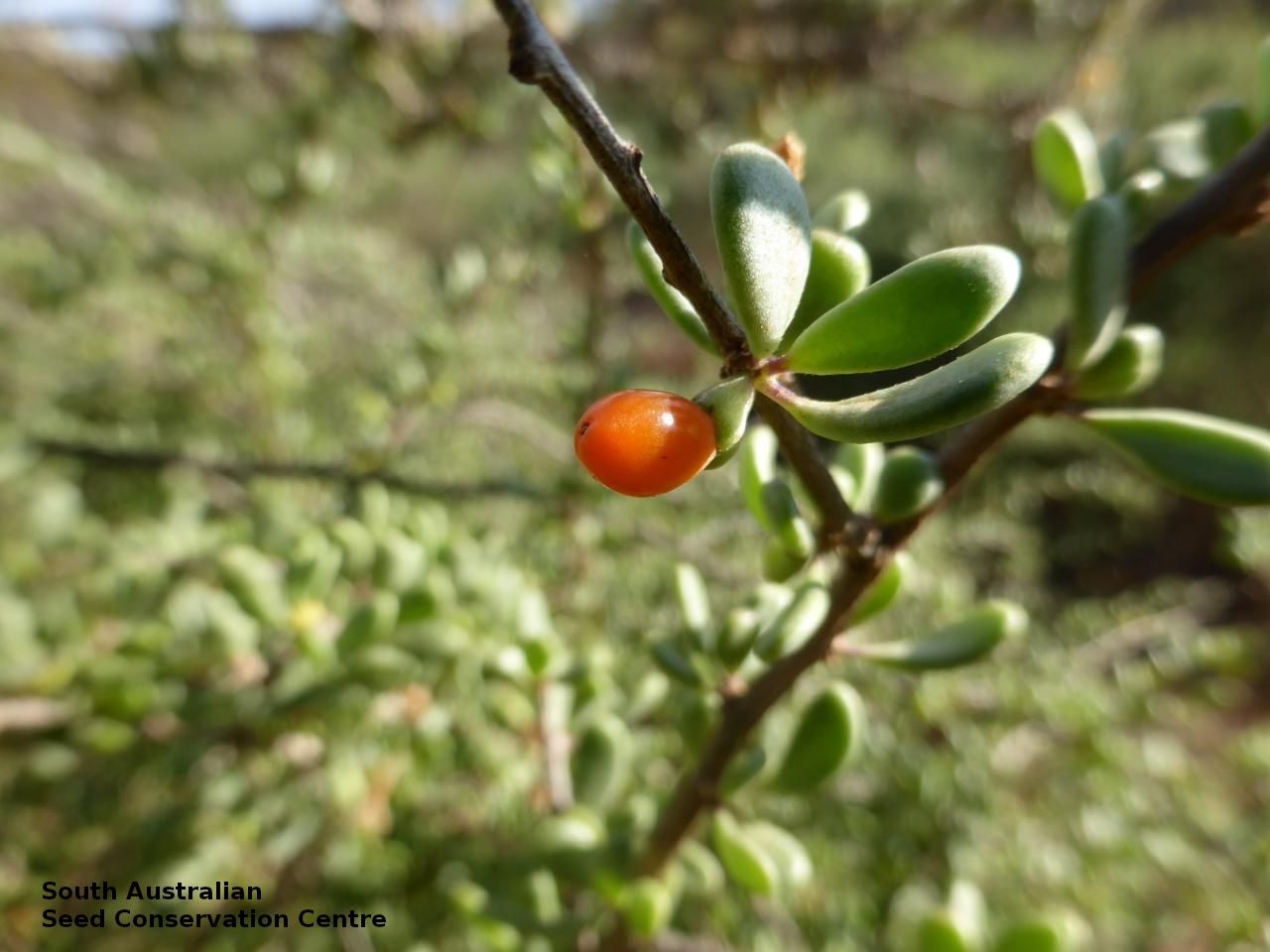
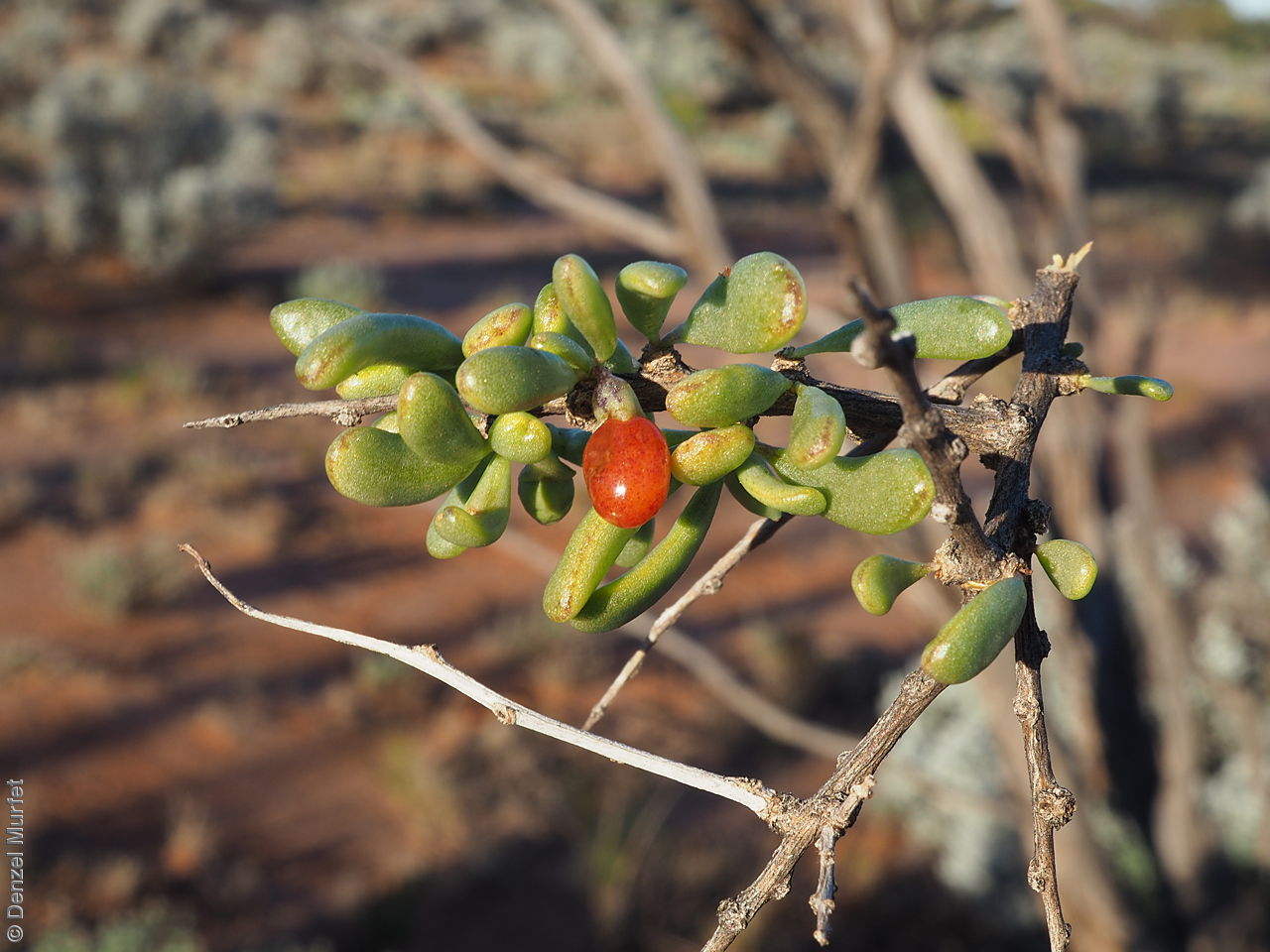
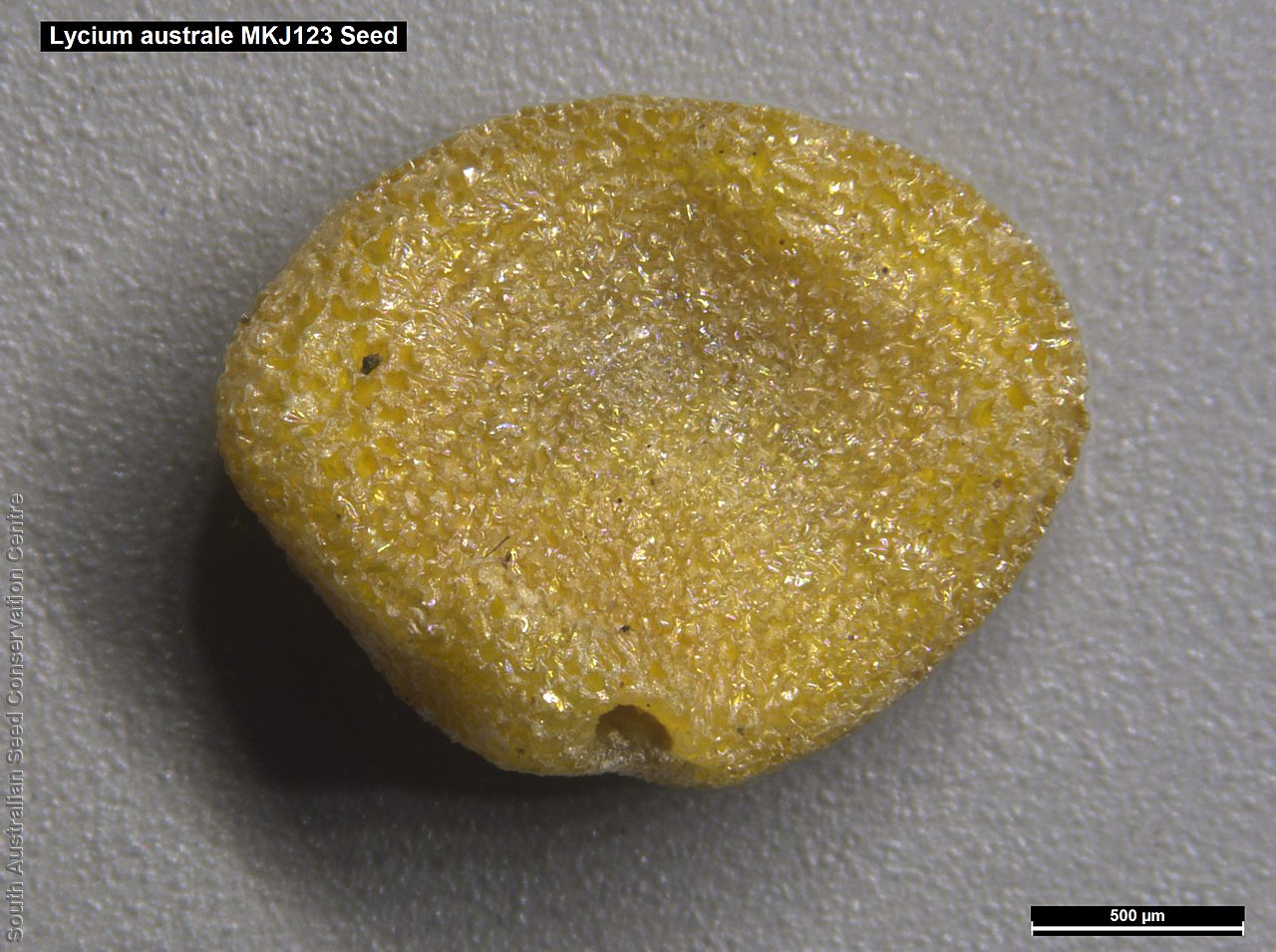
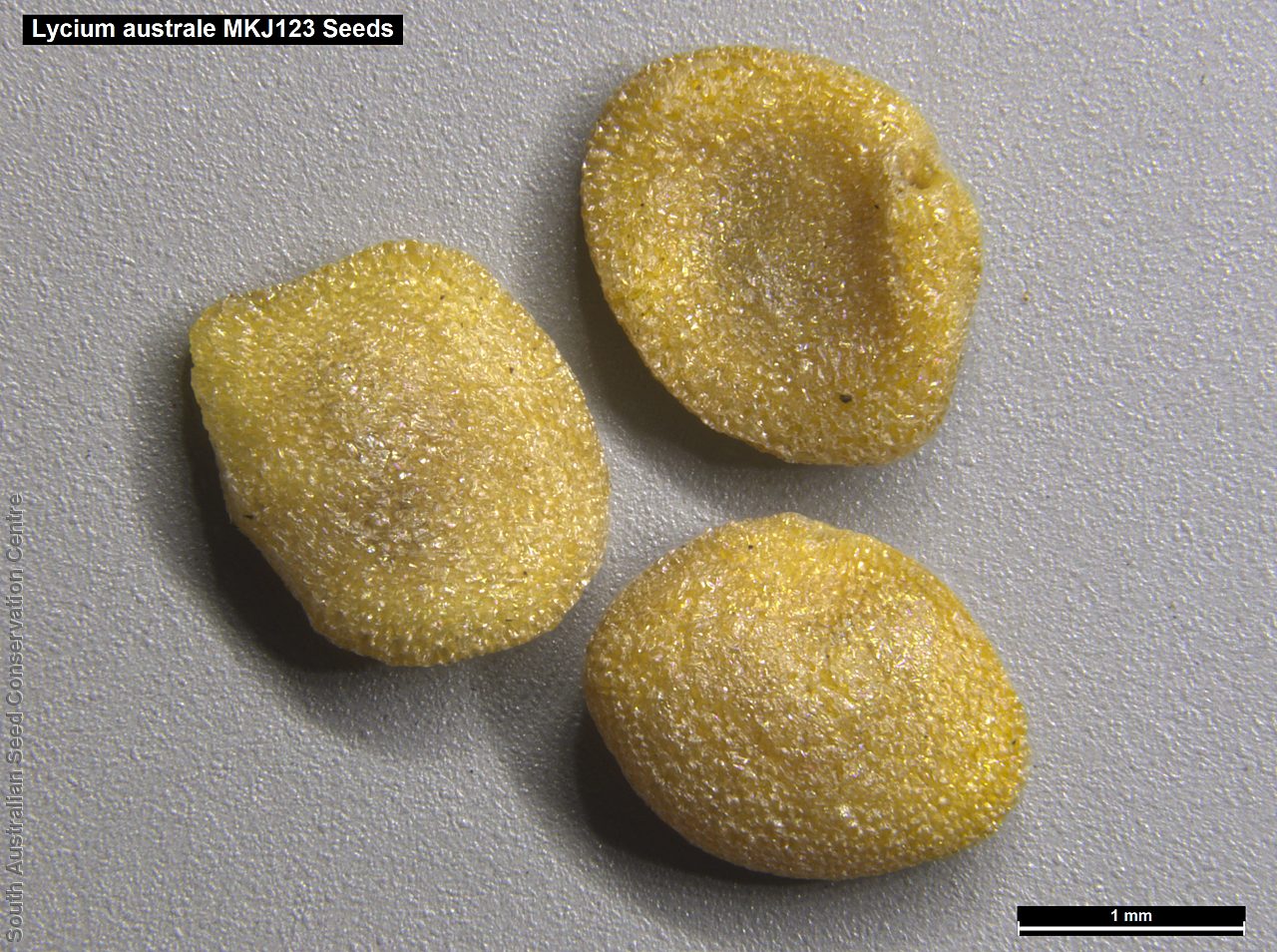
Intricately branched shrub to 2.5 m high with rigid branches with lateral branches leafy and often ending in a spine. Leaves usually clustered, oblanceolate to ellipsoid, to 25 mm long and 3 mm wide; fleshy, glabrous, grey-green. Inflorescence solitary in axils, with creamy white to lilac flowers. Flowering mostly during spring and summer. Fruits are orange-red ovoid berry to 8 mm long and 5 mm wide. Seeds are flat ovoid to circular dull yellow seed to 2.5 mm long and 2 mm wide. Seed embryo type is linear, fully developed.
Seed collection and propagation
Collect seeds between November and February. Collect berries that are ripe, orange-red with soft flesh and numerous hard yellow seeds inside. Place the berries in a bucket of water and rub with your hands to separate the seeds from the flesh. Wash the mixture with clean water and drain. Place the mixture on paper towel and leave to dry overnight. Then rub the dried material by hand to remove any remaining flesh from the seeds. Use a sieve to remove the unwanted material. Store the seeds with a desiccant such as dried silica beads or dry rice, in an air tight container in a cool and dry place From one collection, the seed viability was high, at 90%.
| Location | No. of seeds
(weight grams) | Number
of plants | Date
collected | Collection number
Collection location | Date
stored | % Viability | Storage
temperature | BGA
MSB | 7,000 (9.61 g)
7,000 (9.61 g) | 100+ | 10-Nov-2005 | MKJ123
Gairdner-Torrens | 9-Aug-2006 | 90% | -18°C |
Location: BGA — the seeds are stored at the Adelaide Botanic Gardens, MSB — the seeds are stored at the Millennium Seed Bank, Kew, England.
Number of plants: This is the number of plants from which the seeds were collected.
Collection location: The Herbarium of South Australia's region name.
% Viability: Percentage of filled healthy seeds determined by a cut test or x-ray.
Germination table:
Display












